Municipal budgetary educational institution "Kindergarten No. 2"
Prepared by: educator
Moskaltsova A.I.
Ardatov, 2017
Technologies of valeological education of parents
The main educators of the child are the parents. The mood of a child and the state of physical comfort depend on how the child’s day regimen is properly organized, what attention parents pay to the child’s health. The healthy lifestyle of the child, to which he is taught in Kindergarten, can either find everyday support at home, and then gain a foothold, ornot find, and then the information received will be superfluous and painful for the child.
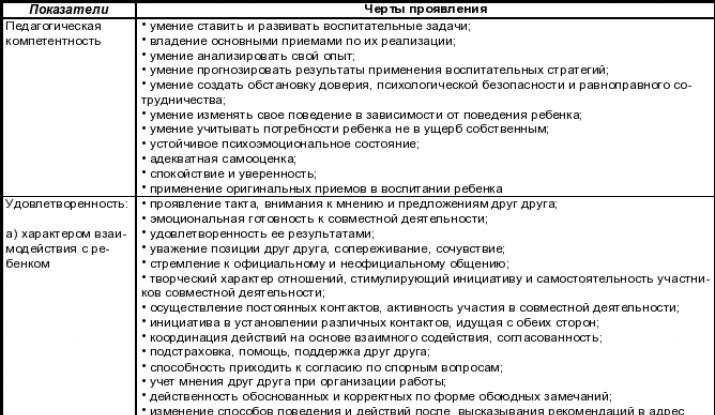
Improving the psychological and pedagogical competence of parents, involving them in active participation in the educational process is an integral part of the valueology education on familiarizing with a healthy lifestyle.
Outreach is expressed in
the formation in parents of a healthy lifestyle as a value,
in acquaintance of parents with various forms of work on physical education in Kindergarten,
informing about the state of health and physical development, about the level of physical fitness of their child,
attracting parents to participate in various joint physical leisure activities and holidays
We use a variety of forms of interaction with parents, both individual and group.Along with traditional forms, such as parent-teacher meetings, oral and written consultations, workshops, folders, sports festivals, entertainment, booklets, newspaper production, etc.,we try use more interactive forms of interaction:
- photo contests on the topic of introducing children to sports and healthy lifestyle,
Variousstocks , for example, every year we involve parents in the all-Russian campaign "I choose sports as an alternative to addictions";
-! invitation of parents to physical education classes;
- joint morning exercises;
- joint leisure, holidays;
- parent meetings We carry out in the form of business games, using trainings.
One of the effective forms of involving parents in the educational process isproject activities
So recently we implemented an interestingproject "Sports portrait of my family" . Within the framework of the project, I suggested that families who lead an active lifestyle draw up a sports portrait of their family. Families creatively approached this assignment and at the final lesson the children presented: newspaper, album, photo collage, presentations. I bring to your attention one of them......
Also, an important task of valeological education of parents is the dissemination of positive family education experience.
For example, this year at the parent meeting devoted to the health care of pupils, the SINITSIN FAMILY presented an interesting video about how healthy lifestyle skills are raised in their family
and thereby set an example to the rest.
Thus, the use of various technologies of valeological education of parents allows not only to actually take an individual approach to each child, but also to attract parents to joint systematic efforts to improve the health of the child’s body throughout their stay in a preschool.
Joint work with the family should be based on the following basic principles that determine its content, organization and methodology.
- The unity that is achieved if the goals and objectives of raising a healthy child are well understood not only by educators, but also by parents, when the family is familiar with the basic content, methods and techniques of fitness and health work in kindergarten, and teachers use the best experience of family education .
- Consistency and sequence of work (in accordance with a specific plan) throughout the year and the entire period of a child’s stay in a preschool.
- An individual approach to each child and to each family based on the consideration of their interests and abilities.
- Mutual trust and mutual assistance of teachers and parents on the basis of friendly criticism and self-criticism. Strengthening the authority of the teacher in the family, and parents in the kindergarten.
It is kindergarten that is the place of parental education. Forms of interaction with parents are diverse; they can be both individual and group, as well as traditional and non-traditional.
In accordance with this, valeological education of parents includes:
- familiarization of parents with the results of the diagnosis of the state of health of the child and its psychomotor development;
- participation in the preparation of individual programs (plans) for the rehabilitation of children;
- purposeful sanitary education, promoting general hygiene requirements, the need for a rational regime and a balanced diet, quenching, optimal air and temperature conditions, etc .;
- familiarization of parents with the content of physical education and health work in kindergarten, aimed at the physical, mental and social development of the child;
- training in specific techniques and methods of healing (exercise therapy, respiratory gymnastics, self-massage, various types of hardening, etc.);
- familiarization with the treatment and prophylactic measures carried out in the preschool educational institution, training in individual non-traditional methods of healing the child’s body (herbal medicine, aromatherapy, etc.).
To implement these tasks are widely used:
The basis in the technology of valeological education is an individual program (plan) of recovery, developed for each child at the beginning of the school year, together with parents on the basis of a deep diagnosis of his health and psychomotor development, which includes:
Of particular importance in promoting a healthy lifestyle in preschool educational institutions is given visual aids that are designed to familiarize parents with the conditional tasks, content and method of raising healthy children, overcome their often superficial judgments about the importance of a healthy lifestyle for children, and provide family with practical assistance.
A special form of visual propaganda of children's health among parents is valeological newspapers, booklets, and memos. The material for them is chosen by the teachers, they are drawn up and included in the plan of valueology work with parents. They reflect the most pressing problems of a healthy lifestyle for children. Visual aids help parents to better understand the conditions, tasks and methods of raising healthy children. Recommendations of specialists on the problem of children's health protection of parents, as well as articles for parents taken from other newspapers and magazines, can also be selected. The subjects of newspapers can be varied: "Daytime sleep: whether and when to refuse it", "Respiratory gymnastics and child’s health", "Secrets of healthy food", etc.
Improving the psychological and pedagogical competence of parents, involving them in active participation in the educational process is an integral part of the valueology education on familiarizing with a healthy lifestyle.
Thus, the technology of valeological education of parents allows not only to actually take an individual approach to each child, but also to involve parents in joint systematic efforts to improve the health of the child’s body throughout their stay in a preschool.
- information in the parent corners, in the folders, folders, in the library of the DOE;
- consultation;
- oral magazines and discussions with the participation of a psychologist, physicians, physical education specialists, as well as parents with experience in family education;
- workshops;
- business games and trainings with listening to tape recordings of conversations with children, analysis of problem situations by video filming, solving pedagogical crosswords, etc .;
- "open days" for parents with viewing and conducting a variety of classes in the gym, at the stadium and in the pool, hardening and healing procedures;
- joint sports activities and holidays, etc.
- a history of incidence for a previous period of time;
- examination of the child by "narrow" specialists and general examination (conclusion of a pediatrician);
- functional diagnostics;
- analysis of children's skills in the main types of movements;
- questioning of parents on the issues of raising a healthy child.
Sections: Work with parents
INTRODUCTION
People like to dream. From generation to generation, they do not abandon this dubious occupation, and even more than that: with minor variations, from century to century, they dream about the same thing. Three major human dreams: to fly, live forever and predict the future. So, dreaming, a man came up with an airplane and medicine, but the most difficult thing is with the last point. The future continues to frighten and intrigue, fascinate and dizzy. It does not come into hand, and fortune-telling on the coffee grounds is comforting weakly. However, to make the future predictable at least partially helps ... traditions. Family traditions and home rituals are more important for children than for adults. It may seem to us that dear mother’s habit - telling a baby a nightly tale to a baby does not oblige her to anything. For the child’s psyche, rituals acquire, in the language of psychological terms, support and stabilizing functions. With the help of them, the little one is guided in time, in them he draws confidence that everything goes as usual in the house, and the parents' loyalty to the child’s home habits is nothing more than an everyday expression of love for the baby. The meaning of the rituals and home traditions is precisely in the fact that events follow one after another in a once wound up sequence: day after day, month after month, in that they are observed no matter what. Confidence in this brings a sense of stability to children's life, relieves anxiety and comforts in moments of grief. A reverent and careful attitude to rituals is especially important if the baby is sick, upset or offended. The seriousness and respect with which adults relate to the child’s habits that they themselves have created contributes to the development of a self-esteem among the little one. The kid learns to respect his words and promises, to be consistent, to keep his word.
We will not reveal the big secret by saying that a small child perceives the world through the eyes of adults - his parents. Dad and mom form a children's picture of the world from the very first meeting with their baby. First, they build for him a world of touches, sounds and visual images, then they teach the first words, then they convey their attitude to all this. How a child subsequently reacts to himself, to others and to life in general - depends entirely on his parents. Life can seem to him an endless holiday or a fascinating journey, or it can be seen as a frightening sortie through wild places or as a boring, ungrateful and hard work awaiting everyone right outside the school gates. If most of the usual family rituals are not limited, but only joy and pleasure, this strengthens the sense of family integrity in children, the feeling of the uniqueness of their own home and confidence in the future. The charge of inner warmth and optimism that each of us carries within us is acquired in childhood, and the more it is, the better.
Of course, the character of the child is not formed on the same day, but we can say with confidence: the more childhood was like a holiday, and the more joy it has, the happier the person will be in the future. Creating the individual traditions of your home, it is worth remembering that any rules are good if they make life better, and not complicate it. Rigid traditions, even if they do not regulate everyday life, but only holidays or another joyful event, have a depressing effect on the spontaneous children's psyche. Some events in life just need to be allowed to happen, without fitting them under the script.
If you want to diversify the lives of your children and make family everyday life more interesting, you can create your own home traditions. Children of all ages love to do funny and joyful things with serious faces, under the strict guidance of adults. Think about what each member of your family knows how to do well and try to turn this into a pleasant custom.
In Russia, the traditions of home education were significantly weakened as a result of the policy of nationalizing the practice of education. Currently, Russian society is reviving the understanding that the family is almost the main source of development of intelligence, moral and aesthetic formation, emotional culture and physical health of children. However, these tasks must be solved in conjunction with the school.
EXPLANATORY NOTE
The purpose of the Family Traditions program is to increase the pedagogical culture and educate parents. Within the framework of the program, various forms of work with parents can be used: parent-teacher meetings, conferences, meeting-disputes, organizational-activity and psychological games, parent lectures, family living rooms, round tables, questions and answers evening, pedagogical workshop, training for parents and others.
The program consists of nine thematic blocks:
- Parenting is a great thing: it decides the fate of a person (The origins of family education )
- My son, and he has his own mind (I and he: how to live in harmony with a child)
- Reading Beauty, Not Reading - Dryness (Family Tradition: Family Reading)
- Examples of Useful Instructions (Family Traditions: Family Outbreak)
- Children must live in a world of beauty, games, fairy tales, music, drawing, imagination, creativity (Family traditions: free time)
- Disrespect for ancestors is the first sign of immorality (Family Traditions: Family Archives)
- He who hopes for heaven sits without bread (Family Traditions: Work in the Family
- Health is the most expensive (Family traditions: a healthy lifestyle)
- The word is not a sparrow: it will fly out, you won’t catch it (Family traditions: dialogue in family communication)
Goal: assistance in the revival of the best domestic traditions of family education, restoration of the traditional way of life.
Tasks:
- to form an active pedagogical position of parents, to involve them in active inclusion in extracurricular leisure activities;
- warn parents of the most common mistakes in raising children;
- summarize and disseminate the positive experience of family education.
Expected results:
- Creation of a system of assistance to parents in the formation of a moral lifestyle of the family, in the prevention of negative manifestations in children and adolescents.
- Improving the pedagogical culture of parents, revealing the creative potential of parents, improving family education using examples of family traditions.
- Strengthening the role of the family in raising children.
- The formation of youth qualities of the future family man and parent.
Month |
Class |
Topic |
September |
Education is a great thing: it decides the fate of man |
|
What is the tree, such are the apples (Traditions of folk pedagogy) |
||
My day - my century: what has come down to us has come to you (Traditions in Russian pedagogy) |
||
There is a reason for everything (Sources of deep affection in parent-child relationships) |
||
Not the father - the mother who gave birth, but the one who sang, fed, taught the good (The power of good traditions) |
||
A child, that wax: what you want, then merge (Gold placers of parental pedagogy) |
||
Out of little comes the great (Creating your own family traditions. Family business card) |
||
A good example in a circle comes back ... (L.A. Seneca) or One for all and all for one (Birth of class traditions) |
||
A good example is the best sermon (Education of masculinity and femininity on the example of family traditions) |
||
Russian is proud in words and firm in deeds (How statesmen were raised) |
||
Soul - measure to everything (Spiritual origins of education) |
||
The soul of man is the greatest miracle of the world (Dante Alighieri) (The role of culture and religion in the upbringing and development of personality) |
||
October |
My son, and he has his own mind |
|
Teach the child, while lying across the bench, and how to lie along the bench, then it’s too late to teach (Age characteristics of younger students) |
||
Who indulges children, then sheds a tear (The influence of parental attitudes on the development of the child.) |
||
And crow crow praises (Parental expectations as an important factor in the formation of the personality of the child) |
||
From moose - moose, from pig - pigs (Styles of parental behavior) |
||
What to be, not to be avoided (Psychological adaptation of students and ways to correct it) |
||
Children are small - they won’t give food, children are big - they won’t give life (Age and individual psychological characteristics of a teenager.) |
||
In a good life, curls curl, in a bad split (Emotional atmosphere in the family) |
||
Great figure, but a fool (The first signs of a feeling of adulthood. The desire for self-esteem) |
||
Raise children - do not count chickens (taking into account physical and psychological characteristics, a combination of respect for the individual with exactingness for her, the coherence of the impact of the family and the school, a reasonable adjustment of the diverse influences on the student) |
||
Children are more like their time than their parents (Youthful age. Psychological aspect) |
||
The one who does nothing is not mistaken (The psychological meaning of supporting another person) |
||
November |
Reading is beauty, not reading is dryness |
|
You’ll lead a book, you’ll be crazy, the song is red in harmony, and the fairy tale will be in storage (Tale hour for younger schoolchildren) |
||
Books do not speak, but they tell the truth (Family Library)) |
||
From time immemorial, a book raises a person (The collection is the debate “Reading is the best teaching!”) |
||
The newspaper accustoms the reader to reflect on what he does not know and to know what he does not understand (V.O. Klyuchevsky) (Review of family newspapers and magazines) |
||
Is the pen great and writes large books (“Sharks of the pen” (Adults get acquainted with the work of their children) |
||
Do not be lazy to read ancient books, because you can easily find in them what others with such difficulty found in everyday experience and comprehend everything (Vasily I the Macedonian) (Reader interests of adolescents, favorite book and favorite heroes or a series of books by ZHZL) |
||
It’s not hard to do, but hard to conceive (Acquaintance with popular science magazines and books) |
||
One book enriches, and another leads astray (Meetings with writers, poets) |
||
December |
Examples of Useful Instructions |
|
What it feels like at home, and so it is (Long live comfort!) |
||
House like a full bowl (Joy of the family) |
||
One with a bipod, seven with a spoon (Big family. Joy and difficulties) |
||
Our Cossacks have such a custom (The traditional way of family is with ...) |
||
At home to live about everything (Family laws) |
||
No value versus love (Family love) |
||
Money about white day, money about red day and money about rainy day (Children and money, family budget) |
||
Happiness is like health: when you do not notice it, it means that it is (Recipes of family happiness) |
||
Any guardianship that continues after adulthood turns into usurpation (V. Hugo) (The specifics of family education: positive and negative) |
||
True ethics begins where words cease to be used (Schweizer Albert) (Ethics and aesthetics of family life) |
||
January |
Children must live in a world of beauty, games, fairy tales, music, drawing, imagination, creativity (V.A. Sukhomlinsky) |
|
To amuse people, to the whole world to wonder (Games for entertainment) |
||
Why go, then you will find (Games for the good of the cause) |
||
Whatever the child is amused, if only he would not cry (Children with motor hyperactivity syndrome. Games to calm children) |
||
And the casket just opened (Games for the mind) |
||
Many children's games are an imitation of the serious activities of adults (Y. Korchak) (Game Library) |
||
In the matter of education, the development of skills must precede the development of the mind (Aristotle) \u200b\u200b(Communicative games) |
||
Such miracles that stand on end of hair (33 family contests) |
||
Who cannot take affection, he will not take with severity (A.P. Chekhov) (Games for interactions) |
||
What is tricky is not easy (Entertaining tasks) |
||
The head is the beginning of everything, where the mind is, there is sense (Mind games, computer games) |
||
February |
Disrespect for ancestors is the first sign of immorality |
|
From an old memory, like a letter (Family memories of ....) |
||
A young umok with an old mind is fastened (Secrets of a grandmother's chest) |
||
What kind of tribe? (Pedigree of my family) |
||
I will be alive - I will not forget. I will remember before the age (Storage of relics) |
||
According to dignity and honor (Cult of the older generation) |
||
Remember a lot, but don’t go back (Photos of our childhood) |
||
Where there are no good old people, there are no good youth (Presentation of family generations, organization of meetings for ...) |
||
Great components of happiness: to have, what to do, what to love and what to hope for (E. Chalmers) (Family Values) |
||
Honor head guard (Family honor) |
||
Inheritance is neither a gift nor a purchase (Familiarity with the Family Code) |
||
The fatherly word is also true according to a fairy tale (Blessing of parents) |
||
March |
He who hopes for heaven sits without bread |
|
Tackle what you are good for (Child labor and its organization) |
||
Harmony of three concepts: necessary, difficult, beautiful (Content, forms and methods of labor education) |
||
You can’t take a fish out of a pond without labor (Basic mechanisms of labor education) |
||
As you drown, you rumble (Domestic self-service. 1001 ways to wash dishes with pleasure) |
||
For the company and the Jew strangled himself (Meeting - dispute "Subbotnik - labor or punishment)" |
||
If you suffer for a long time, something will turn out (Creative character of labor) |
||
Patience and labor, all will grind (Laws of child labor) |
||
Nightingales do not feed fables (Incentives for child labor) |
||
Did the thing, walk boldly (Discipline of labor) |
||
I would drink and eat, but I would also like (Culinary recipes) |
||
Edible houses and straw (Family Lunch Culture) |
||
April |
Health is the most expensive |
|
To judge a child fairly and correctly, we need not to transfer him from his sphere to ours, but to move to his spiritual world (N.I. Pirogov) (Mental health of the child) |
||
Healthy is great (Home Break) |
||
Sport is great! |
||
Appetite runs from the patient, and rolls to the healthy (Four laws of healthy eating) |
||
The disease will not catch up with quick and agile (School of safety at school and at home) |
||
Away at a party is good, but at home is better (Safety School on a Campaign) |
||
The day will come - it will bring care (Where better to start a working day) |
||
Marriage must fight the devouring monster - habit (Habits and health) |
||
Mind and health are the most expensive (cheat sheet for parents) |
||
Do not pray for a sore, but heal yourself (Family Doctor) |
||
The word is not a sparrow: it will fly out, so you will not catch |
||
To talk with you that honey gets drunk (Communication is so easy) |
||
God gave and dumb speech (Our facial expressions, our gestures) |
||
Smart speech is good and listening (Parent hour of communication) |
||
The language opens the mind (Helping children with communication disabilities) |
||
The same word, but wouldn’t say so (Can we communicate?) |
||
Do not rush to answer, hurry to listen (Can we listen and hear?) |
||
Kind speech that there is a stove in the hut (Compliment and laudatory word) |
||
Do not let the soul be lazy (The art of communication. The inclusion of mental vision, elements of training). |
||
Understanding is a two-way street (Eleanor Roosevelt) (“Difficult People” and Communication with Them) |
||
He doesn’t talk much, but thinks a lot (Business speech and computer) |
||
Do not joke with such jokes, who is sensitive to every word (Conflict-free communication between boys and girls) |
||
Literature:
- Falkovich A.T. Unconventional forms of work with parents [Text] / A.T. Falkovich, N.S. Tolstoukhova, L.A. Obukhova. - M .: 5 for knowledge, 2005 .-- 237 p.
- Bogatenko V.D. Organization of summer holidays and work of schoolchildren: results and prospects [Text] / V.D Bogatenko, G.V. Gavrilova. - Kemerovo, 2002 .-- 145 p.
- Miklyaeva A. I am a teenager. I am among other people [Text] / Anastasia Miklyaeva. The program of psychology lessons. Part 3. - St. Petersburg: Speech, 2003. - 119 p.
- Kulinich G.G. Bad habits [Text] / G.G. Kulinich. - M .: VEKO, 2008.
- Cyril and Methodius Big Encyclopedia [Electronic resource] / Cyril and Methodius, 2006, 2007
- Scientific and methodical journal of the deputy director of the school for educational work [Text] / 2005. - No. 6.
- Bulletin of Education of Russia, 2002. - No. 23
- Dahl V. Proverbs of the Russian people [Text] / V. Dal. The collection in two volumes. - M.: Fiction, 1998.
- Dahl V. Russian folk riddles, proverbs, sayings [Text] / Dahl. - M .: "Enlightenment", 1980.
Municipal Autonomous Educational Institution "Secondary School No. 1 with in-depth study of individual subjects to them. I.A. Kuratova "city of Syktyvkar.
The program of pedagogical education of parents of students in grades 5-6.
Tyulkina Ekaterina Pavlovna.
syktyvkar
Explanatory Note ………………………………………………… 3
Age-related tasks for the development of children ...........................
Purpose, objectives, terms of the program ……………………… .10
Calendar-thematic planning of activities for pedagogical education of parents, forms and methods of its implementation ……………………………………………………… 19
Expected results of the program ........ ................... 23
Methods of control and verification of the expected results of the PPR program ...
Appendices ............................................... 33
Bibliography …………………………………………………………… .43
Explanatory note.
The central place in the formation of the child’s personality is occupied by the family. According to researcher L.B. Schneider 1, it depends on the family on 70% how the child grows up, and what character traits will form his nature.
In the family, the child receives primary skills in the perception of reality, learns to recognize himself as a full representative of society.
The concept of modernization of Russian education emphasizes the exclusive role of the family in solving educational problems. Achieving success in the process of raising children is possible only if the efforts of the family and other social institutions are combined, the most important of which is the general educational institution (hereinafter referred to as the public-educational institution), which ensures real interaction between parents and teachers in the educational process.
This is what a new form of working with the family leads to: parents are responsible for raising children and their development, and all other institutions of upbringing and education, including community-based institutions, are called upon to contribute to this.
Family and school are two important institutions for child socialization. And although their educational functions are different, for the full development of the child their interaction is necessary. If OS contributes to the integration of the child in society, then the family is called upon to ensure the individualization of child development.
The change in state education policy entailed recognition of the positive role of the family in raising children. Article 18 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On Education” states: “Parents are the first educators. They are obliged to lay the foundations of the physical, moral and intellectual development of a child’s personality at an early age. ” In article 2 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On Education” the following are formulated principles of education:
the humanistic nature of education, the priority of universal values, human life and health, and the free development of personality. Education of citizenship, industriousness, respect for human rights and freedoms, love for the environment, Motherland, family;
unity of the federal cultural and educational space. Protection and development by the educational system of national cultures, regional cultural traditions and characteristics in a multinational state;
general accessibility of education, adaptability of the education system to the levels and characteristics of the development and training of students and pupils;
secular nature of education in state and municipal educational institutions;
freedom and pluralism in education;
democratic, state-public character of education management. Autonomy of educational institutions.
In this law, respect for the family is recognized as one of the principles of education, that is, the family from the means of pedagogical influence on the child turns into his goal.
The school should not only maintain close ties with the family and the public, but also have an impact on the activation of the educational activities of parents, increase their responsibility for raising children. By combining pedagogical efforts, teachers and parents should be well aware of those problems on the solution of which they should work together. The range of these problems is quite wide and with some degree of conventionality they can be divided into three main groups.
Crisis phenomena characteristic of modern society affect the state of spiritual, physical, moral and psychological health of the younger generation.
Trying to find ways to solve these problems, the school is looking for new forms of interaction with the family, realizing that parents and teachers are educators of the same children. The result of their activities can be successful only if teachers and parents become allies. Their union should be based on mutual understanding, respect, trust, responsibility and aimed at developing the personality of the child.
Pedagogical education parents are most often implemented in traditional forms:
Their common disadvantage:
work with parents is not differentiated, without taking into account the characteristics of the family;
parents have limited access to stay in the OS: open days and other events are carried out strictly according to a pre-drawn up plan;
parents cannot influence the pedagogical process, they are attracted only to the implementation of organizational moments, and they get acquainted with educational work only when considering "visual agitation" - stands prepared by teachers;
the leading role in organizing work with the family is given to teachers: the goal of many forms is to help parents, recommendations, tips, correcting errors in family education. This indicates that the family is perceived as a pedagogically imperfect factor in the formation of the child’s personality. And the forms of working with the family themselves do not give proper results, as they are aimed at interacting with a wide range of parents. In these conditions, it is impossible to discern the problems of each family individually.
That is why a new form of interaction between the OS and the family is needed.
However, before talking about the implementation of a new form of interaction between the teacher, the class teacher and parents, you need to analyze the prerequisites for this approach and the readiness of both parents and teachers for it.
In recent years, the level of parental culture has sharply decreased, from year to year there are fewer families where the child feels loved, where mom and dad really care about the health and development of their child.
Of course, for the sake of the child, his full development, it is necessary that parents are constantly interested in his well-being, mood, know how to help him in failures, how to stimulate success, the desire to receive knowledge, to be the best of the best.
Therefore, in order for the children to fully develop, grow not only good sons and daughters, but also later become good citizens, patriots of Russia, parents and OS must constantly be in interaction.
Relevance This program of pedagogical education of parents is that it is aimed at helping parents learn to understand and educate their children. In this regard, we need a well-thought-out model for organizing psychological and pedagogical education of parents. The Interaction program is dedicated to the organization of cooperation between the teaching staff, the class teacher and parents in the process of educating schoolchildren.
Relevancethis problem is also the fact that many modern vices of society (alcohol, drug addiction, crime, mental disorders, etc.) are the result of parenting children with a low level of psychological and pedagogical culture, which is expressed in an irresponsible attitude towards the performance of their educational functions , the strongest motivational limitation in solving problems related to the upbringing and development of a child in the family, illiteracy in solving problems of family education
One of the hallmarks of the program is the increased public participation of parents in school and classroom life.
Parents will have the opportunity to directly influence the educational process and will be more actively involved in managing the classroom and school.
An important place in the program belongs to the formulation of guidelines for parenting, which allows us to build a unified system of education for schoolchildren. These recommendations cover parent-teacher meetings of traditional and non-traditional forms, classroom and school evenings, meetings from grades 5 to 6.
The success of this program depends on how “parents” get involved in the educational process, how much they understand the essence and expected results of innovations, and the achievement of these results and the quality of education in general depend.
Age-related tasks for the development of children.
This program of pedagogical education of parents is formed taking into account the psychological and pedagogical characteristics of the development of children 10-14 years old, related:
with the transition from learning activities to mastering learning activities at the primary school level, to a new internal position of the learner - focusing on independent cognitive search, setting learning goals, mastering and independently implementing control and evaluation activities, and the initiative in organizing educational cooperation;
with the implementation at each age level (10-12 and 13-14 years) of a qualitative transformation of the educational activities of modeling, monitoring and evaluation and the transition from independent setting of new educational tasks by students to the development of the ability to design their own educational activities and build life plans in the long term;
with the formation of the student’s scientific type of thinking, which focuses it on cultural patterns, norms, standards and patterns of interaction with the outside world;
with the mastery of communicative means and methods of organizing cooperation and cooperation; the development of educational cooperation implemented in relations between students with a teacher and peers;
with a change in the form of organization of educational activities and educational cooperation from classroom to laboratory-seminar and lecture-laboratory, research.
The student’s transition to primary school is characterized not only by the middle stage of adaptation, but also coincides with the pre-critical phase of the child’s development - the transition to the crisis of young adolescents (11-13 years, grades 5-7), characterized by the beginning of the transition from childhood to adulthood, which the central and specific neoplasm in the personality of a teenager is the emergence and development of self-awareness in him - the idea that he is no longer a child, that is, feelings of adulthood, as well as an internal reorientation of the teenager with Fork and restrictions associated with the morality of obedience to adult standards of behavior.
Taking into account the features of age, the success and timeliness of the formation of neoplasms of the cognitive sphere, the qualities and properties of the personality is associated with the active position of the teacher, as well as with the adequacy of the construction of the educational process and the choice of conditions and teaching methods.
Objectively necessary for the preparation for the teenager’s future life, the development of his social maturity also requires parents (legal representatives) to solve the corresponding problem of raising a teenager in the family, and to change the old type of relationship to a new one.
In conclusion, it should be noted that interest directly depends on an understanding of the relevance and their importance for the organization of the educational and educational process of the child, which, in turn, is associated with an accessible level of presentation of the material, an optimal ratio of time and activities, a comfortable psychological climate, and the presence of feedback . Proposed program takes into account age-related characteristics and development goals of children Grades 5-6 (10-14 years).
Program goal Parent teacher education “Interaction” is the development and implementation in practice of a model for organizing psychological and pedagogical education of parents in the new socio-economic conditions, the prevention of family problems and the revival of family education based on the cooperation of teachers, students, parents and various special services of the city.
Tasks:
to form psychological, pedagogical and socio-legal knowledge of students' parents;
warn parents of the most common mistakes in raising children;
to form an active pedagogical position of parents, to involve them in active inclusion in classroom, school, extracurricular leisure activities;
to develop, together with the family, a unified tactic of education;
to study the family atmosphere of the student, his relationship with the family;
to intensify the interaction of the family and the school in order to form a positive attitude of the family towards students and prepare them for future family life;
to foster a valuable attitude towards Russia, its people, the region, the domestic cultural and historical heritage, folk traditions, and the older generation;
Program participants:
Students;
Classroom teacher;
Parents of students;
OS Administration;
School psychologist (psychologist of social services);
School paramedic, other medical services of the city;
Inspectorate for minors of Syktyvkar, social teacher of the school.
on pedagogical education of parents.
To determine the content of activities for pedagogical education of parents, we offer a diagnosis, which determines the typology of parents. This is needed for:
characteristics of the educational space of the school - how much the general level of pedagogical culture of parents can contribute to the development of children in the process of their life.
differentiation of adults in the design of the content of PPR and its forms.
identifying the most active parents who can become assistants in the organization of PPR.
The typology of parents is determined by two indicators: the level of pedagogical competence and the level of satisfaction with the nature of interaction with children. Conventionally, there are 4 types:
competent satisfied (“harmonious”) - “I know a lot about education, knowledge helps me build a good relationship with a child”;
competent dissatisfied (“theorists”) - “there is a lot of knowledge about education, but for some reason I can’t apply it”;
incompetent satisfied (“practices”) - “I was raised without special knowledge, but everything is in order with the child”;
incompetent unsatisfied ("helpless") - "I do not know what to do with the child, who will tell?".
In order for interaction with parents to be as effective as possible, it is necessary to determine the optimal time for classes (presumably no more than 1 hour 30 minutes).
It is advisable to start the lesson with a small warm-up (interactive exercises, test, game, etc.) and end with reflection (discussion of new information and exchange of impressions). You can provide participants with handouts (booklets, memos, diagrams, etc.) that reinforce or complement the knowledge that parents received in the lesson.
We propose to distribute handouts not only in paper form, but also to create a class teacher (class) on the website parents' electronic diaries,in which not only information on pedagogical education of parents will be stored, but also individual and collective work of the class teacher with parents will be organized.
We consider it necessary to include knowledge on the formation of a family lifestyle, on creating a favorable psychological climate in the family, on ethnic culture and relationships with people of different nationalities, on artistic and aesthetic, physical development and others.
Formsthe presentation of the material is the most diverse: discussions, conferences, questions and answers evening, round tables, business and role-playing games, trainings, family sitting rooms, discussions, oral magazines, workshops, parent evenings and parent readings, master classes and others. In this case, it is necessary to use new pedagogical technologies for the development of human intelligence, his personal qualities.
So, along with traditional and non-traditional forms of classroom hours, we offer testing webinar 2 as alternative and convenient forms of work with the parent committee and parents of the class as a whole. We note the positive experience of this technology, as it allows you to reach most of the parents, to orient at a convenient time for the cool parent-teacher meetings. Provided that the parents (or members of the parent committee) cannot, due to objective reasons, be at the PC at a certain time, the webinar allows recording on the Internet, which is convenient for further viewing at any convenient time.
At the heart of the organization Parent education will use a personal-active approach: not only the level of education of parents, but also the level of parental culture is taken into account. Dads and mothers are subjects of the educational process - in this we should be helped by educational technology. Each lesson with parents will end with individual and collective reflection.
Through the entire educational process will be carried out family portfolio. Portfolioacts as a mechanism for parents' self-development, helps to adjust their positions in life, build a way of life for a modern family.
To activate and stimulate parents are encouraged to use family activity cards, family cohesion contests (“The Best Parent Team”), family airborne assaults and other events.
To summarize psychological and pedagogical education of parents, you can use not only questionnaires and diagnostics, but also such forms as family presentations, contests for the best connoisseur of the child's soul, contests "Father of the Year", "Mother of the Year", etc.
Parental education is most often implemented traditional forms:
Conversations and consultations;
School-wide and cool parent-teacher meetings;
Visual propaganda (stands, thematic exhibitions, etc.).
In the technique, we can distinguish the so-called non-traditional forms of cooperation class teacher with student’s family. These include the following forms:
Parent evenings
Parent readings
Open Day
Individual consultations
Parent Lecture Hall
Group consultations
Thematic consultations
Keeping communication notebooks
Extracurricular activities involving parents
Trainings
Parent meetings with children
Thematic Activities by Parents
Round tables
Discussions
Oral Journal
Workshops
An effective means of assisting the family in raising children is the organization of pedagogical education of parents, since many of the troubles of family education are caused by ignorance of the elementary pedagogical truths of working with children.
An important factor in the influence of schools on family education is individual work with parents. It covers various aspects of students' training sessions, their moral formation, work organization and vocational guidance. At the same time, it is necessary to dwell on the identification of certain psychological and pedagogical rules for their interaction and ways of establishing contacts with the family.
The basis of the work of the class teacher is actions and activities aimed at strengthening and increasing the authority of parents.
A moral, edifying, categorical tone is intolerant of the work of the class teacher, as this can be a source of resentment, irritation, awkwardness. The need of parents to consult after the categorical “must”, “obligated” - disappears. Most often, parents know their responsibilities, but not everyone in practice brings up the education as it should be, it is important for them to know not only what to do, but also how to do it. The only correct norm for the relationship between teachers and parents is mutual respect.
Confidence in the educational opportunities of parents, increasing the level of their pedagogical culture and activity in education. Psychologically, parents are ready to support all the requirements, deeds and undertakings of the school. Even those parents who do not have teacher training and high education, with a deep understanding and responsibility, relate to raising children.
Pedagogical tact, inadmissibility of careless interference in family life. The class teacher is an official person, but by the nature of his activity, he should relate to the intimate aspects of family life, often he becomes a free or involuntary witness to relationships hiding from strangers. A good class teacher in a family is not a stranger; in search of help, parents trust him inmost, they advise.
Life-affirming attitude in solving the problems of upbringing, reliance on the positive qualities of the child, on the strengths of family education, orientation on the successful development of personality. The formation of the character of the pupil is not without difficulties, contradictions and surprises. They should be taken as a manifestation of the laws of development, then complexity, contradiction, unexpected results will not cause negative emotions and confusion of the teacher.
To criticize or scold the child, to indicate problems, the class teacher should only be alone, and to praise, indicate positive qualities, for all.
In providing individual assistance and influencing parents, teachers should exercise the necessary pedagogical tact.
The educational activities of parents at school are carried out in the form of conversations with students, conducting reports and lectures. They are devoted to the development of science and technology, to familiarize students with the industrial successes of people. The topics of these performances include questions of medicine, art, stories about the life and creative activity of prominent people, etc. A common form of parental participation in extracurricular activities of the school is to conduct student excursions to industrial enterprises and scientific institutions, as well as the organization of local history work.
Thus, family-school collaboration can have a positive impact on the upbringing of the younger generation.
Appendix No. 1
| 7 | 1 - Diagnostics | 2 - Compilation of the program of PPR |
| 6 | 3 |
|
| 5 | 4 |
|
The program is based on the following principles:
Principle of timeliness provides for the early detection of family troubles, difficult life situations in which families and children find themselves, as well as factors of child neglect and social orphanhood. The implementation of this principle makes it possible to prevent the family from sliding to a critical border, beyond which lies complete alienation from parents, and social deviations in the life of the latter develop into antisocial, illegal activities. Timely identification of a dysfunctional family helps to avoid an extreme measure - deprivation of parental rights.
Principle of humanism expresses the willingness of employees to come to the aid of the child and his family, to promote their social well-being, to protect rights and interests, despite deviations in the lifestyle of the family.
The principle of individual approach involves taking into account the social, psychological, functional characteristics of a particular family and its members when choosing forms of exposure, and in the future, interaction and rehabilitation.
The principle of stimulating the domestic resources of the family - the family’s mood for self-help by changing the way of life, restructuring relations with children, making a decision to seek the help of specialists (for example, a narcologist), if necessary.
The principle of integration of efforts, an integrated approach - combining the efforts of social services, government agencies and public organizations to most effectively contribute to the restoration of family ties.
The implementation of these principles in the framework of the implementation of the PPR program involves a partnership of parents and professionals in establishing family relationships, revealing and maintaining family potential.
A targeted, targeted system of psychological, pedagogical, medical and social work on optimizing parent-child relationships, developing various forms of family living arrangements
Calendar-thematic planning of activities for pedagogical education of parents,
forms and methods of its implementation.
Grade 5 (8 lessons)
| month | purpose of/ expected results |
||
| september | An unconventional form of parental meeting with the participation of a school psychologist "Adaptation of fifth graders to new conditions of study." Training "How to help a teenager gain confidence?" | Class teacher, parents, school psychologist | |
| october | Unconventional form of parent meeting. Round table “It was evening. There was nothing to do. " How to organize extracurricular activities of the child. Express survey "My leisure 20 years ago." Speech by a juvenile inspector (or social educator) on the causes of juvenile delinquency and crime. Modeling "ideal leisure for the child." | Invitation of specialists from various centers of further education. The help of a school psychologist in modeling "ideal leisure". | Nurturing social responsibility and competency, |
| november | Unconventional form of parent meeting. An evening of questions and answers in the form of a round table "First problems of adolescence." | A short lecture by a psychologist about problems of adolescence. Then the psychologist answers the prepared questions of the parents. Questions are formulated by parents, written on special leaflets, dropped into a single container (box, hat, etc.), then taken out by the class teacher and announced to the entire audience. In this way, confidentiality is maintained. After the parent meeting, individual consultations are possible. | cognitive activity aimed at awareness of one's “I”. |
| december | Unconventional form of parent meeting in the form of parental readings “Who is asked the lessons? And how to succeed in doing homework? ” | The class teacher, psychologist and teaching staff working in the classroom, prepare information for parental readings, select material. At the end of the workshop, reminders are distributed to parents, and they are sent to their electronic diaries. | |
| february | Traditional parent meeting in the form of a lecture by a school assistant and gynecologist / andrologist “A healthy child is a healthy society.” "How to tell a child that he is growing up?" | Class teacher, parents, school assistant, gynecologist / andrologist invitation | |
| march | An unconventional form of parent-teacher meeting in the form of discussion “Methods of family education. Punishment and encouragement in the family: pros and cons. ” | Class teacher, invitation of a school psychologist. | |
| april | Unconventional form of parent meeting. Round table "Distribution of household duties." “Internet: good or evil ?!” Labor landing: fathers and boys make feasible repair of the office, mothers and girls are engaged in gardening the office, its ennoblement. | Class teacher, parents studying. | Education of social responsibility and competence, choice in the media. The education of industriousness, a conscious, creative attitude to education, work and life |
| An unconventional parental meeting aimed at the development of patriotism, in the form of an oral journal "WWII in our family." Participants prepare an oral presentation, presentation, etc. about the pride of your family! General tea party. All results at the stage of reflection should be made out (school newspaper), we suggest presenting presentations on the class website. | The meeting is attended not only by parents, but also children, the older generation! Particular attention must be paid to the fact that the meeting is likely to require more time. | Education of citizenship, patriotism, respect for human rights, freedoms and duties |
After stage 1 (1 academic year), it is proposed to carry out diagnostics, analyze the work of the program of pedagogical education of parents, and make adjustments as necessary.
Grade 6 (8 lessons)
| month | lesson topics, forms and methods of implementation | organizers and actors | purpose of/ expected results |
| september | Creating family conditions for strengthening the health and physical training of adolescents. Tourism and excursions with children. Campaign with a preliminary parent meeting. | Cl. hands., parents, students, school teacher physical. Culture, Tourism Specialist. | Education of ecological culture, culture of healthy and safe lifestyle |
| october | The traditional form of holding a parent meeting. Lecture of a school psychologist "Self-esteem of a teenage student." | Class teacher, parents, school psychologist. | cognitive activity aimed at awareness of one's “I”. |
| november | Unconventional form of parent meeting. Workshop "Types of personality. What if he is not like me? ” At the class hour, the same workshop is held as with the parents. All information is collected on the board in the office. A unified homework is given to parents and children: to analyze communication in determining their personality types. | Class teacher and school psychologist. | cognitive activity aimed at awareness of one's “I”. |
| december | Unconventional parent meeting in the form of a webinar “Our Family Traditions”. Discussion of a unified New Year celebration style. | Class teacher, parents. Perhaps the participation of children with their parents (negotiated in advance). | Education of moral feelings, beliefs, ethical consciousness |
| february | An unconventional parent meeting in the form of parental readings. “Formation of legal awareness in a teenager, responsibility for his actions in his family, at school.” | Class teacher and social educator. Reminders are given to parents, mailing is carried out in their electronic diaries. | Education of moral feelings, beliefs |
| march | The traditional form of the parental meeting is “Moral development of the student”. | Class teacher, lecture of the Deputy Director for BP. | Education of moral feelings, beliefs, ethical consciousness |
| april | Unconventional form. Parent evening "songs that our children sing." Discussion of the need to revive family education, family traditions. | Class teacher and parents. Without the presence of children! | Raising a positive attitude towards family traditions |
| Summing up the program for pedagogical education of parents, conducting diagnostic tests, surveys. Identification of problems, questions of the need for such a program for grades 7-8. | All program participants. |
Also, the PPR program “Interaction” assumes the active participation of parents (through the parent committee) in the life of not only the class, but also the school and the municipality:
active parents help not only in organizing, but also in conducting school contests, tournaments, promotions, and other events.
representatives from the parent committee of the class help in the development and implementation of school programs for the prevention of family problems (together with the school social teacher and juvenile inspectors, they carry out raids, examine families, attend conversations with parents, and work closely with the SRCH-social rehabilitation center for minors and other).
a representative of the parent committee has the opportunity to attend school prevention councils.
Expected results of the program.
All parties benefit from the successful interaction of the Shelter, class teacher and parents. A positive result of cooperation for teachers is an increase in respect from parents and society as a whole, an improvement in interpersonal relationships with them, an increase in authority in the eyes of children, parents and the school administration, greater satisfaction with their work, and a more creative approach to it.
For parents, the result of the interaction is a better knowledge of the children and school curricula, confidence that their opinions and wishes are taken into account during the training, a sense of their importance at school, a stronger family and better communication with children
A huge role in the work of a teacher is played by diagnostics. Some educators may object, arguing that psychologists work in the school, and they are engaged in diagnostics. However, this is not about psychological diagnosis in its purest form; it is a psychological and pedagogical diagnosis. Without the use of psychological and pedagogical diagnostics, it is impossible to plan educational work in a children's team, to establish relations with a collective of parents. Any information that a class teacher can get from parents and children can provide an invaluable service to the family and child.
The family and school play a major role in the life of the child, and his development as an individual depends on how he feels in them. Therefore, neither a school without a family, nor a family without a school can not cope with the most subtle, complex tasks of becoming a schoolboy. The school should invite the family to cooperate, taking into account its capabilities.
The family should consider the school as its friend in the education of the student. The cooperation of the school and the family is the result of a focused and lengthy work, which, first of all, involves a comprehensive and systematic study of the family, the characteristics and conditions of the child’s family upbringing. The interaction of the participants in the pedagogical process should be planned and organized. The essence of the interaction between the teacher and the family is that both parties are interested in studying the child, disclosing and developing the best qualities in him.
Appendix No. 2

The most important indicator of the level of pedagogical culture of parents - the degree of awareness and implementation of the goals of upbringing, which coincide with those social needs that are presented today by society to the individual.
These basic goals of family education are dictated not only by the objective need to prepare the child for adulthood, but also meet the educational opportunities of the family.
A significant drawback of the parents' goal-setting in terms of vocational guidance is that far from always the attitude towards a particular profession is linked to the ability and abilities of children, their inclinations and interests. However, these opportunities remain largely unrealized due to a lack of relevant knowledge and the ability of parents to guide the development of the child’s abilities.
Obviously insufficient attention in the modern family is paid to the culture of child behavior. In the best case, parents try to ensure that their children observe basic courtesy skills and instill some hygiene skills. Culture of behavior - this is a comprehensive and rich area of \u200b\u200bhuman relations with other people, including a culture of communication, a culture of appearance, a culture of satisfying needs, etc.
Thus, the success of family upbringing, its socially valuable result, largely depends on the parents having that pedagogical sensitivity to the dynamics of social development and the requirements that it requires for a person, which cannot be comprehended intuitively, but must be introduced from the outside, interpreted as scientifically based pedagogical task.
So, among the expected results of the PPR “Interaction” Program for grades 5-6, we can distinguish:
Creation of a system of assistance to parents in the formation of a moral lifestyle of the family, in the prevention of negative manifestations in adolescents.
Improving the pedagogical culture of parents, revealing the creative potential of parents, improving family education using examples of family traditions.
Parents' awareness of the importance of health conservation (not only physical, but also emotional).
Strengthening the role of the family in raising children.
The formation of the qualities of the future family man and parent in adolescents through the system of cohesion in the family.
Parents' awareness of their importance in the pedagogical process, the possibility of influencing the educational and educational process in the framework of educational institutions.
The ability of parents to apply their knowledge in practice.
Valuable attitude to Russia, its people, the region, the domestic cultural and historical heritage, folk traditions, the older generation.
| Predicted Results |
||
| For the family | For parents | For a child |
| optimization of parent-child relationships; the formation of social skills for effective interaction with the child at different stages of his development; | raising the level of family culture. the formation of constructive behavior skills; awareness of parental roles and responsibilities; improving parental effectiveness; unconditional acceptance of the child; | mastering the role of a supporting parent. readiness for positive contacts with adults; mastering the skills of cooperation, effective interaction; the formation of a positive family image; gaining experience of adoption, support; solving urgent development problems. |
Ways to control and verify expected results
pPR programs.
The program of parental education for parents “Interaction” involves such methods of monitoring the expected results as intermediate monitoring (after the first year of the program, at the turn of grade 5-6 for possible adjustments) and final monitoring (at the end of the program, grade 6).
Monitoring is a system of diagnostic studies aimed at a comprehensive assessment of the results of the effectiveness of the program.
The main indicators and objects of research on the effectiveness of the program are the characteristics of parent-child relationships and the degree to which parents (legal representatives) are involved in the educational and upbringing process.
The basic principles of organizing monitoring of implementation effectiveness are systemic principle (involves the study of the planned results of the development of students as components of the general process of education and socialization of students) and principle of personality-social-activity approach (focuses the study of the effectiveness of activities on the study of the process of upbringing and socialization in the unity of the main social factors of their development - the social environment, upbringing, the personality’s activity, its internal activity).
The Interaction program provides for the use of the following methods:
Testing;
Poll;
A nquetting;
B eseda;
Psychological and pedagogical observation.
The main objective of the study is to study the dynamics of the process of involving parents in the PPR program. Within the framework of psychological and pedagogical research, three stages should be distinguished:
Appendix No. 3

Stage 1.
Stage 2.
Stage 3.
Appendix No. 4
| What comes to light | Methods |
||
| (questioning, conversation) | Observation | Testing |
|
Criteria effectiveness The implementation of the PPR program is the dynamics of parent-child relationships and the degree of involvement of parents (legal representatives) in the educational and upbringing process.
It is necessary to indicate the dynamics of pedagogical education of parents:
Appendix No. 5

It should be noted that the mismatch of the content, methods of education and socialization of students with the age characteristics of personality development, the formal attitude on the part of teachers and the unfavorable psychological climate in the educational institution can cause inertia of positive dynamics and the emergence of trends in the negative dynamics of the process of education and socialization of students.
Appendix No. 4

When considering the issues of training and education, the provision on the need for joint efforts of the school and the family to educate students was repeatedly emphasized. In particular, when revealing the essence and patterns of upbringing, it was said that its success largely depends on the unity and consistency of the educational influence of the family and school.
The school cannot but reckon with the fact that the influence of the family on the development and formation of children is largely due to the effect of early education. Many educators and psychologists noted that the foundations of a person’s personal development are laid in early childhood, before the age of five. However, the influence of parents and family continues in the years of the subsequent formation of man.
The value of the educational activities of the family has a great influence on its own strengthening. Children cement the family, bring a spirit of harmony and healthy unity into it. The better the family brings up the children, the more successfully their personal development takes place, the more joy they bring to parents and contribute to maintaining healthy relationships between them, which strengthens their educational potential.
Given the large role of coordinated educational work of the school, family and the public, this work must be skillfully coordinated and directed. Only a school is able to cope with this task.
Currently, the school has begun to perform basic functions in general education and the comprehensive development of youth. She also has qualified teachers and builds educational work on a scientific and pedagogical basis. Given that in some cases, parents do not have the necessary knowledge in the field of pedagogy and psychology, teachers are called upon to provide them with appropriate scientific and methodological assistance, to help improve the culture of family education. More P.P. Blonsky noted that children cannot be raised without raising their parents.
Applications
Appendix No. 1
Stages of creating a parent teacher education program
| 7 - Design of PPR for the next period | 1 - Diagnostics (identification of needs and determination of the typology of participants) | 2 - Compilation of the program of PPR (selection of topics, forms and determination of the resource base) |
| 6 - Analysis of the results | PPR program for 2011-2012, 2012-2013 academic year years | 3 - Joint discussion, correction of the educational strategy (or educational program) |
| 5 - Implementation of the PPR program + performance monitoring with timely correction | 4 - Informing the public about the PPR program (if education is organized on a school-wide scale) |
|
Appendix No. 2
Parent Education Indicators
Appendix No. 3
Stages of psychological and pedagogical research

The control stage of the study (diagnostic section)it is focused on collecting data from social and psychological-pedagogical research before the implementation of the PPR program.
Formative stage of researchinvolves the implementation of the main areas of the PPR program.
Interpretation phase of the studyit is focused on collecting data from social, psychological and pedagogical research after the implementation of the PPR program. The final stage involves the study of dynamics.
Appendix No. 4
Methods for studying the effectiveness of PPR
| What comes to light | Methods |
||
| (questioning, conversation) | Observation | Testing |
|
| The level of pedagogical competence of parents | |||
| Parent-child relationship style | |||
| Parental satisfaction with child relationship | |||
| Parental satisfaction with teacher education | |||
| The activity of parents during the teaching sessions | |||
Appendix No. 5
Dynamics parent education

Appendix No. 6
Characterization of the performance levels of PPR
Appendix No. 7
Questionnaire for parents
Dear Parents!
Please answer the questionnaire. It is necessary to note the answer option with which you agree. To facilitate the processing of information, please indicate any sign or symbol by which you recognize your profile.
Do you know the age characteristics of your child?
2. Are you familiar with your child’s communication styles?
I have an idea, but not enough
3. Do you know the regimen of the day of the child, ensuring the preservation of his health?
I have an idea, but not enough
4. Do you know the concept of family structure, and how is it defined?
I have an idea, but not enough
5. Do you manage to build trusting, good relations in the family?
Not always
6. How often do you read specialized literature on parenting?
Constantly
Occasionally
7. Who do you think should be involved in the development of a child’s abilities?
Family and school
Does not matter
8. To whom would you attribute yourself when raising your child?
Newbie
Graduate
Experienced
9. What do you think it means to educate a person?
(formulate 2-3 sentences)
Appendix No. 8
Test for parents.
Dear Parents!
Try to use a test that determines the giftedness and orientation of the child in some area of \u200b\u200bactivity. The proposed questions must be answered in the affirmative (“yes” - 1 point) or negative (“no” - 0 points). Then the points add up. The answer is determined by the result scale:
Does a child find unusual use for any object?
Does he change his inclinations?
Does she like to draw imaginary objects?
Does she like to draw abstract pictures?
Does he like fantastic pictures?
Does he write stories and poems?
Does she like to cut intricate shapes out of paper?
Has he ever done something that he did not know, or something that does not exist?
Does he have a desire to remake something to his taste?
Is he afraid of the dark?
Did you try to rearrange the furniture as you saw fit?
Was this plan successful?
Has the thing ever been used for other purposes?
Could your child, while still small, guess the purpose of different objects?
In choosing clothes, does he prefer his taste to your taste?
Does he have his own world, inaccessible to others?
Is he looking for an explanation for what he still does not understand?
Does he often ask to explain the phenomena surrounding him?
Does it portray its own games or entertainment?
Does he remember and tell his dreams or experiences?
Results Scale:
From 18 to 21 points: the child is very smart, able to have his own point of view on the environment.
From 12 to 17 points: the child does not always show his abilities, he is resourceful and quick-witted only when he is interested in something.
From 7 to 11 points: great wit, enough for many areas of knowledge.
From 4 to 6 points: your child shows creative thinking only when he reaches an important goal
Less than 4 points: the child lacks ingenuity, but he can achieve success as a good performer.
Appendix No. 9
Stages of the implementation of the program of pedagogical education of parents "Interaction".
Stage 1. Preparatory.
| activity | Responsible | Mark from execution |
||
| Acquaintance with the program of teachers, the administration of the OS | ||||
| Familiarization with the draft members of the parent committee | ||||
| Approving a project at a cool parent meeting. | ||||
| Interview with a group of organizers and project participants in order to motivate them, | ||||
| Organizational and active game with project participants on the topic "Diagnosis of problems". | ||||
| Preparation of a package of diagnostics of the level of parental culture: Development of questionnaires for parents; Acquisition of test discs for children and parents, psychological family tests. | ||||
| Diagnostic package approval team meeting | ||||
| A survey of parents in order to determine the level of parental culture, preparedness for PPR (stage 1, control). | ||||
| Summarizing the questionnaire of parents, predicting the participation of parents in the implementation of the project. | ||||
| Determining the content of the program of psychological and pedagogical education of parents. |
2 stage. Partial project implementation
| activity | Responsible | Progress mark |
||
| Conducting an informational meeting of the creative team for the project and parents to familiarize themselves with the goals and objectives of the project, with the results of the survey. | ||||
| Conducting a business meeting of parents and teachers participating in the project to agree on a project implementation schedule, to diagnose the problems of psychological and pedagogical education of parents. Familiarization with the rules for filling out the portfolio. | ||||
| A training seminar for teachers participating in the project on the methodology of conducting master classes and trainings. | ||||
| Opening of a self-diagnostic laboratory for parents (individual computer testing) | ||||
| Development of the theme of master classes with teachers, project participants. | ||||
| Expanded pedagogical Council of teachers and parents on the presentation of the program | ||||
| Testing the program of psychological and pedagogical education of parents in (5th grade) | ||||
| Summing up the partial implementation of the project |
3 stage. Implementation of the program of psychological and pedagogical
parent education.
| activity | Responsible | Progress mark |
||
| The work of the program on psychological and pedagogical education of parents on calendar and thematic planning. | ||||
| Conducting contests "Best Parent Team", "Father of the Year", "Mom of the Year" | during the school year, according to plan | |||
| Reflection of the progress of the project at the stand "If you are a good parent" | during the school year | |||
| Correction of the program of psychological and pedagogical education of parents on educational requests of parents | according to monitoring results (Once a year) | |||
| Summing up the results of the program | at the final meeting | |||
| Awarding of the best parents according to the results of the contests “Best Parent Team”, “Father of the Year”, “Mom of the Year”, etc. | at the final parent conference, according to plan | |||
| Improving the material and technical base, conditions for the implementation of the project | Quarterly | |||
| Further training of lecturers | during the program |
4th stage. The final.
| activity | Responsible | Progress mark |
||
| Preparation of a substantial report on the implementation of the project. | ||||
| Preparation and publication of articles in the media, school newspaper, on the progress of the project | During the project implementation period | Creative Group. | ||
| Preparation and publication of a collection of materials on the results of the project. (as agreed with parents !!!) | ||||
| Conducting seminars for class teachers of the school in order to transmit experience on the basis of the project. | By agreement with the administration of the OS |
Intended use of the results of the Interaction program
Dissemination of experience in pedagogical education of parents among class teachers of public education.
Translation of the organization model of psychological and pedagogical education of parents in other educational institutions.
Conducting a parent conference with providing parents with the results of the project.
The inclusion of the Interaction program in the school development program as one of the subprograms for interaction with students' families.
Bibliography
Andreev V.I. Health-saving training and education. - Kazan, 2000.
Ananyev N.I., Blinova E.G. Modernization of education, health and some issues of adaptation of students. Actual problems of human adaptation. Issue No. 2. - Surgut, 2002.
Bazarkina E.L. Conversations about morality. - Volgograd, 2006.
Bazarny V.F. Neuropsychic fatigue of students in a traditional school environment: the origins, approaches to prevention. - Sergiev Posad, 2004.
Belov V.I. The psychology of health. - M .: KPS; St. Petersburg: Respex, 2000.
Bezrukikh M.M. Health-saving school.- M.: Mosk. Psychological and Social Institute, 2004.
Ksenzova G. Yu. How to ensure a situation of success for a teacher and a student: Textbook. - M .: Pedagogical Society of Russia. 2005.
Meleshko Yu.V., Lezhnev Yu.A. Parental universal education. - Minsk, 2002.
Miroshnichenko T.A. Family and school: the brink of cooperation: an event development program. - Volgograd, 2009.
Salyakhova L.I. Parent meetings: traditional and non-traditional forms. Grades 5-9: method. The allowance.- M, 2007.
Smirnov N.K. Health-saving educational technologies in the work of teachers and schools.- M .: ARKTI, 2003.
Modern technologies for preserving and strengthening children's health: a Training manual. / under total. Ed. Sokratova N.V. - M.: SC Sphere, 2005.
School and student mental health. // Ed. S.M. Grombach. - M., 2002.
Shepel V.M. How to live long and joyfully. - M .: Antikva, 2006.
Schurkova N.E. Educational technology. Second edition supplemented. - M .: Pedagogical Society of Russia, 2005.
Internet resources:
http://rudocs.exdat.com/docs/index-218357.html
http://www.parus-nad.ru/roditel/shkola-effektivnogo-roditelstva/
1 Psychology of family relationships. M., 2000.
2 Online workshop (web conference, webinarEnglish webinar) - a type of web conference, conducting online meetings or presentations over the Internet in real time. During a web conference, each participant is located on his computer, and communication between them is maintained via the Internet through a downloadable application installed on each participant’s computer, or through a web application.
Skulyabina L.V. - primary school teacher of the highest qualification category
Education of parents as one of the important factors in the development and education of schoolchildren.
The first year of schooling is of great importance. It largely depends on how the child will learn in the future. The first class is a serious test, both for the child and for the parents. Many parents believe that preparing a child for school means teaching them to read, count, and write. However, not knowing the modern school requirements, parents run the risk of teaching the child so that the teacher will be forced not to teach him, but to retrain and make great efforts to eliminate the results of the incorrect preparation of the child for school.
The main thing is that children come to school with the desire and ability to learn, so that the child is psychologically ready for school. Therefore, it is important not only to prepare the child for school, but also their parents, that is, the teacher should engage in educational activities.
Pedagogical education is one of the traditional forms of interaction between school teachers and parents. We use various forms of work with parents, they are interconnected and represent a single harmonious system. These are lectures, and workshops, and seminars, discussions, consultations. We introduce parents to the basics of theoretical knowledge, with innovative ideas in the field of pedagogy and psychology.
Parents need to be taught to ask themselves questions: how to love their child for who he is ?; Is it necessary to protect the child from difficulties ?; How to help a child believe in himself? How to develop a child’s abilities? An important role in the child’s readiness for learning is played by the stock of knowledge that he, with the help of adults, independently acquired in the first six years of his life.
The baby, barely born, is completely open to the outside world. To loving and attentive parents, his behavior seems simple and understandable. But time passes, and the inner life of the child becomes more hidden. Often his parents cannot explain the behavior. Intuition often becomes powerless, education - a complete contradiction. This is where the need arises for scientific knowledge about the life of a small person. In a rural school, parents can get such knowledge from a teacher. Therefore, primary school teachers begin to educate parents from the preschool age of children, and throughout, according to the definition of psychology, all of middle childhood (from 5 to 11 years). At this time, the child forms a sense of duty, the concept of morality and the pursuit of achievement. Communication skills are developing. The child learns to set and solve real problems, he has a desire to receive praise, a positive assessment of his actions.
Teachers of our school use such forms of pedagogical education in their work as parental meetings, pedagogical universal education. It is the most important form of work of the class teacher with the family of the student, a means of increasing the effectiveness of the educational process. At parent meetings, we familiarize parents with the content and methodology of the educational and educational process. We give a description of the programs used, training methods, talk about ongoing extracurricular activities, circles. At pedagogical education, we inform parents about the characteristics of a particular age, the conditions for successful interaction with children. We offer parents to conduct joint games with children: games for the development of thinking in preparing children for school; games to prepare children 6-7 years old for school; learning to read children - sound games.
For example, a game on the development of thinking “Whose number is greater” In a box, lay out two groups of objects, in each of which there are no more than five. It is necessary to tell the child the name of the items that are hidden in the box without naming their quantity. Let's say this buttons and pebbles. The child chooses one of the groups. For example: "My buttons, your pebbles." After that, he takes out of the box and counts how many objects in both groups and which more. If the child has made up objects, which will be more, then he gets as many points as there are more objects in this group. If the child chose those items that are smaller, you get the difference. The game is repeated several times. The one who gets the most points wins. If the guesser makes a mistake in the calculations and is noticed by the partner, the chip does not count towards him. Repeating the game, switch roles with the child.
We will also give an example of a reading teaching game, since one of the many questions facing parents during this period is whether to teach a child to read before he goes to school, if so, when is the best time to start? If the parents of preschoolers have a desire and the opportunity to read with the child, then let him come to school, able to read. Learning to read at five is easier than at seven to eight. We educate parents about how to easily, safely, and have fun typing their children in writing, how to make their child a fun reading technique and instill a taste for independent reading, while avoiding the standard mistakes of home literacy.
If the child speaks late or has serious pronunciation defects, the poor vocabulary builds short phrases, in this case you should not rush to learn written language. Acquaintance with alphabetic characters will be unsuccessful if the child does not know what exactly is indicated by this sign.
The path to literacy lies through games of sounds and letters. In order to learn to read and write, a child needs to make two important discoveries: first, to find out that speech is “built” from sounds, and then to discover the relationship of sound and letter. The methods of accentuation, intonation, the allocation of sounds in a word to a child are best conveyed in a game: games - onomatopoeia; sound lotto; forbidden sounds; house of sounds; house in the forest. All these games help to analyze sounds in a speech utterance, to distinguish between soft and hard consonants, focus on stressed vowels, teach the definition of the complete sound composition of a word.
After the proposed information and the joint work of parents and children at home, we collect a parent meeting, where parents talk about what they could learn about their child. How much the proposed games were useful to them in communicating with children. How the child has changed as a result of collaboration, etc.
In the classes of pedagogical universal education, the pedagogical needs of all parents cannot be satisfied. Therefore, there is a need for individual work, which allows you to privately discuss problems of concern to parents, give qualified advice. Teachers note the importance of individual work with parents in the process of their pedagogical education. Individual work with parents is also necessary because the family is a deeply intimate team and discussion of individual pedagogical situations and issues that arise with parents is possible in some cases only during individual work. The main form of individual work is pedagogical consultation. Its value lies in the fact that parents go to the consultation on their own initiative, are set up to discuss problems that concern them, and strive to obtain the knowledge necessary for targeted impact on the personality of the child. Usually, a school draws up a system of consultations that are held individually or for a subgroup of parents. The goals of the consultations are the assimilation by parents of certain knowledge, skills, and assistance in resolving problematic issues.
As the child grows and develops, the child changes, sometimes gradually, sometimes rapidly and unrecognizably. And the course of this process depends not only on the will of chance, but also on the directed efforts of loving and understanding adults.
When a child begins to attend school, we invite parents to open lessons so that they can better understand the capabilities of children, their requirements, and monitor their intellectual growth. In open classes, parents have the opportunity to make sure that the game, the game situation is very helpful in learning. Observing children in the classroom allows parents to understand what they should pay special attention to, how and what help to provide to the children. Gradually, parents become convinced that the child’s interested work brings more tangible results than prompting, shouting and begin to use the techniques and methods that teachers demonstrate in open lessons. At the end of the school year, such lessons show what children have learned during the school year. They see that children learn here not only to write, read, count, but also to be inquisitive, inquisitive, kind, responsive. And this is achieved thanks to the joint work of the teacher, students and parents.
We involve parents in joint activities with children. These are extracurricular activities, contests, excursions, holidays. Extracurricular activities are conducted with the participation of parents. At general holidays, parents are both participants and organizers. Children's holidays turn into close cooperation of three parties - children, parents, teachers. They summarize a specific piece of learning activity. In addition, during the holidays and during preparation for them, there are many opportunities for children and parents to communicate. At this time, the abilities of the children, their affection, are revealed. Preparatory work contributes to the expansion of students' knowledge, creates an atmosphere for creativity, manifestation of activity, independence, imagination. This kind of activity makes it possible to educate parents about how the child is brought up, what stages of the development of the child exist, his individual characteristics. The parent should be guided in this knowledge and skills, i.e. to know the general stages of the child’s development (physiological and mental), to understand their connection, to realize the basic principles of development - what, how and how to develop.
Once a year we carry out parental readings. They give parents the opportunity not only to listen to lectures by teachers, but also to study literature on the problem and participate in its discussion.
The content of the teacher’s work with parents includes, in fact, all the issues of raising and educating children. In the course of pedagogical education, parents receive knowledge about the features of the development of the child, the tasks of upbringing, methods of organizing the game environment, and preparing children for school. Working with parents is a complex and important part of the teacher’s activities. One of the main goals of pedagogical education is the involvement of parents in the pedagogical process. Whatever form of work with parents the teacher chooses, the main thing is his personal interest in the work, a friendly attitude towards the children, their parents, as well as the systematic nature of the work.
List of references
1. Aleshin Yu.E. Individual and family psychological counseling: Social health in Russia. - M.: Class, 1994. - S.25-37.
2. Belskaya EG Basics of psychological counseling and psychotherapy. Tutorial. - Obninsk: IATE, 1998. - 80 p.
3. Ed. A.A. Bodaleva. Popular psychology for parents [Text]: a book for parents M .: “Pedagogy”, 1989. -256 pp. - 300,000 copies.
4. Davydov, V.V. Types of communication in learning [Text]: a book for a teacher / V.V. Davydov. - M .: "Pedagogical Society of Russia", 2000. -480 p.
5. Karabanova O.A. Psychology of family relations and the basics of family counseling. - M., 2004.S. 112 - 121
6. Martsinkovskaya T.D. History of Psychology: Textbook for students. higher textbook. institutions .- M.: Publishing Center "Academy", 2001
7. Matveeva A. Practical psychology for parents or what I can learn about my child. - M "AST-PRESS" South - Ural Book Publishing House, 1997.
8. Obukhova L.F. Children's (age) psychology. M., 1996.
9. Ovcharova R.V. Psychological support of parenthood. - M .: Institute of Psychotherapy, 2003.S. 222