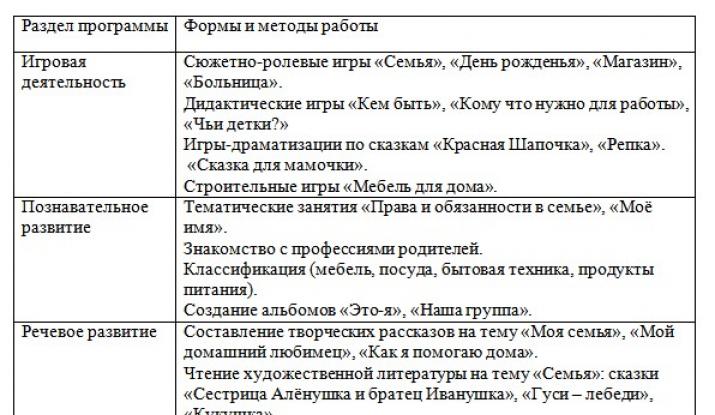
Project activities in the second junior group
Type of project: cognitive-research, health-saving. Includes creative, cognitive and practical activities.
Duration: medium-term (September, October, November.)
Participants: educator, children, parents.
The relevance of the project: the project is intended for children of the second youngest group of preschool educational institutions with the aim of expanding children's knowledge of vegetables and their significance for human health; consolidation of knowledge about where vegetables come from on our table.
The project unites educators, parents and children in a common creative work.
Project Goals:
- creation of conditions stimulating interest in; expansion and generalization of children's knowledge about vegetables through different; parents into joint creative and research activities.
Problem: in urban conditions, where everything is bought ready-made, children do not have a clue where vegetables come from and what conditions are necessary for their growth and development.
- to expand children's ideas about vegetables, their beneficial properties; to develop cognitive activity of children, creative imagination and thinking, communication skills; to teach children to portray vegetables, fruits and berries in the classes for drawing, modeling, using various methods and means of representation; clarify ideas about adult work, cultivate diligence and respect for plants.
Design idea: create a window garden in a group.
Expected results:
- Children will get acquainted with cultivated plants. With the help of experimental work, children will gain knowledge that vegetables are grown from seeds that are planted in the ground and create the necessary conditions for their growth. Intensification of speech activity on the topic "Vegetables". To show a desire in children to eat vegetables. Involve parents in the implementation of the project.
Forms of implementation
- Classes by. Conversations with children and parents. Game activity. Performing works on visual activity. Exhibition of children's creativity. Conducting entertainment.
This project contributes to the development of cognitive research and creative abilities of children.
Experimental activities and observations teach children to draw the first conclusions: "From a seed, you can grow a plant."
Familiarization with feasible work on the care of plants develops in children responsibility for the task entrusted. It educates children in their desire to participate in work, makes it possible to understand that there is a certain benefit hidden behind each vegetable.
Project Stages
Preparatory stage
- To select, illustrated material on this topic, to conduct a conversation of a cognitive nature. Collect drawings with the children, prepare photo material. Consultation for parents on the topic. To form interest among parents on creating conditions for the implementation of the Miracle Garden project. Offer parents homework: writing stories about vegetables with their children, crafts from salt dough, etc.
The main stage. Cognition
Experience: examining and planting seeds of onion, dill, carrots in a group.
Observations: "Do our plants grow?"
Psycho-gymnastics “I am a plant”
Children sit with their eyes closed.
Educator: “Guys, imagine that you are seeds. You were planted in warm land. Seeds in the ground sprout. You are still very small, weak. Someone's good hands water you, loosen the earth. Look after, care. You are starting to grow. Your petals have grown. The stalk becomes strong. You are drawn to the light, the sun. How good you are. Open your eyes. It will be good and pleasant for the plants if we take care of them. ”
Cognitive conversation “What is a garden and what grows on it?” gives an elementary concept of where and how vegetables and cultivated plants grow.
Fiction
Acquaintance with works of art related to the garden, vegetables: poems by A. Maksakov “Planted in the garden”, K. Chukovsky’s “Garden”, Yu. Tuvim “Vegetables”, fairy tales “tops and roots”, etc.
Speech development. Communication
Compilation of stories “How I Help Plants”, “My Favorite Vegetable”, “Cooking”.
Word games “Guess, we will guess”, “Name, you describe.”
Learning proverbs, sayings, guessing riddles on the subject of "Vegetables".
Daily excursions to the experimental garden of group No. 4, observation of seedlings in the group encourages children to turn to adults with questions, opinions, and verbal communication between themselves.
Art and aesthetic development
- Coloring pictures. Modeling "Carrot for a bunny", "My favorite vegetables" for playing in the "Vegetable Shop". Application "Vegetables on a plate." Dramatization of the fairy tale "Turnip" (develops acting abilities in children).
Didactic games
The games “Find what I will describe”, “Guess to taste”, “Fold the picture”, “Lotto - vegetables”, “Wonderful pouch”, “Tips for the little housewife” contribute to the development of attention, fine motor skills, tactile sensations, memory, speech.
Acquaintance with the works related to the subject of the project (round dance games, songs), developing emotional responsiveness.
Zucchini, zucchini,
Thin legs
Red boots.
We fed you
We watered you
They put me on my feet
They made me dance.
Dance as you want
Choose whomever you want!
Round dance game "We have a garden ..."
We will go to the city
We’ll start a round dance.
We will sing and dance
Harvest to collect.
We have a garden
There, green onions grow.
Here is such a height
Here is such a width.
Labor activity
Caring for plants in the corner of nature. Cooking vinaigrette (tutor) according to the algorithm. Making dummies of vegetables.
Physical development
The mobile game "The garden is in order with us."
We dug up beds in the spring.
(imitate the work of a shovel)
We spilled the garden
(we bend down and get our hands on the floor)
Watered the garden.
(pour water from a watering can)
In the holes of the little is not thick
(palms show)
We planted cabbage.
(crouched, covered his knees with his hands)
Summer, she’s getting fat,
(slowly rise)
Spread in breadth and height
(slowly rise)
And now she is very poor.
Says: "Get out!"
(stand up and stamp your foot).
Finger gymnastics "Cabbage"
We chop cabbage, chop.
We have three carrots, three.
We salt the cabbage, salt.
We harvest cabbage, harvest.
We try, it is very tasty!
Socialization: learn to take care of nature.
The principle of taking into account age-related features allows us to consider various problems at an affordable level, and then return to the studied materials at a new, higher level.
The final stage
- Exhibition of children's works. Parents showed their homework. Leisure "Our cheerful garden."

The story of the turnip
Grandfather planted a turnip. Turnip has grown big, big. It's time to harvest. Grandfather pulls a turnip, pulls, pulls, cannot pull. Grandfather is old, no strength.
Grandfather called Ignat. Ignat came running, grabbed a turnip by her big ears and pulled it out.
“Well done, Ignat!” - the grandfather praises.
“Well done, granddaughter!”, The woman praises.
Ignatushka is satisfied: “One managed!”
Nemtinov Ignat
Pasha in the garden
Pasha went to the garden and drove the car with him: vegetables must be collected. Yes, it hurts the car is good!
“Could I sit in a car and ride for myself?” Pasha thinks. Well, right. Vegetables will not run away from the garden, they will wait!
Bashmakov Pavel
As big as an elephant
In the garden she is a champion
What kind of vegetable is this, kids?
And how can I not know! In her hands held. I will prove it not in words, but in deed.
Shevchenko Olya
We are gardeners
It was one summer hot day. Nastenka wanted to drink some water. Then Ilyusha wanted to. They went to the teacher and asked for a vodice. They drank and thoughtfully: “And the flowers, too, want to drink, I guess. It’s hot after all. ” And the teacher approved, even praised: "Oh, you are my gardeners!"
Lokteva Nastya
My favorite vegetable
Our Zhenechka knows everything about bell pepper. He can also tell you what dishes are prepared from it.
“Peppers are green, yellow, red. He is sweet, juicy, and I love him, ”shares Zhenya.
Senina Zhenya
Want to be healthy - eat garlic!
Mom prepares dinner, and Maxim helps. Mom began to rub garlic on a fine grater, the smell in the kitchen went. Maxim does not like garlic and asks his mother not to put it in the sauce.
Mom teaches: "Eat garlic, Maxim, it is very useful, it kills all bad germs, you won’t be sick."
Maxim agreed, and the sauce was very tasty.
Mom and Maxim Pavlov
Used Books
- Samorukov familiarization of children with nature in kindergarten. - M.: Education, 1991. Shorygin. What are they like? - M.: Education, 1992. Internet resources.
Nomination “Methodical work in a preschool educational institution”
Problem. It is proved that the best knowledge is acquired by the child of the knowledge that the child acquired in practical activities.Unfortunately, in preschool educational institutions, experimentation is unjustifiably rarely used, especially at the younger preschool age.The importance of independent research activities of the child is underestimated, despite its positive aspects, despite the active development of this direction in preschool education.
Despite the fact that in experimental activities there are more opportunities for self-knowledge and self-determination of a child, for personal growth and disclosure of his personality, teachers are reluctant to use this method in everyday activities, leaving it for open classes and mass entertainment events.
The relevance of the project.Preschoolers are born researchers. And this is confirmed by their curiosity, a constant desire for experiment, the desire to independently find a solution in a problem situation.
Experimentation gives children real insights about the various aspects of the object being studied, enriches the child’s memory, activates his mental processes, and includes an active search for solutions to problems.
The younger preschoolers, getting acquainted with the world around them, strive not only to examine the subject, but also to touch it with their hands, tongue, smell it, knock it. Children tear paper, make out toys, play with sand, water and snow.
In everyday life, children often themselves experiment with various substances, trying to learn something new. They watch objects falling into the water (drowning - not drowning), using their tongue in icy frost, etc. Exploratory Behavior for Preschooler- the main source of understanding about the world. We adults must actively help him in this.
Objective of the project: develop cultural practices of interest preschool childrento cognition and research, to support the desire for manifestation independence and initiative, curiosity.
Tasks:
- To acquaint children with some of the properties of water, air, light, paper.
- Develop your own cognitive experience.
- To support the initiative, independence, quick-wittedness in children.
- Encourage friendships during research activities.
- To shape the cultural practice of expressing interest and desire to broaden one's horizons.
Type of project:information research, group.
The participants:educators, children, parents.
Terms of implementation: short term (1 week).
Predicted result:development of the content of cultural practices to implement the objectives of the project:
- a steady cognitive interest in experimentation;
- development of the ability to consciously choose objects and materials for independent activity;
- manifestation of initiative and creativity in solving assigned tasks;
- mutual assistance, active social interaction;
- high-quality and interested participation of parents in the implementation of the project.
The main section of the program: social and communicative development.
Organization of project activities
Preparatory stage:
- problem statement;
- determination of relevance, goals and objectives;
- selection of methodological and fiction;
- selection of experiments for a given age;
- selection of equipment for experiments.
The main stage:
- organization of the subject-development environment,
- conducting experiments, experiments in a group and on a walk,
- individual work with children,
- independent experimental activity,
- outdoor games,
- reading fiction
- conversations
- productive activities of children.
The final stage:
1. Registration of the file of experiments.
2. Exhibition of crafts made by parents with children.
Project flow chart
Social and communicative development
|
Cultural practices |
|
|
Kinds |
|
|
Integration Kp: Game Interaction Practices Communicative practices |
Games: “Find out who called?”,"It happens - it does not happen." D / exercise: “Find and bring a paper item.” Gaming exercises:“Turn a circle into the sun, an apple, a ball, a wheel, etc.” Problematic situations:
Conversation - Exercise"The taste and properties of food." Di“Catch your shadow” |
Cognitive development
|
Cultural practices |
|
|
Kinds |
|
|
Integration Kp: Cognition of the world and self-knowledge, Free practices of children's activities, Communicative practices Identification and interaction of the child with the surrounding society. |
Pilot activity:
Experimenting games:
Game experience"Colored ice"
Study:
|
Speech Development
|
Cultural practices |
|
|
Kinds |
|
|
Integration Kp: Communicative practices Cognition of the world and self-knowledge |
Conversations:
Reading:
Heuristic conversations:
|
Art and aesthetic development
Physical development
|
Cultural practices |
|
|
Kinds |
|
|
Integration Kp: Healthy lifestyle Game Interaction Practices |
Finger gymnastics"Skillful hands", "Dog and cat." Outdoor games:
Gymnastics for the eyes"A drop, a drop two ..". Gameswith paper airplanes, sultans and turntables. Gym "Rainbow Arc." Game m / n:"It's cold and hot." |
Interaction with parents
|
Cultural practices |
|
|
Kinds |
|
|
Integration Kp: Cognition of the world and self-knowledge, Communicative practices |
Familiarization of parents with the purpose of the project and the types of joint activities for its successful implementation. Organization of joint activities with children at home :
Involve parents in the replenishment of the experimentation center with new cognitive literature. |
Activity distribution by activity centers
Theatrical activity center:making characters for the shadow theater "The Tale of the Stupid Mouse".
Center for experimental activities:preparation of all materials necessary for research(soap bubbles, paper of various types, paper boats, balloons, water containers, straws, a screen for a shadow theater).
Project implementation results (total):
The content of cultural practices of children has expanded:
- sustained cognitive interest in experimentation;
- increased ability to consciously choose objects and materials for independent activity
- initiative and creativity in solving the tasks set, the ability to mutual assistance.
- interest of parents in taking part in the implementation of the project has intensified.
- a recommendation was made for parents: “The role of the family in the development of the cognitive interests of a preschooler”
- framed a file of experiments for practical activities.
- organized an exhibition of paper crafts made by parents with children.
References:
1. A. Dietrich, G. Jurman “Pochemuchka”.
2. Van. Cleve J. "200 experiments"
3. Dybina OV, and others. Unknown near: entertaining experiments and experiments for preschoolers / O.V.Dybina (ed.) .- M.: SC "Sphere", 2001.
4. L. L. Sikoruk “Physics for Kids”.
5. Nikolaeva S.N. The methodology of environmental education in kindergarten. M., 1999.
6. Nikolaeva S.N. The education of ecological culture in preschool childhood. M., 1995.
7. Perelman Ya. I. Entertaining tasks and experiences. Yekaterinburg, 1995.
8. “Designing and organizing cultural practices in preschool childhood” / author M.V. Korepanova - doctor of pedagogy, professor, head of the department of pedagogy of preschool education, dean of the faculty of preschool and primary education of the Volgograd State Social and Pedagogical University.
9. Ryzhova N. N. A. Ryzhova The magician - water. M., Link-Press, 1997
10. Smirnov Yu.I. A book for talented children and caring parents. SPb., 1998
11. What is? Who it? M., 1996.
Project activities in kindergarten are very interesting, a certain topic or material is more widely disclosed. I present to your attention a project on Russian folk tales. I hope someone comes in handy!
Download:
Preview:
The project in the second junior group "Tales are always with us!"
Type of project: artistic and aesthetic
By the nature of the contacts: within the group
By the number of participants: collective
Duration: short-term (2 weeks)
Relevance of the project:
Folk tales - the oldest of the common forms of oral folk art, present to all peoples, such a tale reflects beliefs, views, the dominant features of a national character, exposes class relationships, while revealing an old way of life, which is often reflected in individual works - everyday tales, animal tales , fairy tales.
Formulation of the problem:
Children know few Russian folk tales.
Goal:
Create a positive emotional attitude. To form in children ideas about the Russian folk tale through various activities.
Tasks:
- consolidate knowledge of the content of fairy tales
- form a desire to look like goodies
- develop the ability to convey the image of a fairy-tale hero with speech, movements, gestures, facial expressions.
- foster interest in fairy tales
- to instill in children the rules of safe behavior on the example of fairy tales.
Expected Result:
Children will get acquainted with many Russian folk tales, will know their content.
They will learn how to transmit their hero in games - dramatization, puppet theaters, table theaters.
Involvement of parents in further participation in group activities (contests of drawings, crafts, replenishment of the developing environment, etc.)
Game motivation:
During the acquaintance of children with fiction, through the arrival of Grandmothers - storytellers to acquaint children with Russian folk tales (who writes rn.s., who passes them from generation to generation) - names, contents, discussion of the heroes of fairy tales, highlighting the positive and negative features.
Project implementation:
Educational area | Activities | |
Cognition | Communicative | Conversation "Who writes fairy tales?". |
Socialization | Game activity | The game "Puppet Theater". Game Dramatization Table theaters |
Physical Culture | Motor activity | P. / Game "Hares and the Wolf." P. / Game "Geese". P. / Game "Sparrows and the cat." P. / Game "The Bear in the Forest." Round dance "Burn, burn clearly." P. / Game "Fox on the hunt." |
Health | Motor activity |
|
Security | Communicative activity |
Conversation “Do I need to obey adults” |
Communication | Speech activity Game activity |
|
Reading fiction | Reader activity |
|
Art | Painting Applique Modeling |
|
Music | Motor activity Songs |
|
Work | Constructive activity |
|
Final event:
Game Dramatizationaccording to the fairy tale "Teremok" and the art of plasticine painting - the sticking of the walls of the "Teremok", decoration with peas and buckwheat. (Preliminary work - applique roof and small window)
goal : To develop the memory of children, the ability to guess the names of Russian folk tales, according to the riddle and visual pictures of the tale. To form children's skills to convey their character fairy tales "Teremok", speech, facial expressions, gestures and actions. To develop skills in working with plasticine in creating a small tower: to pinch a small piece from the whole and by smearing it with a finger, fill the contour of the object without crawling out of the contour. Develop finger motility using peas and buckwheat to decorate the house. Raise interest in fairy tales, accuracy in working with plasticine.
Move : Arrival of Grandmother - storytellers: “Hello children, did you recognize me? And I came not alone, I brought you friends! Meet them! ” Children in costumes of characters from the fairy tale “Teremok” enter. (Sit down with other children). “And I brought a chest with surprises with me. Here is the first surprise: I told you a lot of tales, showed a lot. Tales are asked, and now, you friends, get to know us! ” (I take out pictures - fragments of fairy tales and read a riddle, children guess:
- Mixed on sour cream, chill on the window,
A round side, a rosy side, rolled ... a bun.
- Oh, you Petya - simplicity,
blinked a little:
I didn’t obey the cat,
He looked out the window ("Cat, Rooster and Fox")
- And the road is far away
And the basket isn’t easy,
Would sit on a stump
Would eat a pie ("Masha and the Bear")
- In a fairy tale, the sky is blue
In the fairy tale, the birds are terrible,
River, save me
You save me and brother ("Geese - Swans")
- Near the forest at the edge
Three of them live in a hut,
There are three chairs and three mugs,
Three beds, three pillows,
Guess without a clue
Who are the heroes of this tale? ("Three Bears")
- Everyone knows in Russia,
Waiting for mom with milk
And let the wolf into the house,
Who are these ... little children ("The Wolf and the Seven Little Kids")
Grandmother is a storyteller:Well done, I guessed all my riddles, everyone recognized tales.
Let's rest and build a house for the gnome:
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, (turns to the right, left, hands on the belt),
We will build and play (squats),
we build a large, tall house (arms up, on toes),
we put the windows, we cut the roof (we show the window with our hands, hands above the head - imitation of the roof),
this is such a beautiful house (hands in front of you, pointing to the house),
the old gnome will live in it (clapping hands)
Grandmother - a storyteller: And now, dear viewers,
A fairy tale to see, do you want?
Every fairy tale has its own good
Girls and boys a lesson.
The game is a dramatization of the fairy tale "Teremok".
2 part:
Grandmother is a storyteller:Make a present"Teremki" for my fairy-tale heroes.You have already begun work, I know, let's continue. Here are your towers (I distribute the work of children). I propose a model of work that should turn out. What painted the walls of the tower? Correctly with plasticine, we pluck off a small piece and spread it on the walls without leaving the outline. When you paint over the entire wall with plasticine, you can decorate with peas or buckwheat, which are in your plates.
Independent activity of children. The storyteller's grandmother provides assistance as needed, a reminder, uses a sample display, etc.
Evaluation from Grandmother - storytellers: Well done, really tried. For this, here is my surprise from the chest - new books with fairy tales and treats (sweets).
Farewell and departure of the Grandmother - storytellers.
Teachers pay great attention to the organization of the subject-development environment in the young group. The age of the children, their desires, the nature of independent play activity are taken into account. To help children feel more comfortable in kindergarten, we decided to involve parents in the design of the reception.
From an early age, children are introduced to folklore (fairy tales, nursery rhymes, jokes). The principle of visibility helps to increase the interest of the kids and show their parents their importance in this process.
Download:
Preview:
State budgetary preschool educational institution
Kindergarten No. 52 of the Kolpinsky district of St. Petersburg
Project Passport
"Gingerbread Man"
Project Information Card
Project "Gingerbread Man"
Type of project: family short-term (three weeks).
District, city: Kolpino district.
Organization Address: Kolpino, st. Raumskaya, 3, GBDOU d / s No. 52, tel. 481-70-56
Project participants: the educator of the 1st junior group “A”, the children of the 1st junior group “A” and their parents.
Children age: 2-3 years.
Location of the project: Kindergarten group, a playground for walking in the kindergarten.
The problem the project aims to solve is: involvement of parents in active participation in the life of the group.
Relevance of the project:Teachers pay great attention to the organization of the subject-development environment in the young group. The age of the children, their desires, the nature of independent play activity are taken into account. To help children feel more comfortable in kindergarten, we decided to involve parents in the design of the reception.
From an early age, children are introduced to folklore (fairy tales, nursery rhymes, jokes). The principle of visibility helps to increase the interest of the kids and show their parents their importance in this process.
Objective of the project: Organization of a developmental environment with the participation of parents. With their own hands they create visual aids, didactic games for the Russian folk tale "Kolobok". The exhibition of works in the reception room will not only enrich the subject-developing environment and delight the kids, but also help parents realize their role in the development of the cognitive interests of the child.
Project Objectives:
For children:
- To help children feel more comfortable in kindergarten.
- Maintain interest in the Russian folk tale through visualization and didactic games.
- Develop children's speech, enrich vocabulary.
- Expand the world around us.
For educators:
- Promote the use of the project method in working with parents.
For parents:
- Attracting parents to actively participate in the life of the group.
- Educational work on the role of the family in raising a child.
- Exhibition of creative works of parents.
The final event of the project:integrated plasticine modeling lesson “Kolobok”
Preparatory stage.
- Selection of fiction for reading and memorization;
- selection of games appropriate for age;
- enrichment of the subject - development environment;
- prospective work planning;
- preparation of recommendations for parents (to pay attention to the role of the Russian folk tale in the development of young children; give recommendations on productive activities: to make a picture, a panel, a didactic game or visual aid (at the choice of parents) for the Russian folk tale "Kolobok");
- selection of demo material.
The main stage.
- The work of the teacher with parents:
Practical assistance in productive activities, advice;
Consultation "The role of the family in raising children"
- Teacher work with children:
Cognitive development:
- The story of the educator about animals from a fairy tale.
- Integrated lesson “What is the form?”
- D / and "Who lives where?"
- Watching the cartoon: "Gingerbread Man".
Speech development:
- Reading to children of the Russian folk tale "Kolobok"
- D / and "Who is gone?"
- Consideration of plot pictures of a fairy tale.
Social and communicative development:
- Theatricalization of the Russian folk tale "Kolobok".
- Performance of a nursery rhyme "Bear-toed"
- C / r game "Feed the Fox porridge"
Artistic and aesthetic development:
- Modeling "Kolobok"
- Drawing: "Decorate a mitten for the grandmother"
- Listening to the musical song “Kolobok's Song”
The final stage:
- An exhibition of the works of parents in the reception group.
- Exhibition of children's works.
- Summarizing.
Project Results:
The children developed an interest in Russian folklore, the prerequisites for telling the tale "Kolobok". Children are happy to show the work of their parents.
Parents took an active part in organizing the subject-development environment of the group: they made manuals with their own hands. These works can serve as illustrative material in classes on the development of speech.
Annex 1
Abstract of an integrated lesson in modeling from Kolobok plasticine
Purpose: To teach children to sculpt a kolobok on the basis of a round shape.
Tasks:
Developing: to develop fine motor skills of hands, the ability of children to distinguish and name colors: yellow.
Teaching: to form an idea of \u200b\u200bthe form: round, to develop skills of rolling lumps of plasticine between the palms with circular movements of both hands, to exercise in rolling lumps of plasticine between the palms with direct movements of both hands.
Parenting: To support in children the desire to complete the work they have begun to the end, following the game motivation for the lesson, to raise interest in the fairy-tale hero.
Preliminary work: Reading the Russian folk tale "Kolobok", a conversation on its content.
Materials: Pieces of yellow plasticine, beads for eyes, nose and mouth, planks, napkins. Pictures from the tale "Gingerbread Man".
Course progress:
The teacher: makes a riddle
In form it looks like a ball.
He was once hot.
Jumped from the table to the floor
And he left his grandmother.
He has a rosy side ...
Who is this? (BOB).
Educator: invites children to create a fun little bun.
But before that, you and I will do exercises for the fingers.
Finger gymnastics:
One, two, three, four, five!
Fingers are clenched into fists, we expand each finger, starting with a large
Fingers went out for a walk!
Squeeze and unclench the fists.
One, two, three, four, five!
We bend each finger, starting with a large
They hid in the house again.
Hit fist on fist
The teacher shows how to sculpt and explains his actions. The guys take a lump of yellow plasticine and roll it in our palms like a ball (circular motion with the palms).
Look at what ball we got, a real bun. Let's attach eyes, nose and mouth from beads to our kolobok.
Educator guys what beautiful koloboks you got. What good fellows you are.
At the end of the lesson, koloboks are exhibited.
Appendix 2
A performance of nursery rhymes"Bear clubfoot ...":
A toed bear is walking through the woods.
Collects cones, sings a song.
Suddenly a lump fell, right to the bear in the forehead!
Bear got angry and foot - top!
Didactic game "Who is gone?" (the teacher offers the children to consider the heroes of the fairy tale; an adult removes one detail, and the children, having opened their eyes, should say what is missing)
Didactic game "What form?"
Purpose: to teach children to distinguish and name geometric shapes they know: a ball, a cube, a brick in a variety of settings: upon presentation (what is this?), Among several others, different in name and color, according to the educator (find the cube).
Class progress
Children sit in a semicircle. The teacher shows and suggests everyone take turns to name the ball, cube, brick. Explains how the cube differs from the brick: “The brick is longer, two cubes can be placed on it (display). And the cube is tall, like a small house. The cube is the house, and the brick is the path to the house. ”
Next, the teacher lays bricks, balls, cubes on his desk. Invites each child to take one item. Children return to their places, show taken to each other. The teacher asks who chose which figure. Checks whether children relate the item to its name correctly. Tips the correct answers.
Then the teacher offers everyone who has cubes to raise them up. If the child is mistaken, he tells him: “I asked to raise the cube. It looks like a house. And you have a brick - a path to the house. ”
Next, the task is to raise the bricks. In the process of completing the assignment, the teacher invites the children to check whether the neighbors on the left and on the right have made a mistake.
Then the teacher places balls, cubes and bricks on the rug. Invites children to take one brick from the rug. Checks how they did the job. Invites to show the bricks to each other. Children share their impressions: “I have a red brick. And I have red. And Oleg’s cube ... ”The teacher praises those who noticed the error, gives the child the opportunity to fix it. Collects bricks and lays them on the carpet again. Children are invited to take one dice. The task is checked in the same way as the previous one. Then, the teacher shows the children the Gingerbread Man. And what shape is the Gingerbread Man? What does he look like?
Finger gymnastics “Quickly knead the dough”
Quickly knead the dough
(Open and close the palms).
Divided into pieces
(Imitate nipping).
Roll out all the pieces
(Three palm on palm).
And they blinded the little buns.
(We show two fists).
Marina Filimonova
Project activities in the second junior group "Kindergarten is my hometown"
Project activities in the second junior group
« KINDERGARTEN - MY NATIVE HOUSE»
Description of work: The project will be useful in the work of educators and children. Conducting focused work to foster a positive attitude towards kindergarten in children of the second younger group.
Implementation period: short term (September October). View the project: informatively - creative. Age children: 3-4 years. Members the project: educators, children second junior groupparents.
Relevance of the problem: Children kindergarten is the first social institution, the first educational institution with which the child becomes acquainted. Therefore, it is from the first acquaintance that the further development of the child depends, the formation of his moral-positive potential. Children junior preschool children do not always show initiative in communicating with adults and peers, therefore, the task of the teacher is to develop the ability of children to communicate with each other, with adults, not to offend others, to show empathy, tolerance, and desire to help. To develop children's interest in the knowledge of the world.
goal the project: Form and systematize children's perceptions of kindergarten, its history, symbols and cultural traditions kindergartenprofessions kindergarten. To create conditions for the establishment of the foundations of moral - patriotic consciousness. It is very important to instill in children a sense of love and affection for to relatives and cultural values native land, since it is on this basis that patriotism is brought up. Formation of a spiritual and moral attitude and feelings for kindergarten.
Tasks the project:
For children:
1. To cultivate love for one’s own kindergarten, employees, pride in kindergarten, respect for his spiritual values.
2. To form an idea of \u200b\u200bthe motherland on the basis of familiarization with the objects of the nearest surroundings: children’s garden and its territory.
3. Create psychologically comfortable living conditions for children in kindergarten. Create a happy atmosphere in kindergartenwhere the relationship between people (adults and children) built on the basis of goodwill and mutual respect, where the child will feel welcome and protected.
4. Expand children's perceptions of professions in kindergarten, their social significance, to cultivate respect for the work of people serving children.
5. To form the children’s ability to communicate with each other, with adults, not to offend others, to show sympathy, tolerance, a desire to help others. Encourage children to perform socially significant tasks, to do good deeds for the family, home, kindergarten.
Exercise children in the manifestation of compassion, caring, attentiveness to relatives and friends, friends and peers, to those who care about them.
6. Consolidate children's ability to express in a productive the activities your knowledge and experience.
7. Develop the communicative qualities of children.
8. Expand horizons and enrich the vocabulary of children.
For parents:
1. To acquaint parents with the features of social, personal, cognitive development of children junior preschool age and their adaptation to the conditions of a preschool institution.
2. Familiarize parents with traditions kindergarten. Promoting the active involvement of parents in joint the activity with a child in a family setting and kindergarten.
For educators:
The formation of social personality traits of the child, necessary for successful adaptation in kindergarten. instill in children a feeling of love and affection for to relatives and cultural values native land, since it is on this basis that patriotism is brought up. This approach contributes to the effective and systematic assimilation by children of knowledge about their kindergarten, native land, country, cultural traditions.
Kinds the activities: game, informative, productive, work with parents.
Expected Result:
Children should know and name kindergarten, kindergarten groups, premises and their purpose.
Children must have adequate work responsibilities in kindergarten, be responsible for their implementation.
Feel pride and respect for the work of employees kindergarten.
Experience love and affection for kindergarten, native land, city, country, cultural traditions, patriotism.
Implementation plan the project
Preparatory stage:
1. Setting goals and objectives the project.
2. Drawing up an implementation plan the project.
3. Collection, accumulation of material.
4. Inclusion in the plan the project« Kindergarten is my second home»
5. Activities, games and other types children's activities.
6. Homework for parents and their children.
7. Design project folder.
8. Wall newspaper “We are a friendly family”
9. Creating a layout "Our Kindergarten» .
Main stage
Cognitive development
Review illustrations about kindergarten. Room Tours kindergarten. Fixing the names of premises in group and their purpose. Pin names and
appointments of facilities such as a medical office,
music and sports hall.
Acquaintance with walking areas of different groups.
Social and communicative development
Didactic games: "What is good, what is bad?", "My good deeds", "How do we live in kindergarten» , “My family, my family tree”, "Birthday", “I give presents”, "My name", "My house", "My room", “Find items”. "Professions" Role-playing games: « Kindergarten» , "House", "A family", "Who works in kindergarten?» , "The profession of my parents", "Birthday". Communicative games: “I am growing”, “Call me sweetly”, "Let the name go in the wind", “I have a head”, "Happy Birthday".
Art and aesthetic development
Reading art literature: K. Ushinsky “Together closely, bored apart”, S. Marshak “On boys and girls”, E. Uspensky “If I were a girl”, E. Blaginina “That's like mom”, “Do not bother me to work.”
Fine the activity: Collective modeling "Our site". Drawing on the topic "Our kindergarten»
Labor the activity. Book repair with a nanny. Labor commission: Help mom or dad clean up your locker.
Joint activities of parents and children
Pick up photos of kids to create wall newspapers “We are a friendly family”.
Layout Creation "Our Kindergarten» .
Results achieved during implementation the project:
1. Implementation the project contributed to the favorable adaptation of children in kindergartenestablishing positive relationships with caregivers and children in the group.
2. Children develop a sense of affection for kindergartento loved ones and loved ones, kindergarten has becomereally second home.
3. The work done, contributed to the development of cognitive activity of children, enrichment of their ideas about kindergartenabout people working in children’s garden and their professions.
4. Children enjoy communicating with familiar adults people: understand the speech addressed to them, answer questions.
5. Children take initiative in communicating with by adults: apply with a request, a message about their condition, desire, about emotionally significant events for them.
6. Children use generally accepted simple forms in communication etiquette: greet and say goodbye to the teacher and children, thank you for lunch, help provided, politely express a request using the word "you are welcome".
7. Each child is interested in communicating with peer: attracts him to a joint game, he himself willingly joins in game communication, showing speech activity.
8. The work done, contributes to the development of creative manifestations of children, interest in participating in the play and art the activities with elements of creativity, experiencing success and joy from the implementation of their ideas.
9. All planned work took place with the involvement of parents, which contributed to the development of cooperation with the family, helped parents to feel confident in their pedagogical capabilities.
Literature.
1. Dybina O. V. “Familiarization with the subject and social environment” Moscow: "Mosaic-Synthesis", year 2014.
2. Kutsakova L.V. “Labor education in kindergarten» Moscow: "Mosaic-Synthesis", year 2014.
3. Yagodinsky V. N. "How to behave". Moscow: "Knowledge", 1991 year.
4. Kupina N. A. The ABC of Behavior. Sverdlovsk: Ural University Publishing House, 1991 year.
5. Lykova I. A. "Fine art in kindergarten»
6. Kazakova T. G. “Develop creativity among preschoolers” Moscow: "Education"1985 year.
7. Krasnoshchekova N. V. "Role-playing games for preschool children". Rostov: "Phoenix"2007 year.
8. The story of E. Permyak "How Masha Got Big".
9. The story of E. Permyak "The worst thing".
10. The story of E. Permyak "How Misha wanted to outwit mom".
11. The story of Y. Yakovlev "Sick"
12. The story of Yu. Sinitsin “Trouble is with a man”.
13. The story of I. Turichin "Man got sick"
14. The Tale "Dr. Aibolit" K.I. Chukovsky.
15. Poem by Z. Alexandrova "Katya in the manger"
16. The poem « Kindergarten» (N. Yaroslavtsev)
17. The poem "Preschool children" (I. Gurina)
18. The poem « Second your home» (G. Shalaeva)
19. The poem « Kindergarten» (O. Vysotskaya)
20. The poem "IN kindergarten» (A. Vishnevskaya)
21.. Poem "Our beloved kindergarten» (E. Grudanov).
22. Song « Kindergarten» words by T. Volgina, music by A. Filippenko.
23.. Song "House windows in childhood» (N. Agoshkova)
24.. Song « Kindergarten» (T. Kersten)