The placenta is an important organ in the female body that facilitates the transport of nutrients to the fetus and provides sufficient oxygen. The final formation of the organ occurs at the 6th week of pregnancy, so the heterogeneous structure of the placenta should not bother the mother.
Norms and deviations
What does the heterogeneous structure of the placenta mean? In the process of carrying a child, the placenta changes its structure and is characterized by the degree of maturity at a certain time. It also happens that the second stage of maturity occurs before 34 weeks. This does not indicate a hectic pregnancy.
Structure. The state of the organ can be traced clearly at 12 weeks. The homogeneous structure of the placenta is characterized by a smooth choral coating. The indicator refers to the zero degree and indicates homogeneity.
Thickness. With the help of an ultrasound examination, the thickness of the organ is determined. Up to 32 weeks, it increases and is normally no more than 30 mm. Rapid thickening or, conversely, a decrease indicates the process of premature aging of the organ. The reasons are: mismatch of the Rh factor, the development of an infectious disease, diabetes mellitus in a woman.
Indicators of heterogeneity there may be inclusions of various nature, areas of an echo-negative state. They indicate a violation in the functioning of the placental organ. An inhomogeneous placenta with hyperechoic inclusions indicates a serious disorder that affects the development of the child.
On examination, great attention is paid to the thickness of the placenta at 20 weeks of gestation. The normal indicator is from 1.5 cm to 5 cm. If the placental organ is thin and less than 1.5 cm, then there is a risk of fetal underdevelopment. But this phenomenon is quite rare.
Diagnostics
The ultrasound procedure is an important stage in monitoring the state of the body during pregnancy. Diagnostics allows you to detect the formation and accumulation of calcifications, tumors and the threat of detachment.
Degrees of heterogeneity:
- 1 degree. The uniformity is noticeably lost. Characteristic changes in the structure appear;
- 2nd degree. Formation of plots similar to a comma;
- 3 degree. The process of salt deposition on the dead tissue parts is significantly enhanced. Calcification occurs.
In the process of passing the ultrasound, with an accuracy of a millimeter, the placenta attachment point in the uterus is determined. Starting from 10 weeks, the doctor records the fact of the location of the fetus. The third examination procedure shows the stage of the child's development and identifies the initial pathologies.
The method of ultrasound examination makes it possible to detect not only changes in the embryonic organ, but also to determine the thickness, exact location, stage of maturity. Since the final development takes place at 16 weeks of gestation, the structure should not change up to 8 months.
The practice of conducting an ultrasound examination includes cases of expansion of the intervillous space. MEP is the space in the embryonic organ where metabolism takes place between mother and fetus. As the child grows, the amount of nutrient intake increases.
Timely diagnosis allows you to detect calcifications on dead tissue. This is a common phenomenon associated with natural aging of the embryonic organ. The doctor controls the volume of salt formation. After 33 weeks of gestation, the number of calcifications can increase dramatically. The rate of growth and development of the child must correspond to the degree of deterioration of the placenta. Only in this case you should not worry.
Causes and symptoms
The main reasons for the heterogeneity of the placenta can be infectious diseases, even those that were previously, or the negative consequences of drinking in large quantities and smoking. This leads to impaired blood flow from mother to child. Oxygen starvation of the fetus or freezing of the pregnancy process occurs. A striking symptom is a change in the movement of the child inside. Quitting smoking and alcohol reduces the risk of a placental defect
If the changes occurring in the structure are detected by the doctor at 30 weeks, this fact is the norm in development. The main condition is the absence of serious abnormalities in the fetus. The causes of heterogeneity are most often a combination of the mother's wrong actions, including nervous experiences. The more comfortable and calm the mother is, the better the future baby will feel. The psycho-emotional state determines the state of the female body.
You should refrain from contact with sick people, as you can get infected with an infectious disease. And this is another negative factor leading to the wrong development of the structure.
20 - 27 weeks. The heterogeneous structure of the placenta at 20 weeks is common among mothers. In the event of a negative change in the state of the organ, the ultrasound procedure will immediately report the initial stage of the pathology. The placenta can remain heterogeneous up to 27 weeks, after the reached period it normalizes. Do not panic, each individual organism with its own developmental features.
30-32 weeks. Upon reaching the period of 30 weeks, the structure of the organ should become homogeneous. If the structure remains heterogeneous for a period of 30-32 weeks, then this indicates the presence of pathology in the female body. A heterogeneous placenta at week 32 indicates a serious pathology in the body.
Treatment and childbirth
Complete restoration of homogeneity with drugs is not possible. The absence of stress and anxiety has a beneficial effect on the entire period of pregnancy.
A heterogeneous placenta during pregnancy is directly related to hypoplasia and hyperplasia. The doctor prescribes medications to improve uterine tone, blood circulation, and proper oxygen delivery to the fetus. As an additional method - a healthy lifestyle and giving up bad habits. Undergoing an ultrasound scan before due date is also a necessary aspect of health monitoring.
Treatment of placental heterogeneity:
- elimination of stress and depression;
- decreased tone, hypoxia;
- therapy of diseases: hypoplasia and hyperplasia;
- delivery.
A woman should strictly follow the doctor's recommendations and take medications if they have been prescribed. Control over the development of the fetus should take place at all stages of gestation. If you follow the rules and lead a healthy lifestyle, then you should not fear for the unborn child and childbirth.
The tactics of conducting childbirth with placental insufficiency is prescribed by the attending physician based on the state of the woman's body. Premature aging of the placental organ is an abnormal indicator that even a doctor is worried about. With proper treatment, the problem is fixable.
Calcifications
Calcifications are salt formations that are deposited in areas of dead organ tissue. The placental organ contains multiple blood vessels. They transport vital substances to the unborn child. In the event of a vessel spasm or failure, it leads to the death of the site. Calcium salt deposits form on the dead tissue.
The deposition of calcifications in the placenta can lead to:
- pathological process of the uterus;
- severe anemia;
- gestosis and its manifestations;
- infection and diseases of a chronic nature;
- sexually transmitted diseases;
- bad habits.
In order for the pregnancy to proceed positively, periodic examination by a doctor is required. A modern way of observing the process is the ultrasound method, that is, ultrasound. With its help, pathology is detected in the early stages and the detection of calcifications in the areas.
Symptoms In the case of a single deposition of calcifications, the woman will not feel discomfort. This will not harm the unborn child. If multiple foci of salt deposits form on the dead tissue, this seriously harms the fetus. With a strong phenomenon, a woman notices a change in the nature of the child's behavior inside. He becomes too active or, on the contrary, calms down. Disrupted work leads to the failure to perform proper life support functions. The baby is not getting enough oxygen. In severe cases, the death of the fetus occurs inside the female body.
Treatment. It is impossible to completely remove salt deposits inside the body. To begin with, the doctor determines the specific cause of the appearance of salts and tries to eliminate the possibility of a relapse. If salts were noticed in the late period of pregnancy, and their amount is small, then periodic examinations of the woman in labor are prescribed. The doctor controls the situation using ultrasound, observes the heterogeneous placenta with calcifications. Examination reveals a large number of foci of salts, but the functioning of the placental organ can take place without disturbances. If the fetus continues to receive the necessary vital substances, then the intake of therapeutic drugs is not required.
Complications. If a dysfunction is detected, if the fetus suffers from the fact that it does not receive oxygen and nutrition, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment. It includes taking medications that normalize blood circulation, as well as vitamins. Additional drugs in treatment are metabolic stimulants.
Close monitoring of the structure of the placenta is required during pregnancy. Also, do not forget about the normal, comfortable development of the fetus inside the mother's body. According to his behavior, well-being, conclusions are drawn about the normal process of bearing.
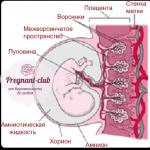
The placenta is the most valuable organ of the female body during pregnancy. Its main functions are to deliver the necessary amount of nutrients to the fetus and provide it with oxygen. The normal course of pregnancy, as well as childbirth, directly depends on the state of development of the child's place. In addition, the embryonic organ performs protective functions, preventing various infections from getting to the child, and monitors the supply of a sufficient amount of hormones that allow the fetus to grow and develop.
Diagnosis of the condition of the placenta is extremely important and should be carried out throughout pregnancy using ultrasound (ultrasound).
This method allows you to timely detect any deviations in the development of the embryonic organ. And the sooner pathologies are detected, the more chances for successful treatment are. With the help of an ultrasound scan, doctors determine its structure, location,. In the course of such a study, the expectant mother can be diagnosed with a heterogeneous structure of the placenta.
Causes of heterogeneity
In most cases, the heterogeneous structure of the embryonic organ should not be a cause for concern, because is the norm. The final formation of the placenta falls on, after which, up to the thirtieth week, its structure should be unchanged. And if at this time any changes occur in the structure of the child's place (the doctor can detect echo-negative areas, or other inclusions), then these changes can lead to serious disruption of the functioning of the placenta.

The main reasons for such disorders can be the presence of any infection in the mother's body or the consequences of drinking alcohol, anemia, smoking, etc. The heterogeneous structure of the placenta can provoke a violation of blood flow between the pregnant woman and the fetus, which will result in a slowdown in the intrauterine development of the child, difficult labor. If, during the ultrasound, after changes in the structure of the child's place are detected, then there is nothing wrong with that, and the pregnancy is proceeding normally. Sometimes changes in the placenta that are detected on are considered the norm, this is provided that the child continues to develop fully and according to its term. When examining with ultrasound, the following phenomena associated with a violation of the structure of a child's place can be detected:
- The structure of the placenta with the expansion of the MEP (intervillous spaces). The MEP is the place in the embryonic organ where metabolism takes place between the woman in labor and the fetus. As pregnancy progresses, the baby requires more and more nutrients to grow and support vital functions. To meet his needs, the profit center increases. The expansion of this space does not lead to, but does not exclude it. Additional studies are not carried out when expanding the profit center.
- Heterogeneous structure of the child's place with calcifications. These accumulations of calcium salts prevent the embryonic organ from performing its functions quite effectively. As a rule, calcifications are detected in the placenta after (in 50% of cases). At a later date (after 37 weeks), the presence of calcifications does not pose any threat to pregnancy, because this is due to the natural aging of the placenta.
Treatment
The heterogeneous structure of the child's seat can be associated with or as well as her. In this case, additional studies may be prescribed, such as Doppler, cardiotocography.
Complete restoration of the heterogeneous structure of the placenta is impossible. However, there are medications that normalize the tone of the uterus, oxygen delivery, and improve blood circulation. Also, the absence of stressful situations, all kinds of anxiety has a positive effect. And the key to the normal course of pregnancy is the timely conduct of the necessary diagnostics, proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle.
The normal development of pregnancy and the course of the birth itself largely depends on the state of the placenta. It is she who is responsible for feeding the baby and supplying him with oxygen. Therefore, doctors monitor this organ throughout pregnancy.
Regular ultrasound will allow you to identify certain deviations in time and take appropriate measures. In the course of the study, the location of the child's place, the degree of its maturity, and structure are determined.
And if a woman is told that there is a heterogeneous structure of the placenta, this, naturally, causes anxiety and concern. And this is not surprising, because the placenta, in addition to nutrition and respiration, plays the role of a protector against infections, a supplier of necessary hormones and a transporter of the child's waste products in the womb.
Why is there a heterogeneous placenta?
Not always placental heterogeneity is a cause for concern. In some cases, this condition is considered the norm. The placenta is finally formed by 16 weeks. And after that, until the 30th week, the structure of the placenta should not change. And you need to worry if it is during this period that the doctor discovers changes in its structure.
The reason for concern is the structure of the placenta of increased echogenicity and the detection of various inclusions in it. In this case, the heterogeneous structure of the organ indicates a violation of its normal functioning.
The cause of these disorders can be infections present in the woman's body. Smoking, alcohol, anemia and some other factors negatively affect the development of the placenta. As a result of the heterogeneity of the placenta, blood flow between the mother and the child can be disrupted, from which the latter will suffer. As a result, the development of the fetus may slow down and even completely stop.
If changes in the structure of the placenta are found after 30 weeks, this means that everything is fine and going as expected. Sometimes, even at 27 weeks, changes are considered the norm, if there are no abnormalities in the development of the fetus.
There is a record "structure of the placenta with expansion of the MEP" in the conclusions of the ultrasound. MEPs are intervillous spaces, a place in the placenta where the exchange of substances between the blood of the mother and the baby takes place. The expansion of these spaces is associated with the need to increase the exchange area. There are several options for expanding the MEP, but all of them are not associated with the development of fetoplacental insufficiency. With such a diagnosis, there is no need for additional research.
The heterogeneous structure of the placenta with calcifications is another variant of the violation of the structure of the placenta. At the same time, the danger is not the calcifications as such, but their presence. They interfere with the placenta to perform its functions to the fullest.
The structure of the placenta with fine calcifications in late pregnancy is not a cause for concern. This rather indicates the aging of the placenta, which after 37 weeks is quite normal. In 50% of cases, after 33 weeks, calcifications are found in the placenta.
 The degree of maturity of the placenta and its structure
The degree of maturity of the placenta and its structure
The placenta is clearly visible on ultrasound, starting from 12 weeks. During this period, its echogenicity is similar to the echogenicity of the myometrium. At maturity 0, a homogeneous structure of the placenta is noted, that is, a homogeneous structure, bounded by a smooth chorionic plate.
Already at grade 1, the structure of the placenta loses its homogeneity, echogenic inclusions appear in it. The structure of the 2nd degree placenta is marked by the appearance of echo-positive areas in the form of commas. And grade 3 is characterized by increased placental calcification.
The placenta is one of the most important temporary organs of pregnancy. A few decades ago, the function of the placenta could be assessed only indirectly - by the state of the fetus itself. If the fetus is okay, then the placenta is working well. With the development of medicine and, especially, ultrasound diagnostics, it became possible to examine the placenta in utero.
What is placental hyperplasia?
Hyperplasia is an ancient Greek word meaning "overdevelopment", "enlargement." This term applies to any organ of the human body. In the case of the placenta, the term hyperplasia usually refers to an increase in its thickness, mass, and circumference. However, on ultrasound scanning, it is possible to accurately measure only the thickness of the placenta, therefore, they are repelled from this indicator. It should be noted that a single ultrasound examination is inappropriate to diagnose placental hyperplasia. It is necessary to monitor the pregnant woman, the opinion of several doctors, extended research. Moreover, self-assessment of ultrasound results is unacceptable.
Hyperplasia or diffuse thickening of the placenta implies its edema, as well as a compensatory increase in the number of structural units. There are several reasons for this:
- Infections. This is perhaps the most common cause of placental thickening. Bacteria, viruses and other foreign agents can penetrate into the uterine cavity, amniotic membranes and water both ascending from the vagina and with blood flow from other foci. The placenta rarely becomes infected in isolation. Inflammation of the baby's place is called placentitis and very often it is combined with inflammation of the membranes and intrauterine infection of the fetus. With the development of the inflammatory process, edema of the placenta and an apparent increase in its thickness occur.
- Immunological conflict between the mother and the fetus, for example, for the Rh factor. In this case, the picture will be similar to the infectious process, only the placental tissue is affected not by viruses and bacteria, but by the mother's antibodies. In simple terms, in this case, the mother's body tries to kill the fetus and all the temporary organs of pregnancy, mistaking them for foreign.
- Severe or long-term current gestosis. With gestosis, blood pressure rises, protein appears in the urine and edema increases, including hidden ones. Such hidden edema includes edema of the placenta. In addition, gestosis affects the placental vasculature, also leading to edema.
- Severe anemia in the mother. When the hemoglobin level falls below 80 g / l, the fetus begins to experience oxygen starvation. In this case, the placenta begins to grow compensatory in order to increase the area of \u200b\u200bgas exchange and thus help the fetus.
- Natural feature. It is not necessary to exclude the possibility of an increase in the placenta simply as a development option. Large children often have massive placentas, or this feature is passed down through the generations.
Very often, the thickening of the placenta is combined with polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios, as well as the expansion of the intervillous spaces (MVP) of the placenta. In the first two cases, these are additional manifestations of infection or immune conflict. Expansion of the MEP indicates that the placenta is trying to compensate for its function. Isolated enlargement of the MEP is not a diagnosis, but can only imply an infectious process, anemia, placental insufficiency, or simply a developmental feature.
Symptoms and diagnosis of placental hyperplasia

The placenta is devoid of pain innervation, therefore, with the initial signs of its defeat, nothing bothers the pregnant woman. Usually, the main symptoms appear after weeks or even months.
- The main symptoms of impaired placental function are signs of fetal oxygen starvation: delayed growth, impaired fetal blood flow, acute hypoxia. The woman notes a decrease in fetal movements, a decrease in its activity. During the examination, the doctor pays attention to a decrease in the growth rate of the pregnant woman's abdomen, poor heart rate or cardiotocography.
- The manifestations of the infectious process can also act as the main complaints. A pregnant woman complains of fever, weakness, headaches and muscle pains, chills, discharge from the genital tract. Often, when questioned, a woman recalls a recent exacerbation of a chronic inflammatory process (otitis media, sinusitis, pyelonephritis) or an acute illness (ARVI, flu, tonsillitis, thrombophlebitis).
- General analysis of blood, urine and blood biochemistry to search for inflammatory changes, as well as to determine the level of hemoglobin and ferritin.
- Vaginal culture and smear, examination for sexually transmitted infections and the TORCH group.
- Determination of the level of antibodies to the Rh factor and blood groups to exclude Rh sensitization.
- Blood for glucose.
- Consultations of a therapist and a cardiologist to exclude preeclampsia, an infectious disease specialist in difficult cases of intrauterine infection.
Continuous CTG monitoring and ultrasound dopplerometry of the fetus are included in the observation protocols for such pregnant women.
Placental hyperplasia: consequences for mom and baby
Since the placenta is a temporary organ for the existence of the fetus, the consequences of a violation of its functions affect mainly the child:
- chronic;
- fetal growth retardation;
- acute fetal hypoxia;
- intrauterine fetal death;
- premature childbirth.
The danger to the mother is not so much the placental hyperplasia itself, but the cause that caused it. Gestosis and eclampsia, an infectious process, severe anemia certainly threaten the health and life of a woman.
Placenta thickening treatment

Placental hyperplasia therapy consists in treating the immediate cause that caused this complication:
- Antibacterial and antiviral therapy in case of infection.
- Treatment of preeclampsia, as well as early delivery.
- Treatment of Rh-conflict, which consists in periodic intrauterine blood transfusion to the fetus and mother's plasmapheresis. In this case, the fastest possible delivery is also shown with the obligatory prophylaxis of the Rh conflict with anti-Rh immunoglobulins in the next pregnancy.
- Therapy with iron preparations for anemia in a pregnant woman, as well as transfusion of erythrocyte mass in case of a decrease in hemoglobin below 75 g / l.
Given the impaired function of the placenta, the use of various drugs that improve placental blood flow is shown: Curantil, Actovegin, Piracetam, Pentoxifylline.
Alexandra Pechkovskaya, obstetrician-gynecologist, specially for website