A modern pregnancy monitoring program provides for triple mandatory screening of a woman in the perinatal period. The main task of a comprehensive examination is to monitor the quality of women's and children's health, as well as to identify possible congenital malformations and developmental abnormalities.
Genomic pathologies such as Edwards syndrome, Turner syndrome, Down syndrome on ultrasound are diagnosed with an accuracy of 91%. This allows a woman to decide whether to terminate or maintain her pregnancy. Signs of severe genetic damage to the fetus are determined during the first or second screening, when there is still the possibility of abortion (up to 22 weeks). In the future, if a woman refuses to give birth to a deliberately sick child, the gynecologist can offer only artificial births. This procedure is unsafe, painful and can seriously injure the psyche.
Downism
Downism has no gender and ethnicity and is not treatable. In the process of growing up a child with Down syndrome, you can adjust his behavior using special developmental programs, but you cannot get rid of the genomic syndrome. The occurrence of Downism is due to intrauterine chromosomal failure. A full set of chromosomes of a healthy body is 46 pieces.
With Down syndrome, an additional copy of the twenty-first chromosome is formed, as a result, there are 47 of them. The causes of the disease have not been determined, but it has been established that they are not derived from the negative effects of environmental factors, psychosomatic health, or the antisocial lifestyle of parents. The disease is called a “mistake of nature,” which cannot be predicted and prevented.
Factors determining the risk of having a baby with a mutated chromosome:
- hereditary genetic abnormalities (the disease is not directly inherited, but if the mother has genetic diseases, the chances of being born are great);
- the age of the future mother. In women 35+, the risk increases five times, compared with 25-year-old ladies. By the age of 45, this figure is 50;
- strong radiation exposure (the factor has not been thoroughly studied);
- unfavorable obstetric and gynecological history (numerous miscarriages and missed pregnancies).
Anomaly of the 21st chromosome is the main cause of pathology
In the case of multiple pregnancy, the disease affects both identical twins and only one if the children are heterogeneous. With a chromosomal mutation, the threat of spontaneous abortion and the birth of a dead child increases several times.
Ultrasound in the perinatal period
Examination of a pregnant woman through ultrasound is one of the essential points of perinatal screening. If the process of bearing a child goes without features, an ultrasound scan is performed once in each trimester. With a complicated pregnancy, the doctor prescribes additional ultrasound procedures. Ultrasonic waves are safe for the baby and mother, therefore, the study has no restrictions on the multiplicity of sessions.
Diagnosis is carried out in an abdominal way (externally), without causing the woman and the fetus uncomfortable sensations.
Types of ultrasound
Scanning can be done in several ways:
- 2-D ultrasound - black and white image, only a medical specialist (uzist) can decode a flat image;
- 3-D ultrasound - data received from the sensor is processed by a computer program, a three-dimensional image of the embryo is projected on the monitor;
- 4-D-method - the baby is displayed on the screen in three-dimensional projection, while you can observe his movements in the womb.
In the last two cases, the procedure takes a longer period of time. At the request of the parents, the doctor can print a photo of the baby. In order to prevent serious problems with the health of the mother and child, it is strictly forbidden to ignore the ultrasound examination in the perinatal period.
Diagnosis of the first trimester
At the first ultrasound scan, conducted from 10 to 14 weeks, the doctor evaluates fetometry (total size of the baby), his position in the womb and the nature of the pregnancy. To identify downism, certain markers (normative indicators) are used, with which the real picture of the study is compared.
The main defining markers include:
- TVP (the size of the collar space in thickness). The normative indicator of the amount of fluid under the skin of the embryo in the neck should not exceed 2.7 mm. With Down syndrome, TBP is markedly increased;
- the size of the upper jaw. On ultrasound, the shortened upper jaw of the baby is clearly visible, which is a characteristic sign of downism;
- anatomical structure of the outer part of the ears. Underdeveloped auricles are the basis for suspecting a genomic abnormality;
- Heart rate (rhythm or heart rate);
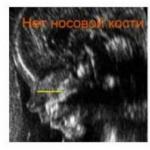
- absence of the main nasal bone. Downs, as a rule, have a flattened face shape. This symptom indicates the presence of pathology.
For a child in the first trimester, the following indicators are considered normal:
Tachycardia (increased heart rate) is not one of the main signs of the syndrome, but can be indirect. An experienced doctor will not disregard this indicator. According to medical data, the accuracy of determination of Down syndrome at the initial examination is about 90%.

Symptom of Downism (absence of nasal bone) in a 2-D ultrasound scan
Second trimester scan
The definition of downism in the second trimester of pregnancy is carried out according to the following indicators:
- hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of the nasal bones. The nose is not visible on the monitor screen, since its size does not exceed 2.5–3 mm;
- heart disease. Children with autosomal syndrome suffer from cardiac pathologies in more than half of cases;
- mismatch with the norm of the size of the femur, ilium and humerus along the length. In the image, these indicators are significantly underestimated.
In addition, the doctor can see a violation of the functionality and size of other internal organs. Changes are characteristic of the genetic abnormality: cerebral structures (cerebral hypoplasia, frontal lobes), bladder (organ enlargement in size).
Is it possible to determine down syndrome with ultrasound with 100% certainty by ultrasound? Yes, it is possible, but only in the third trimester, when the visual signs acquire an absolute character. The decision to terminate the pregnancy through artificial birth or to give birth to an unhealthy child remains with the parents. The doctor can only give advice, but not insist on any position.
Additional analyzes
To confirm or deny the alleged pathology in the first half of the term, in addition to the ultrasound of the fetus, the woman takes a blood test for hormonal biochemistry and undergoes invasive testing of the state of amniotic fluid and placenta.
Blood test
Down syndrome is determined by comparative results of the following blood counts:
- Alffetoprotein (AFP protein). Responsible for providing the child with essential nutrients. Analysis for genomic syndrome shows a low level;
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), aka “pregnancy hormone”. It appears in the blood from the second trimester. Under Downism has an overestimated rate;
- Free Estriol (EZ). Female sex hormone. It determines the condition and development of the uterus and utero-placental blood circulation. With chromosomal abnormalities reduced.
The results of laboratory tests significantly increase the accuracy of the diagnosis.
Biological material testing
Invasive testing is more informative. If an ultrasound scan shows the presence of the syndrome, you must pass the following tests:
- biopsy of the external membranes (chorion). A small fragment of the temporary organ is examined at the first screening;
- placental biopsy. Assessment of placental cells for a period of 14 to 20 weeks;
- amniocentesis. A puncture biopsy of amniotic (amniotic) waters, carried out after the 18th week of pregnancy;
- cordocentesis (umbilical cord puncture). It is produced through the anterior abdominal wall under ultrasound control. Carrying out is possible only in the second half of the term.

Amniocentesis is a procedure for taking amniotic fluid (figure)
The biopath is taken in a hospital, as the procedure involves a certain risk to the fetus. She is not held without the consent of the woman. The analysis is carried out in a genetic laboratory.
Objective results
Diagnostics carried out according to all the rules reliably establishes the presence of a chromosomal mutation in a child. Survey results are evaluated only in a complex. A positive value with respect to gene pathology should be: direct and indirect signs of an ultrasound study, hormone tests, and biopsy results. According to statistics, for 700-800 newborns, there is only one baby with a chromosome anomaly of Down. In 85% of cases, parents decide on an abortion or abandon a child in a maternity hospital.
From a medical point of view, Down syndrome is an extra chromosome. But in life, this is a heavy burden on the shoulders of parents, since a child with such a diagnosis requires increased attention to himself. Children with Down Syndrome are physically and mentally underdeveloped. Almost half of them are diagnosed with heart disease. Therefore, raising such a baby is not easy in every sense.
According to statistics, every 600-800 baby is born with Down syndrome. Risks increase in late pregnancy (after 35 years). But young women are not safe from this. Although, for example, in a 20-year-old girl without the presence of genetic diseases in her and her husband's families, the risk of developing this pathology is 1: 2000.
So that after the birth of the child does not have to be sadly surprised, doctors offer expectant mothers to undergo screening diagnostics to determine possible pathologies in the development of the fetus, including Down syndrome.
Pregnancy Screening
There are several diagnostic methods that allow you to suspect the development of pathology in the fetus in the prenatal period. Today, women are offered, if they wish, to undergo such studies. The most popular is non-invasive antenatal (i.e. prenatal) diagnosis. This is primarily a blood test for (human chorionic gonadotropin) and (alpha-fetoprotein), as well as the fetus.
We already wrote a lot about hCG on our website - we suggest reading it. We only note that the analysis for hCG is given for a period of 10-13 weeks.
Alphafetoprotein is a special protein that produces the fetal liver. It is secreted into the amniotic fluid, from where it enters the blood of a pregnant woman. And on the level of AFP in the venous blood of the expectant mother, you can draw certain conclusions. So, an underestimated level may be evidence of the development of Down syndrome in the fetus, and an overestimated one - pathologies of the neural tube. The level of AFP is constantly increasing with increasing duration. However, the difference between normal, overestimated and underestimated indicators is most evident in the period from 16 to 18 weeks. It is at this time that it is most advisable to do this.
Regarding ultrasound, for the purpose of screening diagnosis during pregnancy, it is carried out from the 10th to the 13th week. A good specialist already at this time can notice the formation of cervical folds in the fetus, since subcutaneous fluid accumulates in the back of the neck with Down syndrome, which makes it possible to judge the developing pathology in the early stages of pregnancy. Down syndrome can also be indicated by the absence of the nasal bone in the fetus (in 70% of cases of the development of this pathology, it is not visible).
Despite the fact that the early is very important for expectant mothers, such screening tests do not give absolute guarantees of accuracy. With the same probability, studies can show both false positive and false negative results. And then the question may arise about the biopsy of the chorionic villi. A probe with a mirror is inserted through the vagina, less often a sample is taken for analysis by introducing a needle through the abdominal cavity into the uterus. However, the risks of miscarriage as a result of such a procedure increase significantly and amount to 1: 360.
Another more accurate diagnostic method compared to ultrasound and blood tests is amniocentesis, but it does not give one hundred percent guarantee of reliability.
Amniocentesis involves the study of amniotic fluid. For this, a pregnant woman is pierced with a stomach to take an amniotic fluid for a biopsy.
Do a screening test or not?
However, not all so simple. Non-invasive diagnosis can only suggest the development of Down syndrome in the fetus. And note that for this an ultrasound examination must be carried out by a highly qualified specialist. Regarding the analysis of blood for AFP, it also can not be taken as a diagnosis. The results depend on many factors, since the level of alpha-fetoprotein can change, for example, under the influence. Of great importance in the correct reading of the results is the very accurate determination of the gestational age. In addition, there are no clearly defined indicators of the level of AFP in the blood, which could clearly indicate the presence of pathology. Therefore, we are only talking about suspicions or assumptions, about the possible likelihood of vice.
If the results of screening studies reveal a high risk of developing pathology, the woman is offered to undergo amniocentesis. Only after this can a final diagnosis be made, and even that, as we have already said, is not completely reliable. But amniocentesis can be done no earlier than the 18th week, since before this amniotic fluid is still not enough. Keep in mind that results will come in about two to three weeks. And this is a period of 5 months, when a person lives inside you. And when confirming fears, a woman will have a serious choice: to kill him or not? It is also important that from a physiological point of view, abortion (and in fact artificially induced childbirth) at this period is very dangerous. And in the psychological, perhaps, she will not be better.
Why do we tell you all about this. There is statistics that in the vast majority of cases of development of fetal chromosomal abnormalities, such a pregnancy naturally ends (mainly up to 8 weeks). There are other statistics that indicate that in the vast majority of cases, invasion of the fetus by piercing the abdomen and taking amniotic fluid has certain consequences. Among them: spontaneous miscarriage, infection of the fetus, damage to the fetal bladder, exacerbation of the Rh conflict, the absence of any results of amniocentesis (which occurs in 5% of all cases) and other complications.
And there are statistics that in the vast majority of cases this happens with completely healthy children, whom they decided to check. If a woman refuses to perform amniocentesis, then often she gives birth to a healthy baby. But if she had previously passed a screening test that suspected something was wrong, then right up to the very birth of the baby, obsessive fear still does not leave her.
We do not urge you to refuse screening. You just need to know that this anomaly is not amenable to treatment. And the final diagnosis can only be made to you by the end of the fifth month of pregnancy.
And we recall once again that in most cases, women who were at risk for the results of non-invasive diagnostics, but refused further research, gave birth to healthy babies. What we, in fact, sincerely wish you!
Especially for - Elena Kichak
Now all pregnant women, among numerous other tests, are recommended to undergo a screening test to identify a risk group for the birth of a child with Down syndrome and some other types of congenital malformations of the fetus. At the same time, they always talk about the need to take an analysis (well, after all, such a serious analysis should definitely be done for genetic diseases!), But doctors in antenatal clinics almost always (with an extremely rare exception) “forget” to tell about further developments. Or do not consider it necessary. But it would be worth ... This analysis should not fit into the general series of tests prescribed during pregnancy. It is necessary to provide detailed information about these analyzes, and, in particular, about further studies prescribed in case of being at risk, so that women can consciously choose whether they want to take this analysis.
To start, I’ll tell you my story. For clarity, when I was pregnant with my youngest daughter, I did not get registered with the district antenatal clinic and did not intend to take all the crazy bunch of tests that are now prescribed to pregnant women. She was going to pass only the main ones, at first she was observed simply by a gynecologist she knew. And the doctor, whom I trust (a very good person, but brought up, unfortunately, by the system), said that it was necessary to pass this same screening test. Well, I went through it. As expected, an ultrasound at 10 weeks, then immediately a blood test. After about 2 weeks, the result comes - THE THRESHOLD risk of having a baby with Down Syndrome ... Of course, I tensed up. The doctor says - take it again at 16 weeks. I did an ultrasound again - on an ultrasound, everything seems to be in order. Retake blood, two weeks waiting for the result. The result comes - HIGH RISK. I don’t remember exactly the ratio, unfortunately, but I am being sent to some special center where they are doing all this. I decided to start by studying in detail all the information about these analyzes. And here is what I found out: by combined screening - ultrasound + blood test for AFP and hCG - we can only ASSUME the presence of such a deviation in the fetus. The diagnosis can be made (and this is not 100% ...), exclusively using invasive methods of prenatal diagnosis - biopsy of chorionic villi and amniocentesis (the study of amniotic fluid, which is taken with a special needle directly from the fetal bladder). And such methods are associated with a risk of a number of pregnancy complications: miscarriage, the development of a conflict on the Rh factor and blood type, infection of the fetus, the development of hearing loss in a child, etc. In particular, the risk of developing a miscarriage after such studies is 1: 200, and according to some reports and above. In addition, when diagnosing a malformation, treatment is impossible, and the woman simply faces a choice - either to leave the child (why then have an analysis? ...) or an abortion. Taking into account the fact that I received repeated tests at 18 weeks, if not later, then even if I went to do an amniocentesis, the diagnosis would have been no earlier than 20 weeks, and possibly later. And this is already full 5 months, when abortion is already very dangerous for health. And I absolutely absolutely understood that I would not do amniocentesis for any reason, for a number of reasons - firstly, the idea of \u200b\u200bputting a possibly healthy child at great risk led me and continues to terrify me. Secondly, I wouldn’t do an abortion anyway, all the more so at that time. Therefore, at the family council, we decided that we forget this whole story and are expecting a healthy child. I pulled myself together, tuned in the right way. But the worm still sat inside, whatever one may say ... And on the subconscious, thoughts about it still remained, and this, believe me, does not give much emotional calm. So it turns out: why, in fact, was to take an analysis? To tickle your nerves ???
Fortunately, Sveta was born healthy, to the delight of all. But if I happen to get pregnant for the third time, under no circumstances will I do a screening. By the way, when I later called the doctor who advised me to take the test, she told me “What a smart girl you are that you didn’t go for amniocentesis and decided to give birth! I’ve got one girl here, an infection happened, and as a result, she lost a healthy child ... "
Such is the story. And nowstop more on the studies themselves.So, a complete combined screening of I - II trimester of pregnancyconducted to identify the following congenital malformations in the fetus:
Down Syndrome (trisomy for the twenty-first pair of chromosomes) Edwards Syndrome (trisomy for the eighteenth pair) Neural tube defects (spina bifida and anencephaly) (only at 16-18 weeks)The test includes:
Ultrasound examination at 10-13 weeks of pregnancy (by the date of menstruation)In the first trimester, the main dimensions for calculating risks are the width of the cervical transparency (wclear transparency is how an ultrasound examines the accumulation of subcutaneous fluid on the back of the fetal neck in the first trimester of pregnancy.) and the definition of the nasal bone (inend of the first trimester nasal bone not determined using ultrasound in 60-70% of fruits with Down syndrome and only 2% of healthy fruits). By the way, I want to note that an ultrasound scan can reliably determine whether the fetus has any problems, and a three-dimensional ultrasound scan for a period of 4-5 months of pregnancy, made by a good specialist, further improves accuracy.
2. Blood test for hCG (chorionic gonadotropin) at 10-13 weeks and for AFP (Alpha-feto-protein) at 16-18 weeks.
AFP is a substance that is synthesized by the baby’s liver and transferred to the amniotic fluid, and from there to the mother’s blood. AFP concentration is continuously increasing, peaking at about 30 weeks. From 16 to 18 weeks, the gap between normal, low (with Down syndrome) and high (with neural tube defects) AFP levels is especially large. However, a level that clearly defines the pathology of the child does not exist. The level of AFP is very dependent on many factors, for example, you need to know the gestational age very accurately, it affects smoking, and many other factors, and it can be high or low without any pathology of the fetus.
Recently, more and more women, according to the results of a blood test, fall into the high-risk group for the birth of a child with Down syndrome. Moreover, these are young girls whose ultrasound did not reveal any deviations. We will not discuss why this is happening, although the author of the article has his own thoughts on this matter ... But in the vast majority of cases, if a woman decides not to do further research and give birth, a healthy child is born. Only the whole pregnancy proceeds with a constant question in my head ...
In fact, according to statistics, children with Down syndrome are born on average in one case out of 600-800. Moreover, for a mother under the age of 30 without genetic diseases in the family, the risk of having such a child is very low (for example, at 20 years old - 1 in 2000 newborns). The risk increases after 35 years, and at 40, from the point of view of statistics, the probability of having such a child is approximately 1: 110. However, this is nevertheless less than 1%.
It is important to note that approximately half of all cases of chromosomal abnormalities, including Down syndrome, result in a natural miscarriage in the early stages of pregnancy (up to 6-8 weeks).
If a high risk is detected according to the test results, the woman is invited to do an amniocentesis - taking amniotic fluid from the fetal bladder. It is done not earlier than 18 weeks, since before this period there is not enough amniotic fluid. The results of the analysis are usually ready another 2-3 weeks later, that is, a less reliable conclusion can be obtained only by the end of the fifth month of pregnancy. Since treatment is not possible, the woman is invited to have an abortion. This late abortion has very severe physical and emotional consequences. At this time, the woman’s body will respond to abortion as a premature birth of a child, up to the release of milk from the breast.
In addition, amniocentesis is associated with the following risks:
1) spontaneous abortion with the loss of a healthy child, which occurs in about 1.5% of cases. This risk is increased in the presence of fibroids or fibroids in the uterus. If a woman has previously had a miscarriage, the risk also increases.
2) One in 200 women teaches infectious and other complications
3) In some cases, damage to the fetal bladder is noted, and the woman should be in the hospital from several days to several months
4) If the mother has a negative Rh factor, the doctor makes a special injection, and in some cases this injection itself causes a miscarriage.
5) In about 5% of cases, doctors are not able to get an effective analysis, and mom still remains in the dark
6) Most women experience labor for several hours during and after the procedure.
And the main thing to remember is that amniocentesis does not correct developmental disorders. It only gives information about a person who already lives in his mother’s stomach. And the woman is faced with a choice: whether to accept this man or to take his life.
Therefore, before undergoing a screening test, seriously think - if you are at risk, are you ready to take the risk of amniocentesis, and when confirming the diagnosis, do you decide to have an abortion at a later date? And think what is worse for you - to kill a healthy child, the movement of which the mother already senses at this time, or give birth to a daunenka ...
Down Syndrome was first described by the famous British physician John Langdon Down, who began his research work in 1882, and in 1886 publicly published its results.
This is one of those pathologies that every person has an idea about. This disease is especially worrying for expectant mothers who cautiously await the first screening. According to recent decades, this pathology occurs in every 700 babies born.
The statistics of the last few years show a different figure - 1 born child with a pathology for 1100 newborns, which was made possible thanks to high-precision prenatal diagnosis and early termination of such a pregnancy.
About 80% of children with this pathology are born in women younger than 35 years old - despite the relatively low risk of the fetus developing this chromosomal pathology, a peak in fertility is observed in this age group. Every year, around 5,000 newborns with Down syndrome are added worldwide.
Down syndrome affects both girls and boys equally, the disease has no ethnic spread and is found everywhere.
On March 21, 2006, International Day for People with Down Syndrome was introduced. This day is held in order to increase public awareness of this common pathology and improve the quality of life of sick people. The number 21 was chosen due to the cause of the disease - trisomy on the 21st chromosome, and the month of March represents trisomy, since it is the third month of the year.
Causes of Down Syndrome
The causes of Down syndrome lie in the intrauterine formation of the chromosomal pathology of the fetus, characterized by the formation of additional copies of the genetically embedded material of the 21st chromosome, or the entire chromosome (trisomy), or sections of the chromosome (for example, due to translocation). The normal karyotype of a healthy person consists of 46 chromosomes, and with Down syndrome, the karyotype is formed by 47 chromosomes.
The reasons for the occurrence of Down syndrome are in some way not related to environmental conditions, parental behavior, taking any medications and other negative phenomena. These are random chromosomal events, which, unfortunately, cannot be prevented or changed in the future.
Risk Factors for Down Syndrome
The age of the future mother affects the risk of developing Down syndrome in a child:
- in the age range from 20 to 24 years, the probability of the formation of this pathology is 1 to 1562;
- at the age of 25-35 years, this risk is already 1 to 1000;
- at the age of 35-39 years, the risk increases to 1 in 214;
- over the age of 45, the risk increases to 1 in 19.
As for the age of the future dad, the risk of having children with this syndrome in men over 42 years of age is scientifically proven.
There is a computer program “PRISCA”, which takes into account the data of ultrasound, physical gynecological studies and other factors and calculates the risk of congenital pathology of the fetus. To calculate the risk of Down syndrome, the risk of developing defects of the central nervous system (neural tube defect), the following are taken into account:
- Mother age
- Smoking
- Gestational age
- Ethnicity
- Body weight
- Number of fruits
- Diabetes mellitus
- Availability of IVF
Is inheritance of Down syndrome possible?
Trisomy on the 21st chromosome (which is approximately 90% of cases) is not inherited and not inherited; the same goes for the mosaic form of pathology. The translocation form of the disease can be hereditarily determined if one of the parents had a balanced chromosome rearrangement (this means that part of the chromosome is interchanged with part of some other chromosome, without leading to pathological processes). When such a chromosome is transmitted to a subsequent generation, an excess of 21 chromosome genes occurs, leading to disease.
It is worth noting that children born to mothers suffering from Down syndrome in 30-50% of cases are born with the same syndrome.
How to learn about Down syndrome during pregnancy?
Since the causes of Down syndrome in the fetus are genetically determined, this pathology of the child can be recognized even in the womb. If Down syndrome is suspected, signs during pregnancy are determined in the first trimester.
Diagnosis of Down syndrome determines the risk of developing this pathology in the fetus. The study is carried out strictly in the period from 11 to 13 weeks and 6 days of pregnancy.
- Determination of the level of the β-subunit of chorionic gonadotropin (hCG pregnancy hormone) in the venous blood of the mother. With this chromosomal pathology of the fetus, an elevated level of the CG β-subunit of more than 2 MoM will be determined;
- Determination of the level of PAPP-A - protein-A of the blood plasma of a pregnant woman associated with pregnancy. A high risk of the syndrome is associated with a PAPP-A index of less than 0.5 MoM;
- Determination of the thickness of the collar space using ultrasound of the fetus. With Down syndrome, this figure exceeds 3 mm.
With a combination of the three described indicators, the probability of Dyne's syndrome in the fetus is 86%, i.e. diagnosis is quite accurate and indicative. To make a decision on whether to keep the pregnancy or to terminate it, it is proposed that a woman with signs of Down syndrome in the fetus be given transcervical amnioscopy.
In this study, the chorionic villi are collected through the cervix, which are sent for a genetic study, according to the results of which, with one hundred percent certainty, this diagnosis can be confirmed or refuted. The study does not belong to the group of obligatory, the decision on its conduct is made by the parents. Since it carries a certain risk for the further course of pregnancy, many refuse such a diagnosis.
Diagnosis of Down syndrome in the second trimester is also a combined screening, which is carried out between 16 and 18 weeks.
- Determining the level of hCG in the blood of a pregnant woman - with Down syndrome, an indicator is higher than 2 MoM;
- Determination of the level of a-fetoprotein in the blood of a pregnant woman (AFP) - with Down syndrome, the indicator is less than 0.5 MoM;
- Determination of free estriol in the blood - an indicator of less than 0.5 MoM is characteristic of Down syndrome;
- Determination of inhibin A in the blood of a woman - an indicator of more than 2 MoM is characteristic of Down syndrome;
- Ultrasound of the fetus. If there is Down syndrome, signs of ultrasound will be as follows:
- smaller fetal size relative to the norm for a period of 16-18 weeks;
- shortening or absence of the nasal bone in the fetus;
- reduction in the size of the upper jaw;
- shortening of the humerus and femur of the fetus;
- an increase in the size of the bladder;
- one artery in the umbilical cord instead of two;
- water shortage or lack of amniotic fluid;
- rapid heartbeat in the fetus.
With a combination of all the signs, an invasive diagnosis is proposed for a woman to conduct a genetic study:
- transabdominal aspiration of placental villi;
- transabdominal cordocentesis with umbilical cord puncture.
The selected material is examined in the genetic laboratory and allows you to accurately determine the presence or absence of this pathology in the fetus.
In 2012, British scientists developed a new high-precision test for the presence of Down syndrome in the fetus, the result of which is estimated at 99%. It consists in examining the blood of pregnant women and is suitable for absolutely all women. However, it has not yet been introduced into world practice.
How is abortion resolved to determine the high risk of Down Syndrome in the fetus?
When children with Down syndrome are born, the causes of the genetic malfunction that have occurred are really impossible to establish. Many parents perceive this as a test, and consider themselves endowed with a special function of raising and developing such a child. But every pregnant woman with a high risk of this pathology raises the question of deciding the fate of her pregnancy. The doctor does not have the right to insist on interruption, but he is obliged to clarify this issue and warn about all the possible consequences. Even if pathologies incompatible with life are discovered, no one has the right to persuade a woman to make a decision), and even more so to make her do it.
Thus, the fate of pregnancy with fetal pathology is decided only by parents. Parents have the right to repeat the diagnosis in another laboratory and clinic, to consult with several geneticists and other specialists.
Signs of Down Syndrome in a Newborn
Signs of Down syndrome in newborns are determined immediately after birth:
When children with Down syndrome are born, the external signs listed above will be determined almost everything. The diagnosis is confirmed after passing the genetic analysis for the karyotype.
Can a child with Down syndrome grow up mentally and physically full-fledged person?
This question necessarily arises for those parents who are still deciding whether to terminate or maintain their pregnancy, and for those who already carry a precious bag with a newborn baby.
The consequences of the formation of an additional copy of the chromosome vary greatly and depend on the amount of excess genetic material, on the genetic environment, and sometimes on pure chance. Of great importance is the individual development program of such a child and, of course, associated pathologies, of which there are a lot of such children.
Of course, these are not deeply disabled people, but children who are able to learn, develop and become adapted personalities in the modern social environment. At the same time, it is important to understand that every child with Down syndrome will have a different degree of severity of lag in mental, speech, physical development. Putting them on the same line with healthy children is incorrect, and it’s not necessary, but it’s also impossible to consider “abnormal people”.
A particular phenotype makes this pathology recognizable. Indeed, to hide from prying eyes this feature of your child will not work. But it is better to take your baby from the first breath as he is, be proud of him and not hide from people. Yes, these children are special, but far from hopeless. Moms of children suffering from much more serious pathologies would give everything for the opportunity to swap places with their mothers, so that the child could live and smile.
Many parents worry about the health of their baby. They are especially concerned that the fetus may experience Down syndrome and other chromosomal pathologies.
Antenatal screening helps to identify the likelihood of a baby with various diseases. It is necessary for the purpose of a more detailed diagnosis of pathologies using invasive technologies.
Prenatal or prenatal screening does not pose a threat to the health of the mother and the fetus, as well as for the course of pregnancy. Invasive techniques can cause a number of complications, which limits their use only in case of emergency.
From the results of these studies, the doctor exposes the risks of pregnancy, the possibility of having a sick baby, and also decides on the possibility of bearing a child. If any problems arise, the terms for performing abortion interventions are extended in agreement with the mother.
Pathology Description

Down syndrome refers to chromosomal diseases. Chromosomes are cellular components that carry gene material. In any cell, except for reproductive, they contain 46 broken into 23 pairs. Of these, 23 are the mother's chromosomes, and 23 are the papins, which combine during the fusion of the egg with the sperm.
Gene mutations appear in the first stages of cell division. These changes lead to a decrease or increase in the number of chromosomes, causing a complex of changes in the body of the child with the formation of the disease.
Down syndrome is also synonymous with trisomy 21. A child with this pathology has an additional third chromosome 21, increasing their total number to 47.
Risk factors
The only reliable reason that increases the possibility of having a baby with Down syndrome is the age category of the mother. The frequency of the appearance of a sick baby in a twenty-year-old mother is one case for 1400 newborns, by 40 years it is 1: 100, and by 45 - one case for 35 children.
Among other things, the risk of having a sick baby increases with:
- Dad is over 45 years old.
- The presence in the family of patients with genetic abnormalities.
- Closely related marriages.
- Moms are under 18 years old.
Manifestation of the disease

The first signs of Down syndrome during pregnancy include the occurrence of symptoms of a miscarriage or spontaneous interruption.
The life of a baby with this pathology is complicated by physical defects in appearance, as well as severe malformations of internal organs.
The main manifestations of Down syndrome:
- Flattened face.
- Flat nose bridge.
- Short and wide neck.
- The presence of a skin fold that closes the inner corner of the eye.
- Thick lips.
- Half open mouth.
- Abnormally large language.
- Chest deformity.
- Little finger curvature.
- A solid “monkey” fold in the palm of your hand.
- Strabismus.
- Hearing loss.
- Malformations of the cardiovascular system - ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect.
- Gastrointestinal malformations - narrowing or absence of the duodenum or esophagus.
- Congenital dislocation of the hip.
- Mental retardation.
Prenatal diagnosis
The first screening is carried out at 11-13 weeks of gestation.
Diagnostics of the first trimester will include:
- Ultrasound procedure.
- Determination of the level of human chorionic gonadotropin.
- The study of the content of PAPP-A in the blood.
The second screening is carried out in the period of 15-22 weeks of pregnancy. It consists in:
- Ultrasound procedure.
- Determination of the value of alpha-fetoprotein in the blood of the mother.
- The study of the content of chorionic gonadotropin and estriol, as well as inhibin A.
For pregnant women who are in a group with an increased possibility of having a sick baby, Down syndrome, it is recommended that invasive diagnostic methods be performed:
- Chorionic biopsy.
- Amniocentesis.
- Cordocentesis with fetal karyotyping.
- Consultation of medical genetics.
Ultrasound procedure

To date, there are certain markers of Down's disease in the fetus. Ultrasonic signs of the disease are called visible changes in the development of the baby.
The main markers of pathology:
- Increased collar thickness. It is located at the site of formation of the future neck and lower part of the back of the head. An indicator of the likelihood of a fetal Down syndrome is the thickness of the collar space in excess of three millimeters.
- Lack of nasal bone.
- Short tubular femur and humerus.
- Signs of a lack of various sections of the intestine.
- Anomalies in the structure of the frontal lobe of the brain and cerebellum.
But not one of them is one hundred percent. Only total ultrasound signs allow for consultation and the appointment of invasive research methods.
Laboratory data

This type of examination consists of a blood test for Down syndrome. Determining the content of human chorionic gonadotropin is a reliable diagnostic method. This substance is also called pregnancy hormone. Refers to indicators of well-being during pregnancy.
With an increase in human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) by more than 2 MoM, the doctor prescribes a woman a double or triple test for a more accurate diagnosis of Down syndrome during pregnancy.
A double test is to study the content of human chorionic gonadotropin and PAPP-A (a protein associated with pregnancy) in the first trimester. With an increase in the hCG content of more than 2 MoM, and the value of PAPP-A is less than 0.5 MoM with a confidence of up to 90%, a pregnancy is reported to be pathological.
Perhaps this is when:
- Down Syndrome.
- The threat of miscarriage.
- Frozen pregnancy.
A triple test is to study the level of chorionic gonadotropin, alpha-fetoprotein and estriol at 15-22 weeks of gestation.
For Down syndrome, the following changes in their concentration in the blood of a pregnant woman are characteristic:
- Human chorionic gonadotropin more than 2 MoM.
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is changed to 0.5 MoM.
- Free estriol is less than 0.5 MoM.
- Inhibin A is more than 2 MoM.
Triple test is not a mandatory diagnostic measure. But it is recommended to conduct it in case of:
- Mom is over 35 years old.
- The presence in the family of people with Down syndrome.
- Adverse course of previous pregnancies - miscarriages.
- The presence in the family of patients with genetic pathologies.
- If the mother suffered a serious illness during pregnancy.
With a combination of changes in ultrasound, as well as laboratory data, a woman is invited to perform invasive methods for diagnosing genetic material.
Invasive methods

These studies allow us to accurately establish the development of the genetic pathologies in the fetus.
Chorionic biopsy is a study in which part of the tissue of the chorionic villi from the placenta is obtained. This site is identical to the genetic material of the fetus. The procedures are performed under ultrasound control and with pain relief.
Amniocentesis is the study of amniotic fluid. Material is taken through small abdominal punctures. The accuracy of this method reaches 99%.
Cordocentesis is a cord blood sampling procedure. Diagnosis is carried out under ultrasound control. Material is taken through punctures of the abdomen or cervix.
If there are signs of Down syndrome according to ultrasound, laboratory tests and invasive techniques, the attending physician collects a consultation. After a decision is made by a pregnant woman, the risk of having a sick child is explained. In this case, the term for termination of pregnancy is extended to twenty weeks for medical reasons.