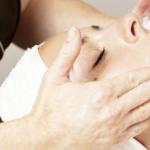
A bruised nail can happen at any time and in the most unexpected place. Sometimes even a slight hit to the nail thumb it is enough for it to turn blue and show signs of peeling. Of course, no one wants to walk around with such a cosmetic defect for several months, and even more so the fair sex.
To avoid the unpleasant consequences of an injury, let's consider how you can save a nail after an impact and what to do if independent actions do not bring results.
Shulepin Ivan Vladimirovich, traumatologist-orthopedist, highest qualification category
Total work experience over 25 years. In 1994 he graduated from the Moscow Institute of Medical and Social Rehabilitation, in 1997 he completed a residency in the specialty “Traumatology and Orthopedics” at the Central Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics named after. N.N. Prifova.

Depending on the severity of the injury, there are several degrees of injury severity:
- mild degree - the nail plate receives minor damage. The pain usually goes away within the first minutes after the injury. The nail may twitch slightly, but no visible changes occur and no hematoma forms;
- moderate severity - soft tissues are slightly damaged, the nail is injured, but the integrity of the plate is preserved. This often happens when a toenail is injured, for example, in children while playing football. The plate may peel off at the edge or receive minor damage on the side. As a rule, in this case, the nail can be cut off, and the damage to the soft tissue can be disinfected and lubricated with brilliant green;
- severe damage is characterized by blueness of the nail plate after injury. Literally before our eyes, the color turns from light pink to dark blue due to the release of a certain amount of blood under the nail. In parallel, the integrity of the nail plate may be compromised beyond the boundaries of contact with soft tissues. Such damage most often occurs during plane impacts;
- very severe damage– pathology occurs with severe mechanical injuries, and according to statistics, damage to the nail on the hand is more common. This could be a hand or fingers getting caught in the mechanism. In this case, the nail receives severe destructive damage, the nail plate can be completely destroyed, and its parts can be pressed into the soft tissue. As a rule, damage is characterized not only by problems with the plate - soft tissue is significantly damaged, open wounds occur, and the finger may be dislocated or broken.
Determining the severity of the injury determines how to treat the patient.
When to see a doctor

If your fingers are injured, it is important to provide proper first aid. In many ways, this will help not only relieve the patient from pain, but also preserve the nail and prevent it from coming down.
First aid for a bruised nail is: applying cold to the damaged area. You can apply a piece of ice, a cold object, or place the bruised finger under the stream. cold water. If the skin around the nail is damaged, it should be treat with antiseptic solution(hydrogen peroxide, alcohol, iodine, etc.). To reduce pain you should give the victim a tablet of any painkiller. After this, if there is a suspicion of a fracture or dislocation of a finger, you need transport the patient to the emergency room.
Seeing a doctor is mandatory for injuries of the third and fourth degree of severity.
In this case, the doctor will examine the nail plate, numb the finger and, if necessary, carry out manipulations to remove the blood that has accumulated under the nail. To drain the blood, a small hole is drilled on the surface of the plate, and the blood comes out freely. You need to see a doctor as soon as possible before the blood clots.
If a nail detachment occurs as a result of an injury, in most cases it is necessary to remove the nail partially or completely. Nail removal occurs under local anesthesia; the procedure does not take much time. After the manipulations, the doctor will apply an antibacterial bandage and give recommendations for further treatment.
Treatment at home

If the damage is minor and the nail has not turned black, then treatment can be carried out at home. To do this, you must complete the following steps:
- Give the injured finger complete rest for the first time.
- Apply cold compresses to the surface of the plate, replacing them one after another while heating. This will help relieve swelling and reduce pain. If small vessels are damaged, cold will help prevent bleeding. If the pain persists, you can anoint the nail and the surface of the skin around it with menthol ointment - it will create a cooling effect and reduce pain.
- If the soft tissues around the plate are damaged, there are cracks and wounds with minor bleeding, then the surface must be treated with hydrogen peroxide, cover the finger with a dry bandage, if necessary, you can apply Levomekol ointment to prevent suppuration.
- When swelling of soft tissues forms, but in the absence of visible damage, You can draw an iodine grid on your finger– it will help eliminate swelling.
- Pain your finger if there is severe discomfort. You can if you take a Paracetamol or Ketorol tablet. For a while, the victim will no longer feel pain from the bruise. If the pain is severe, You can apply a compress to your finger for which they mix Dimexide + Novocaine in a combination of one to three. Several layers of gauze are soaked generously in the resulting solution and a gauze swab is applied to the nail itself, or the entire finger is wrapped in it. After some time, the pain subsides.
At home, badyaga will help cure an injury. Badyaga, diluted to a dough-like consistency, can be used in the form of applications on the nail plate. Used after compresses heparin ointment– it will eliminate swelling and help avoid bruises.

An anti-inflammatory effect is provided by an ointment for nail bruises based on the medicinal plant arnica. The product bears the same name - Arnica. You need to lubricate the damaged finger several times a day. Larkspur ointment has a similar effect, which can also be used for damaged fingers.
Complications and consequences

In some cases, even after careful treatment of the injury site at home, complications arise. Most severe consequences for a finger - if the nail comes off or peels off over time. If there is no suppuration, there is no need to worry in this case - except cosmetic defect, the injury does not threaten the victim. The nail plate will be removed on its own absolutely painlessly, or at the point of origin it will simply grow back to its normal state. You can observe how the light spot will gradually move towards the edge of the nail, and then completely disappear.
Much more serious consequences occur when there is suppuration after an impact. If you miss this moment, the inflammatory process will not only separate the nail from the soft tissues, it can contribute to their suppuration and cause the development of panaritium. You can notice suppuration by a characteristic aching pain, which then turns into twitching of the finger. The finger will turn red, and a yellow-green spot can be seen under the nail - signs of pus. The pain intensifies so much that it prevents the patient from sleeping at night. In the active phase, pus is released from under the nail bed.
If such consequences of injury occur, it is imperative to immediately consult a doctor.

Nail restoration does not occur within a few days.
As a rule, to eliminate a bruise, it takes several months for the nail plate to grow back and the nail to acquire a healthy pink color.
The growth rate of the plate is approximately 1 mm per week, so recovery time can be predicted in advance by measuring the width of the bruise formed on the nail.
It takes a little longer for the nail plate to recover if the nail has completely fallen off, but there is no need to worry - it will actively grow, quickly regenerate, and soon there will be no trace of the injury. The most important thing at the recovery stage is to protect the nail from new damage. so that the nail plate grows smooth and beautiful.
How you can help yourself at home if you have a bruised nail
Anyone can encounter such a nuisance as a nail injury. This does not depend on age, health status, or other characteristics and characteristics of a person.
Causes
The main cause of nail injuries is accidents. Careless handling of doors, falling of a heavy object, or improperly performed manicure or pedicure are the most common causes that lead to damage to the nail plates.
In addition, even the desire to follow fashion can cause damage to the nail. Wearing shoes that are too narrow and put too much pressure on your feet can not only lead to calluses and abrasions, but also injure the nail plates. Sometimes the cause of nail injuries can be a bad habit, for example, the habit of biting your nails (), which is very difficult to get rid of.
Types of damage and their manifestations
If you are careless, a person can get injured, including injury with damage to the nail plate. What nail injuries occur most often?
Injury
A bruise is the most common nail injury.Perhaps the most common nail injury is a bruise. Anyone can get this type of injury. For example, when a heavy object falls on your toes or when you handle a hammer carelessly.
A typical manifestation of a bruised nail is the formation of a hematoma underneath it. A bruised nail quickly begins to turn blue, and if a more serious injury occurs, it turns black. Of course, it is not the nail plate itself that changes color after an injury, it is just that an accumulation of blood forms under it.
Like all other bruises, a bruised nail is accompanied by pain. The severity of the pain depends on how severe the injury was. In addition, swelling may form on the injured finger, and the skin becomes hot. With serious bruises of the nail, a general increase in temperature is possible.
Important! The most difficult situation is for those patients who have suffered a bruised toenail. Because severe pain makes it difficult for them to wear shoes and walk.After a nail bruise, the damaged nail plate often falls off, since nutrition may be disrupted due to injury, and the nail is already dead and not living tissue. A new nail plate begins to grow in place of the fallen nail. At first, it will most likely look unhealthy - wavy and uneven, but over time it will look normal.
However, if the nail injury becomes chronic, it is possible that new nail will not acquire healthy looking, but will remain curved as, for example, with .
Squeezing
Wearing tight and uncomfortable shoes can lead to quite serious damage to the nails and further. External signs injuries from squeezing a nail usually resemble symptoms of a bruise. The nail first turns black and then begins to peel off. However, pain and swelling with such an injury are usually not so intense.
Breaking and cutting
 A broken nail is a serious injury.
A broken nail is a serious injury. A broken nail is not only a ruined manicure, but also quite serious damage. Of course, if the break occurred only on the regrown part of the nail, then nothing bad happened. In this case, there is no pain or other unpleasant sensations.
It is much worse if, due to injury, the nail plastic has cracked on the part adjacent to the nail bed. Such damage causes severe pain, and the formation of a hematoma is possible.
Injuries during manicure (pedicure)
Improper care can also lead to damage to the nail. For example, if sharp metal objects are used for cleaning instead of special tools. In this case, it is quite easy to damage the delicate skin, which can lead to infection and cause serious inflammation.
Nail injuries often occur due to careless cutting of the cuticle. Rough actions can easily damage the nail fold or cut the nail plate. Incorrect actions when filing a nail can cause delamination of the plate and lead to increased fragility. Failure to follow the rules of hygiene during manicure can lead to the development of fungal diseases, for example.
First aid
 When providing first aid for a nail injury, it is necessary to apply cold to stop the bleeding.
When providing first aid for a nail injury, it is necessary to apply cold to stop the bleeding. If a nail is injured, first aid should be provided immediately. The main task at this stage is to stop bleeding. Probably everyone knows that heat accelerates blood flow, and cold, on the contrary, slows down the movement of blood. Therefore, you need to apply a cold object to the bruised finger as quickly as possible.
You can simply place your finger under a stream of cold water, but if possible, it is better to use ice. It is advisable to put the ice in a clean plastic or fabric bag. Using ice not only reduces the intensity of bleeding, but also relieves pain, so the injured person will feel immediate relief.
Important! You should not keep the ice for too long. After 10 minutes of exposure to cold, you need to take a short break and, if the pain does not go away, you can repeat the application of cold several times.In case of a serious nail injury, when the nail plate immediately begins to come off, a compression bandage should be applied to the sore finger and the injured person should be urgently referred to a doctor.
If the nail plate is cut or there is a deep break, you need to apply a sterile bandage to the finger and consult a surgeon.
Treatment
 First of all, it is necessary to remove the hematoma under the plate.
First of all, it is necessary to remove the hematoma under the plate. To save the injured nail and prevent further damage, it is necessary to remove the hematoma under the plate. If this is not done, the increasing hematoma will lead to disruption of the plate’s nutrition and its rejection.
Removal of a hematoma is done by pricking the nail at the site of blood accumulation. Through the hole made, the blood will come out and the nail will be saved. This operation is recommended to be performed in a clinic or emergency room. But, as a last resort, you can do it yourself.
To do this, take a needle or paper clip and heat it in a fire. Then, with a hot needle, you need to burn a small hole in the damaged nail (the plate should be disinfected before performing the operation). You should act extremely carefully so as not to cause even more serious injury to the victim and not cause the development of pathology of the nail plate ().
Then you need to gently press on the nail to remove the blood. After that, a bandage should be applied to the finger or the damaged area should be covered with a bactericidal plaster.
It must be remembered that self-removal of a subungual hematoma should only be done as a last resort, when there is no way to go to a medical facility. Since when performing an operation in unsuitable conditions, there is a risk of infection, which can lead to very serious consequences.
In case of injury associated with a cut in the nail, it is usually necessary to remove the entire nail, or part of it. This is a fairly serious operation that requires subsequent suturing of the skin; it is performed in a medical facility, otherwise the nail may grow incorrectly in the future. Sometimes cutting the nail is the cause of development.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for nail trauma is usually good. If all necessary therapeutic measures have been taken, then complete healing occurs within 2-4 weeks. In this case, detachment of the nail plate occurs, recovery will occur after the new nail grows. This may take 2-4 months, since nails (especially toenails) grow quite slowly.
Prevention of nail injury involves following safety precautions in the workplace and at home. When performing nail care procedures, you should use only a special tool and act very carefully.
Nail plate. It is a tissue derivative arising from three zones of the nail bed. Fully grows in length in 70-160 days.
Nail bed. Consists of three parts: the dorsum, the germinative matrix (also known as the ventral floor), and the sterile matrix (also known as the ventral nail bed). The proximal end of the nail plate originates between the dorsum and the U-shaped germinal matrix of the nail bed.
Nail fold (eponychial fold). The proximal part of the nail plate is located under the nail fold. The skin on the back of the nail fold is the nail fold (it is located on top of the back covering of the nail bed). The thin plate extending from the nail fold to the back of the nail plate is called the eponychium. The lunula is a curved, opaque stripe on the nail distal to the eponychium at the junction of the germinal and sterile matrix.
Hyponychia. This is an accumulation of keratin between the distal part of the nail plate and the nail bed. Thanks to its strong fusion, it is resistant to infection.
Blood supply. Dorsal branch of the terminal trifurcation of the digital artery.
Function
- Support of the soft tissues of the fingertip (hyponychium)
- Used as a tool (scratching, plucking, scraping, grasping and lifting, etc.).
Damage to the nail bed
- Typically caused by a forceful blow that compresses and damages the (soft) nail bed between the (hard) nail phalanx and the nail plate.
- It is necessary to take radiographs in frontal and lateral projections.
Subungual hematoma
The nail bed is well supplied with blood. A closed nail injury causes bleeding under the nail plate with the formation of a tense hematoma, with characteristic throbbing pain.
Treatment of subungual hematoma
Closed lesions (usually a hematoma, less than 25% of the visible nail bed) can be evacuated by perforating the nail plate with a hot needle or paper clip. If a nail bed rupture is suspected, an inspection is necessary.
Nail bed rupture
It may be simple, stellate (resulting from a blast-type injury), or crushed (causing fragmentation of the nail bed). The nail plate may move out from under the nail fold.
Failure to undergo revision in the acute period after injury for these injuries leads to the development of late complications, such as deformation of the nail plate or its detachment from the nail bed.
Treatment of nail bed tears
- Ring block using local anesthetics
- Peel off the nail plate (save for use as a splint)
- Tip: Use a small mucous elevator or anatomical blunt scissors to guide them between the nail plate and the nail bed, then use a thin vascular clamp to peel off the nail plate.
- Wash the sterile matrix.
- Carefully restore the sterile matrix (absorbable suture 6/0-7/0) using a magnifying glass.
- The sterile matrix defect can be replaced with a split-thickness skin graft or a split-thickness nail bed graft (from an adjacent injured toe or the first toe).
- If the nail bed is pulled out from under the nail fold, it should be realigned and stitched (if possible) or held in place using a splint.
- Use the nail plate to splint the nail fold.
- In young children, the replanted nail plate may take root and begin to grow.
- If the nail plate is missing or too damaged, you can use a silicone sheet or foil from a package of suture material to splint the nail fold.
Tears of the nail bed with fracture of the nail phalanx
In almost 50% of cases, damage to the nail bed is combined with a fracture of the nail phalanx. The presence of a tear in the nail bed makes the fracture open.
Treatment of nail bed tears with fracture of the nail phalanx
The following are guidelines for treating nail bed tears. Additionally:
- Intraoperative administration of antibiotics intravenously and oral administration in the postoperative period.
- Copious irrigation until the fracture is repositioned.
- Non-displaced fractures can be treated conservatively after irrigating and restoring the nail bed. They are splinted soft tissues.
- In case of displaced fractures, thin (0.8-1 mm) pins are used for fixation, except in cases with many small fragments, then it is better to splint the bone fragments with soft tissues without fixation with pins.
- Tip: pass a 2-3 mm Kirschner wire below the hyponychium to achieve its precise placement in the nail phalanx.
- Check the position of the needle on the X-ray in the lateral projection - it’s easy to miss and not hit the nail phalanx!
- Seymour's fracture is epiphysiolysis of the nail phalanx with displacement of its distal part to the rear in combination with a rupture of the nail bed. The nail also moves out from under the eponychial fold (see Chapter 5).
Impaired nail growth after injury
Within 21 days after the injury, the nail stops growing in length, and its thickening appears proximal to the injury site. This causes the nail to bulge as it continues to grow. After this, nail growth accelerates compared to normal for 50 days, and then slows down for 30 days, and only after that does growth become normal. Reconstruction of the nail complex
Reconstruction of the nail complex is difficult and often imperfect even in the most experienced hands. Below are possible options reconstruction. The problems often overlap, and the choice of treatment should be approached individually.
Detachment of the nail plate from the nail bed
- Scarring of the underlying part of the nail bed due to lack of fusion with the nail plate.
- Keratin accumulates under the nail and can be mistaken for a fungal infection.
- Treatment:
- Excise scars.
- Suture if possible.
- Replace the defect with a split nail bed graft, usually taken from the first toe.
Splitting nail
- The cause is scarring in the dorsal covering/germenative matrix/sterile matrix complex.
- Treatment:
- Excise scars and restore sterile matrix.
- Excise part of the germinal matrix and replace with a full-thickness complex germinal matrix graft from the 2nd toe with an acceptable but not perfect result.
- Removal of the germinal matrix in severe cases.
Nail spicule (spike)
- Typically a remnant of the germinal matrix complex after distal amputation.
- Treatment:
- Raise the eponychium flap
- Excise the spicule and the remainder of the germinal matrix.
Hook nail (deformation in the fork of a parrot's beak)
- Occurs as a result of suture of the fingertip with tension during distal amputation or loss of bone support for the nail bed.
- Treatment:
- Excise scars on the fingertip
- Raise the nail bed
- Replace a bone defect with a bone graft (may resolve)
- Replace the soft tissue defect with a local repositioned flap
- Microsurgical transplantation of part of the toe (difficult decision)
Absence
- Congenital or post-traumatic.
- Treatment:
- Excise skin or nail-like scars and replace with full-thickness skin graft
- Microsurgical nail bed transplantation.
Nail bruising is a common problem encountered in traumatology practice. This is an unpleasant and very painful injury that occurs due to a violation of the integrity of the nail plate. In some cases, after damage, the nail comes off, but if you follow necessary rules first first aid, this may not happen.
“ICD 10” is the name of the international classification of injuries and diseases adopted in 2016.
Contusion of the nail plate belongs to the block “Superficial injury of the wrist and (S60)”, which includes external injuries to tissues and segments of the hand and wrist.
A nail bruise is classified under a separate subsection, “S60.1 – Bruise of the finger(s) of the hand with damage to the nail plate.”

Causes
Most often, a bruised fingernail is considered a domestic injury, occurring due to an unfortunate combination of circumstances or due to a person’s negligence.
The most common causes of nail injury include:
- hitting your fingers on a hard object or dropping a heavy object on your finger (90% of all cases of injury);
- pinched fingers;
- susceptibility to injury during active image life.
It is believed that fractures and bruises in the area of the phalanges of the fingers most often occur in children, therefore, when walking with a child or playing, it is recommended not to leave the baby unattended. Small child lives in a world of large objects, and his coordination of movements is just beginning to develop - this makes him more susceptible to damage and bruises to his nails.
Symptoms
Damage to the finger and nail is a painful injury, often accompanied by rejection of the nail plate.
Signs of bruised fingernails:
- swelling in the area of the injured finger;
- the appearance of pain syndrome (pain of a pulsating nature until the victim loses consciousness);
- decreased functional ability of the injury site (finger phalanges);
- heaviness and discomfort of the entire hand or nail plate area;
- blood flow and redness of the tissues of the damaged area of the finger;
- formation of a hematoma under the nail (black or bluish nail in the area of the bruise);
- the resulting injury is characterized by partial or complete removal of the injured nail plate;
- the appearance of severe headache;
- increase in body or tissue temperature in the area of this damage up to 38 degrees;
- nausea, signs of general malaise.
A serious injury is accompanied by a small dark bruise and very strong pain.
It is worth noting that the appearance of cyanosis in the area of injury occurs some time after the injury (a period of 8 to 12 hours).
Symptoms of a nail bruise include signs of an inflammatory process that occurs after injury (therapeutic methods have big choice methods and reduction of hematoma, but are used only after completion of the diagnosis).
First aid
 Providing first aid for a bruised fingernail is an important stage of treatment, allowing you to preserve the nail plate and speed up recovery. It is not difficult to help yourself or provide assistance to the victim; to do this, you just need to follow the instructions.
Providing first aid for a bruised fingernail is an important stage of treatment, allowing you to preserve the nail plate and speed up recovery. It is not difficult to help yourself or provide assistance to the victim; to do this, you just need to follow the instructions.
What to do if you are injured
What to do if you have a bruised fingernail? If, due to severe pain, you can get confused and miss the time when it is necessary to do important actions for the affected organ.
Rules for first aid for a bruised finger:
- The first stage of first aid is cooling the affected area of the limb. Cooling helps reduce the formation of hematomas and reduce pain symptoms. This procedure is recommended to be carried out using ice wrapped in a handkerchief or gauze. The anesthesia method is used for 5 minutes, after which the compress must be removed, repeated every 15 minutes, if other methods have not been attempted (the total time of applying ice can reach 2 hours). In addition to ice, any other cold item will do (bags of food from the refrigerator and freezer).
- If the bruise is accompanied by the appearance of wounds and bleeding, the next stage of first aid is to disinfect the injury site with iodine solution, soak a cotton swab with the liquid, and treat the surface under and above the nail. If the nail turns blue and characteristic signs of swelling appear, it is possible to reduce the symptoms.
- After carrying out pre-medical treatment methods, it is necessary to contact a medical facility in order to avoid more serious consequences than hematomas and swelling.
What should you not do if you have a bruised nail? It happens that in order to preserve the nail plate, some patients press down the nail and bandage it tightly. This method is contraindicated and ineffective, since excess compression further impedes blood flow after injury. If you do not interfere with the healing process, swelling and hematomas will begin to resolve much faster.
Diagnosis and treatment
 Diagnosis and treatment of any disease or injury is an important step on the path to recovery. Treatment of a bruised fingernail begins only after determining the cause and extent of the damage; in addition, a consultation with a traumatologist and an x-ray are necessary to identify the concomitant.
Diagnosis and treatment of any disease or injury is an important step on the path to recovery. Treatment of a bruised fingernail begins only after determining the cause and extent of the damage; in addition, a consultation with a traumatologist and an x-ray are necessary to identify the concomitant.
It is to identify the true cause of the appearance of pathological signs that it is necessary to go through several diagnostic stages:
- Finding out the cause and circumstances in which the nail plate was bruised.
- Palpation.
- Taking an x-ray (the damaged area of the body is removed using x-rays to identify internal damage to bone tissue).
These procedures allow you to determine the extent of damage to the fingers and apply the necessary measures to treat the bruised nail.
Diagnosis is carried out:
- traumatologist;
- surgeon.
These specialists also write out directions for x-rays.
How to treat a bruised nail
Treatment of a bruised nail is divided into several stages to prevent and reduce the risk of complications.
- To reduce the risk of suppuration under the nail plate, bandages with antibiotic ointments are used (the bandage should be regularly replaced with a new one).
- With a severe bruise of the nail, you can observe the appearance of pronounced edema, to reduce the manifestations of which, use salt baths three times a day.
- To reduce the severity and size of bruises in case of contusions, heparin ointment is used, and for disinfection in case of large hematomas, Levomekol ointment is used.
- It is also recommended to apply 0.25% novocaine (in a ratio of 1:3) for quick recovery. The compress has an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
- In order to quickly cure a severe nail bruise, it is recommended to use an emulsion castor oil. This drug has anti-inflammatory properties and promotes rapid tissue regeneration.
- If there is a slow rejection of the nail, there is a danger of damage and accidental “removal” of the nail due to negligence. To secure the position of the nail plate, it is recommended to apply a bandage or secure the nail with an adhesive plaster, so it will take longer to tear off, but will be less painful.
Unfortunately, despite the various symptoms, the problem of identifying nail fungus and how to distinguish its bruises often arises (a doctor can help you recognize it, or you can diagnose it yourself). The main difference between nail fungus and bruise is that in the case of a fungal disease there is no pain syndrome and the change in color of the plate occurs much more slowly.
How to treat a bruise at home
 Among the methods for relieving swelling and inflammation there are different ways, developed at home.
Among the methods for relieving swelling and inflammation there are different ways, developed at home.
A dangerous method is to pierce the nail yourself; breaking the pierced plate can lead to serious consequences, since such an operation should only be performed by an experienced specialist in a sterile hospital environment.
One of good ways treatment - a method using plantain and celandine.
To use you need:
- take plantain and celandine leaves in a 1:1 ratio;
- pour 50 ml of hot water into the dry mixture;
- leave for 3 hours;
- put a thick mixture of herbs in cheesecloth to form a bag;
- apply to the bruised finger.
Herbs are a natural source of health that can increase the body's healing rate. Unfortunately, the effect of using traditional methods does not appear on the first day and most often has a cumulative effect. Also, before using any method traditional medicine It is recommended to consult a doctor to avoid the consequences and violation of the treatment method, since the use of such means as a compress with vinegar or ammonia capable of harming an open wound caused by the removal of the nail plate.
“How long does it take to grow and should I wait for a nail to grow back?” — it is important to know that the nail will grow, even after the nail plate completely falls off (growing tissue grows slowly, a temporary change in shape is possible).
If there is a detachment of the nail, you should wait until it comes off completely (the nail comes off at different speeds depending on the degree of injury); it is advisable not to disturb the detached plate.
Complications and consequences
A bruised fingernail has unpleasant consequences if treatment and care are delayed or disrupted.
Complications after a bruised nail:
- severe swelling of the fingers and adjacent tissues;
- formation of pus (when bacteria enter or fungus develops);
- gangrene (finger amputation).
To reduce the manifestation of complications and consequences after injury, it is necessary to take care of the condition of the injured limb as quickly as possible and apply the most effective methods of therapy.
Conclusion
Damage to the nail plate can occur as a result of everyday activities due to an unfortunate combination of circumstances. However, by using effective methods and timely contacting a doctor for diagnosis, complications can be avoided and the nail plate can be saved from falling off.
Dear readers of the 1MedHelp website, if you still have questions on this topic, we will be happy to answer them. Leave your reviews, comments, share stories of how you experienced a similar trauma and successfully dealt with the consequences! Your life experience may be useful to other readers.
4113 0
The nail plays an important role in the function of the finger. First of all, it gives the flesh of the distal phalanx hardness when grasped, and in the absence of a nail, the tip of the finger becomes shapeless. Secondly, the nail protects the fingertip from injury. Thirdly, the nail plate plays an important role in the perception of sensitivity when grasping small objects. Finally, it plays an important cosmetic role.
There are three main zones of soft tissue located around the nail and playing different roles in its regeneration (Fig. 27.8.1).
Rice. 27.8.1. The areas of soft tissue surrounding the nail, which play different roles in the regeneration of the nail plate.
a — nail fold (roof of the matrix); b - lower matrix; c - nail bed (explanation in the text).
The nail fold (roof of the matrix or upper matrix) under normal conditions gives rise to the dorsal-proximal part of the nail, but this role is insignificant, since, ultimately, normal regeneration of the nail is possible without this area of soft tissue. It has been proven that the dorsal ridge and matrix roof prevent uncontrolled growth of the nail upwards and to the sides, directing it distally.
The lower matrix (Fig. 27.8.1, b) is the most vulnerable zone of soft tissue, providing nail growth. When it is damaged, the growth and shape of the nail plate are disrupted, and to a greater extent, the more significant the injury.
The nail bed (Fig. 27.8.1, c) is covered with a smooth layer of epithelial cells and plays a significant role in the formation of a nail of normal size and shape, as it ensures the advancement of the nail plate as it grows. Disruption of the relief of the nail bed during fractures of the distal phalanges with unresolved displacement of bone fragments leads to subsequent deformation of the nail plate. Scarring of the nail bed with changes in its relief can also change the shape of the nail.
The nail grows at an average rate of 0.1 mm/day, or 3-4 mm/month. This indicator can vary significantly: in summer the notes grow faster than in winter; part of the nail plate is faster than the whole; on long fingers faster than I.
After a nail injury, there is a 3-week delay in its advancement in the distal direction. But then the nail grows again at the same speed. As a result of the pause, a thickening of the nail is formed proximal to the site of injury, which persists for about 50 days and then gradually (over the next month) becomes thinner. Thus, after the injury, about 100 days pass before a normal nail plate is formed.
Treatment of damage to the nail and surrounding tissues
According to E. Zook et al., the most common injuries to the nail plate are: simple (36.4%), stellate (27%), multiple and circular injuries of the nail bed (22%), scalped and avulsion injuries with loss or detachment nail bed tissue by more than one third (15%).Subungual hematoma is the most common of simple injuries and is clinically manifested by the accumulation of blood under the nail plate, as well as severe pain, in which the pain can be pulsating. A simple and effective treatment method is to perforate the nail plate in the area of the hematoma with any sharp instrument or the hot end of a paper clip (Fig. 27.8.2). This procedure is painless and immediately relieves pain.

Rice. 27.8.2. Stages of subungual hematoma removal.
a — creating a hole in the nail plate using an injection needle; b — evacuation of the hematoma; c - applying a bandage.
Tears of the nail or part of it (without damage to the nail bed). Taking into account the important role of the nail plate in the function of the finger, after treatment (if necessary, with resection of the damaged area) it can be returned to its place.
This is very advisable for the following reasons:
— the nail plate is a natural splint for the affected distal phalanx;
— the replanted nail plays the role of a natural guide for the new nail;
— the nail plate ensures healing of the tissues of the nail bed with minimal scarring and, what is very important, with the formation of a smooth surface;
— the nail bed covered by the nail plate does not require dressings, and if they are still needed, then changing the dressing is painless.
If a nail is lost or unusable, it is replaced with an artificial nail. The latter can be made from a fairly thin polymer plate with appropriate curvature. Artificial nail(like the nail plate) is hemmed with transverse mattress sutures (Fig. 27.8.3).

Rice. 27.8.3. Scheme of fixing the nail plate (or its prosthesis) with mattress sutures (explanation in the text).
Wounds of the nail fold, lower matrix and nail bed are the most complex injuries and are subject to precision primary surgical treatment with the mandatory use of microsurgical techniques.
The accuracy of comparison of soft tissue fragments plays a decisive role in this case. During the operation, suture material 7/0—8/0 is used. After completing this stage of the operation, the wound surface is covered with a nail plate or its prosthesis.
In case of tissue defects of the nail bed, when areas of bone are exposed, it is advisable to perform cross skin grafting with a de-epidermalized flap from an adjacent finger. If this is not possible, then an islet fat flap can be formed on a peripheral pedicle, for which one of the palmar vascular bundles is used.
Damage to the nail bed due to open fractures of the distal phalanges. If significant displacement of the bone fragments of the distal phalanx is not corrected, there is always damage and deformation of the nail bed, which leads to impaired growth of the nail plate. In this situation, during the initial surgical treatment, the nail can be temporarily removed, after which the largest bone fragments are compared and fixed thin knitting needles. Then micro-sutures are placed on the tissues of the nail bed and the operation is completed with replantation of the nail plate.
Tissue defects in the matrix zone can be closed using one of the methods described above, and after the wound has healed, plastic surgery of the nail bed is performed.
Detachment in the area of the nail phalanx. The surgeon's tactics are determined by three main factors: level, direction and plane of separation. As is known, normal height nail repair is possible only if the proximal third of the nail plate is preserved. But even when this condition is met, claw-shaped deformation of the nail often develops, to prevent which reconstructive surgery is necessary.
The surgeon's tactics and capabilities vary significantly depending on the level of distal phalanx separation.
Separation of the distal third of the phalanx. With guillotine separation, the severed tissue is replanted without suturing the vessels and nerves. When tissues are crushed and their replantation is impossible, the content of the operation depends on the plane of tissue separation.
For transverse separation, a palmar or two lateral sliding triangular flaps are used. In case of oblique palmar separation (when the plane of the wound surface is facing the palmar side), the amount of skin of the palmar surface during plastic surgery with a sliding triangular flap may be insufficient. Therefore, a lateral sliding flap or a palmar digital sliding flap is used.
In case of oblique dorsal separation (when the plane of the wound surface is turned to the back side) while preserving the fatty tissue of the finger pulp, plastic surgery can be performed with a split skin graft. Otherwise, cross-plasty with a flap from an adjacent finger is indicated.
Separation at the level of the middle third of the distal phalanx. In these cases, the nail root remains intact. In case of palmar oblique separation, it is advisable to use a cross digital flap to close the wound surface without shortening the phalanx. With dorsal oblique separation, attempts to save the nail usually end in significant deformation, requiring repeated operations.
Detachment at the level of the proximal third of the nail phalanx. Only replantation of severed tissues with suturing of blood vessels and nerves can preserve the length of the finger and, in some cases, the nail plate. If the level of separation passes through the matrix zone, then deformation of the nail plate as it grows is inevitable. Therefore, excision of the remaining lower matrix tissue may be justified.
Foreign bodies under the nail plate. When foreign bodies are deeply located, the easiest way to remove them is using an operating microscope and appropriate instruments. In complex cases, resection of a minimal portion of the nail under general anesthesia may be required.
Treatment results. When assessing the results of treatment of patients with damage to the nail and nail bed, the following indicators are taken into account:
- shape of the nail (normal, shorter, narrower, with a longitudinal or transverse groove);
- fusion of the nail plate with the surrounding tissues (complete, two-thirds, one to two-thirds, one-third or less);
— condition of the tissues around the nail (normal, disturbed, tissue defects);
- surface of the nail (normal, somewhat uneven, with significant irregularities, with the presence of longitudinal or transverse ribs, the presence of a groove);
- splitting of the nail (yes or not).
Using the principles outlined above in the treatment of damage to the nail and nail bed allows you to get excellent and good results even with severe injuries. Even the presence of a fracture of the distal phalanx has little effect on the final result of surgical removal of displaced fragments.
IN AND. Arkhangelsky, V.F. Kirillov