Reading 12 min. Views 1.3k. Posted on 10.09.2018
90% of the population with the appearance of any formation on the skin immediately diagnose themselves with a cancer. And this is by no means true, since neoplasms have many types, from the most complex to the simplest.
Each of these types has its own structural features, as well as symptoms and whether it is treatable or not. In this article, we will understand the types of neoplasms, as well as methods of treatment and prevention of the disease.
What is a skin growth?
Neoplasms are tumors that develop anywhere on the skin. Such a disease is closely examined by such a science as oncology. In simple words, this disease can be described as follows - several identical cells that are localized on the skin.
Unfortunately, neoplasms are a disease of the 21st century, they can be difficult to treat and progress rapidly. Therefore, if the slightest signs appear, you must consult a doctor.
All neoplasms can be conditionally divided into:
- Benign - develop slowly and do not require serious intervention. However, constant control over the size is simply necessary, the tumor can develop into the next stage - malignant, or disappear altogether.
- Malignant - dangerous to life. Here it is already impossible to do without the existence of metastases, which are absorbed by healthy organs every day.
Causes of neoplasms
There is no exact cause of the appearance of this disease, but there are factors that can influence its appearance. The absence of a specific reason is associated with individual indicators of a person, it is extremely difficult to determine them.
Factors that have a positive effect on the occurrence of neoplasms:
- Bad habits:
- Smoking, the smoke contains harmful substances, namely carcinogens. Therefore, non-smokers are just as susceptible to illness by inhaling these vapors, as are those who smoke.
- Alcoholic drinks. Naturally, we are talking about the daily use of these drinks.
- Hereditary traits, if one of the parents had such a disease in any form, then the child is at risk.
- Reduced immunity in the course of an illness caused by viruses.
- Ultraviolet rays above the norm and radiation. You can get it when staying in an area with increased radiation rates, as well as in case of an overdose in radiation treatment.
- Chemistry poisoning.
- Stress.
- Lack of vitamins and quality food in meals.
Types of neoplasms on human skin
As mentioned earlier, all neoplasms that appear are divided into two types. But there is also a third type - the precancerous stage. This is no longer a benign, but not yet a malignant tumor. Each of these types comes in many varieties, which we'll talk about here.
Malignant neoplasms
These are tumors that grow in a limited time. With this type of disease, pain is felt as nerve cells are destroyed.
There may be severe bleeding caused by the appearance of metastases affecting the vessels. The tumor may or may not be resectable, it may also respond to treatment, or it may not.
It appears from moles of a dark color and is now more common on referral to specialists.
The form of the disease is progressive and dangerous, in 80% of cases the outcome is unsuccessful. Melanoma often occurs from new age spots, which a person does not pay attention to before the onset of pain. Only a doctor can make a diagnosis for certain reasons.

The main signs of appearance:
- A rapid increase in the size of moles;
- Color change, both to the dark side, and vice versa;
- Pain;
- Lack of a clearly defined border;
- Changing the original shape.
A form of cancer in the course of which a compound of the constituent epithelium occurs. The more dominant group are citizens after 50 years. This form does not form metastases and only in 10% flows into a malignant one.
It is necessary to treat basal cell carcinoma when the first symptoms appear. Sores that reach 12 centimeters and are located inside, which is a complication of treatment.

At the initial stage, it is impossible to notice the disease, but still there are symptoms indicating the appearance:
- The appearance of new spots on the body with borders that stand out from the rest of the level;
- There is a depression;
- Itching
- On top of the neoplasm, peeling and bleeding are possible.
- The spots are of different sizes, but have a dense structure.
The disease has its name from the surname of the dermatologist, who was the first to find out that Kaposi's sarcoma affects people who have the human immunodeficiency virus.
A characteristic feature is the appearance of many malignant tumors. When diagnosing such a disease, systematic treatment prescribed by a doctor is necessary. Sarcoma does not threaten a person's life, but spoils the external component. Improper treatment or lack of it can also cause complications to other organs.

Symptoms:
- The appearance of spots ranging from pale pink to dark purple. When stretching the skin, pressing, the color does not change;
- The presence of a rash the size of a ruble coin;
- There are peeling on the spots;
- When you press the nodes, pain occurs.
Liposarcoma
The most popular malignant neoplasm that attacks skin tissue. The disease is often diagnosed in men over 45 years old.
At risk are men who are involved with asbestos and hormonal drugs. It is difficult to diagnose a tumor at an early stage, even when pressed, which makes it difficult for a specialist to make a correct diagnosis
Liposarcoma is also divided into forms:
- Mixed - several forms in one;
- Low differentiation - presented in the form of a compound of fat cells of different sizes;
- Dedifferentiable - the fastest developing form, due to metastases;
- Myxoid - a tumor that tends to grow and develop rapidly;
- Pleomorphic - affects only the limbs.

Characteristic signs of the appearance:
- Pain in the area of \u200b\u200bthe tumor;
- Decrease in body weight;
- Air breathing problem;
- Slow speech type;
- Weakness and fatigue even with banal actions.
The initial stages may be asymptomatic. as the neoplasm grows larger, the above symptoms may appear in a short period of time.
One of the rarest malignant neoplasms. People of different sex, age and race suffer from this type.
The tumor destroys muscle and tendon fibers. Often forms on the lower limbs, namely the feet, legs. The tumor is localized inside, it can be seen only in a complex and advanced case.

Manifestations that may be related to this disease:
- Seal inside;
- The tumor has a color different from the rest of the body;
- No pain;
- Body weight decreases;
- Temperature increase.
- Weakness and apathy.
Benign formations
Formations that belong to this category are usually caused by pathology, but their development is slow, which allows you to start treatment on time and get positive results.
The only danger will be that if you do not provide assistance, then this neoplasm can quickly flow into a malignant one.
People diagnosed with a benign tumor should be monitored by a specialist constantly in order to exclude the growth and development of the disease. We will consider the types of neoplasms below.
Blockage of the sebaceous glands resulting in swelling.
Causes of occurrence:
- Change in hormonal levels;
- Ecology;
- The epidermis layer becomes thicker.

Symptoms:
- A tumor in the form of a ball;
- It occurs only on the scalp, namely the armpit, intimate area, beard, head.
- When touched, there is solid content inside;
- Borders are well defined and differ in color from the body.
Hemangioma
A neoplasm appears during the accumulation of vessels inside. Often appears as a single spot with a red tint. It is more often located on the hairline.
Hemangioma also has different forms:
- Classic;
- Cavernous;
- Combined.
The definitions to which of the forms refers to depends on the location of the localization.

Main manifestations:
- Classic form:
- The appearance of seals ranging from red to brown.
- When pressed and stretched, the stain lightens for a while.
- Cavernous form:
- A tumor with a soft internal component;
- There is blood inside;
- The color changes with the growth of the tumor.
- Combined form:
- Symptoms of both the first and the second of the above form can be observed.
Formed from the cells of the vessels of the lymph nodes. The risk group is newborns and children before they reach one year old, but this is not the limit, there are also lymphangiomas at different ages.
Diagnosis can only be made with an X-ray. Also, a neoplasm of this nature is divided into such forms as:
- Cystic;
- Cavernous;
- Capillary.

External manifestations in different forms:
- Cystic:
- Affects the lymph node area;
- Localized in the neck.
- Cavernous:
- Small neoplasms;
- Soft contents inside.
- Capillary:
- Small neoplasms;
- The location is on the face.
Formed from adipose tissue. The location can be absolutely in a different place, most often the stomach. The tumor is immediately visible with the eye, which causes discomfort to a person with this disease. There are absolutely no painful sensations, so only a specialist can diagnose.

The main differences are:
- Neoplasms are carried out under the skin and the size can reach up to 20 centimeters, and the minimum size can be the size of peas;
- The node always grows, even if a person is losing weight quickly;
- No pain, even when pressing on a large tumor.
- When using clothing and rubbing it against the tumor, complications in the form of pus and blood can occur.
This concept should be understood as small, numerous pimples, which are more like warts. Absolutely all people are at risk.
Cause of occurrence:
- Infection with a special virus:
- Sexually;
- Contact:
- Lack of personal hygiene;
- A visit to the pool does not meet sanitary standards.
There are several forms of warts:
- Flat;
- Ordinary;
- Pointed.

Form symptoms:
- Flat warts:
- The most common;
- Tumor from 1 millimeter to 5 centimeters;
- Children and other citizens are subject to illness until they reach the age of 25.
- Ordinary:
- Raise in relation to other skin by 3-4 millimeters and is rough;
- Pointed:
- Formed on the genitals and mouth.
Moles are popular for their variety. Some moles are congenital and appear as the baby grows.
There are also acquired moles that arise due to changes in hormonal levels or in the presence of various infections. Small formations do not threaten life at all, but large ones can develop into a malignant tumor.
Moles that are on the body need to be known carefully and to monitor their size. And if moles appear and grow, then you need to contact a specialist to diagnose the condition.

Examples of how they should look:
- The size ranges from 1 millimeter to 10 centimeters;
- The color can be from beige to dark brown;
- There are both flat and convex.
It develops from connective tissue fibers. To be present in a person from birth or acquired during the life process.
It is divided into such forms as:
- Soft;
- Solid.
The first type is most common in women.

Description of symptoms:
- Soft:
- Pink colour;
- It can be both single and multiple;
- Has a smooth surface.
- Solid:
- Brown color;
- Occurs near the breast or intimate areas.
It occurs only during inflammation of the membranes of the nerve connections. The disease is always hereditary.

Manifestations that may indicate neurofibroma:
- The appearance of a build-up on the footboard;
- The color is beige;
- The appearance of age spots.
Precancerous conditions
This condition is characterized by pathologies in the form of skin changes, which, if untreated, can lead to malignant tumors. Further we will specifically talk about the types of such a state.
It is quite rare, the disease destroys the skin and mucus membranes. People at risk are citizens over 70 years of age, both men and women.
So the appearance is possible due to the effects of trauma and the advanced stage of dermatological disease.

Symptoms:
- A pink spot with a different location;
- Covering the roughness of the spot, which was smooth literally 2-3 days ago;
- If no treatment has been carried out, then the next stage will be ulcers. And they look like wet sores.
The disease is inherited. It is found in southern countries, usually in children under 5 years of age and mainly in girls. A feature of the disease is in those who are married in kinship.

Symptoms:
- Sudden onset of redness and swelling;
- Borders are like freckles;
- Dryness in this place;
- Damage to vision, reduction occurs by 80%;
- The condition of the teeth is getting thinner.
Precancerous condition in adults who have reached the age of 75. The cause of the disease is the growth of the epidermis. In most cases, the disease occurs externally.

- The appearance of a spot ranging in color from yellow to black;
- Rarely there are single spots;
- If you look at the neoplasm from above, it looks like an even circle;
- In some cases, scales appear on top of the sores.
From the name alone, it is clear that the neoplasm looks like an animal's horn. Appears in a person at any age and condition.
The reasons may be:
- Diseases caused by the virus.4
- Injuries.

Symptoms:
- The appearance of a tumor in the form of a horn;
- The inner component is dense;
- Slow growth and development;
Methods for treating neoplasms on the skin
All methods can be divided into:
- Chemotherapy is an action on a tumor using toxins.
- Radiation therapy - treatment of neoplasms with radiation.
- Surgical intervention is an operation that can remove both the tumor and metastases.
Note! Accordingly, the doctor recommends an individual type of treatment for each type of tumor.
Removal of skin lesions
The operation helps to get rid of benign neoplasms, and in some cases, malignant ones. During the operation, the doctor removes the tumor and adjacent metastases, if any.
Now the more popular surgery to remove a tumor is laser. With its help, the risks of metastases and relapses are reduced.
Prevention measures
There will not be a specific list in this paragraph, since they have not yet been developed by specialists, but there are several rules that will definitely not be harmful:
- You need to eat right, including vitamins in your diet;
- Give up smoking and alcohol completely;
- Less sun exposure;
- If injured, provide yourself with first aid, which will eliminate the risk of infection;
- Follow that. What is already on the body.
As a result, I would like to say that a person should know in what places and what size he has spots or moles. If there is a suspicion of growth and development, consultation and treatment is necessary, which can only be prescribed by a specialist.
Note! If a malignant tumor is diagnosed, then there is no need to be upset at all, since proper treatment and regular examinations by a doctor can help get rid of the tumor.
We often make two big mistakes in skin care. Either we take every neoplasm on the skin too seriously and begin to panic for no real reason, or, on the contrary, we completely ignore them. Both lines of behavior are two extremes that must be avoided. It is important to know that not any neoplasms on the skin are dangerous and difficult to cure, but you also should not let things that give you discomfort and anxiety go by themselves.
The doctor needs to show the problems that concern you when you observe any changes (in size, color and other manifestations of their vital activity).
What are skin growths?
Skin neoplasms (they are also "neoplasias" or "tumors") are many identical malfunctioning cells located in one area of \u200b\u200bthe skin.
Types of neoplasms
 There are two types of tumors: benign and malignant. Also, some classifications distinguish the precancerous stage - a borderline state between the first two types.
There are two types of tumors: benign and malignant. Also, some classifications distinguish the precancerous stage - a borderline state between the first two types.
Benign skin neoplasms
This group includes such neoplasms on the skin of the face and body that do not change and do not pose a danger to the life and health of their wearer.
However, they should not be taken lightly either, since in case of damage or unwanted external influence, they can move to the next stage.
Among benign tumors, the following types are distinguished:

External distinctive features are clear contours, regular round shape, smooth surface and dense structure. It is elastic and mobile to the touch.
 In the absence of suppuration and irritation (which happens in case of complications), it does not cause pain.
In the absence of suppuration and irritation (which happens in case of complications), it does not cause pain.
However, in an advanced stage, it can blush, fester and burst. Removal of this type of tumor is possible only through surgery.

 The fight against this group of benign tumors includes the use of antiviral and immunostimulating drugs, as well as physical impact on the points of damage themselves with acids, laser, liquid nitrogen and other means.
The fight against this group of benign tumors includes the use of antiviral and immunostimulating drugs, as well as physical impact on the points of damage themselves with acids, laser, liquid nitrogen and other means.

 Depending on which vessels are affected, hemangioma may be capillary or cavernous... The first variety forms only in the upper layers of the skin, but without spreading to the lower layers of the skin, it can reach impressive sizes on its surface. Cavernous hemangioma is accompanied by the formation of subcutaneous cavities filled with blood; their structure is elastic and soft. The colors of this type of tumor range from reddish to bluish-black.
Depending on which vessels are affected, hemangioma may be capillary or cavernous... The first variety forms only in the upper layers of the skin, but without spreading to the lower layers of the skin, it can reach impressive sizes on its surface. Cavernous hemangioma is accompanied by the formation of subcutaneous cavities filled with blood; their structure is elastic and soft. The colors of this type of tumor range from reddish to bluish-black.
Treatment is surgery, but the specific method of exposure depends on the type and location of the neoplasia.

 Outwardly, it is a bump (the size of which can vary from the smallest to quite large), does not undergo pigmentation, and the skin color remains unchanged. This neoplasm does not cause painful sensations, however, there are still low risks of tumor growth or its transformation into a malignant one.
Outwardly, it is a bump (the size of which can vary from the smallest to quite large), does not undergo pigmentation, and the skin color remains unchanged. This neoplasm does not cause painful sensations, however, there are still low risks of tumor growth or its transformation into a malignant one.
With a small size, lipoma is very easy to remove using simple cosmetic methods (laser or radio waves), after which there will be practically no marks on the skin.

 Outwardly, it is a protruding growth, the so-called "nodule" spherical in shape with pigmentation from flesh to brown.
Outwardly, it is a protruding growth, the so-called "nodule" spherical in shape with pigmentation from flesh to brown.
It does not show rapid growth, but there is a possibility of an oncological complication: the degeneration of a harmless fibroma into a malignant tumor called "fibrosarcoma".
Malignant neoplasms of the skin

Lacking adhesion to each other, cancer cells can travel throughout the body with blood, which complicates disease control and complicates further diagnosis.

 It is worth contacting a doctor at the first noticeable changes in the color, size or shape of the mole, the appearance of painful sensations and suppuration.
It is worth contacting a doctor at the first noticeable changes in the color, size or shape of the mole, the appearance of painful sensations and suppuration.
Hair loss is already a critical indicator when it is no longer possible to postpone a consultation with an oncologist. Treatment involves surgical techniques in conjunction with chemotherapy.

Prevention
The skin is the largest organ of the human body, and, although not being an internal organ, it carries important protective functions.
 It is due to its specificity that the skin and various neoplasms on it can be subjected to constant independent observation. Therefore, the first safety rule in order to avoid serious skin diseases is to consult a dermatologist in a timely manner when new formations appear or change already existing on the body.
It is due to its specificity that the skin and various neoplasms on it can be subjected to constant independent observation. Therefore, the first safety rule in order to avoid serious skin diseases is to consult a dermatologist in a timely manner when new formations appear or change already existing on the body.
In addition, there are a number of measures that will help reduce the likelihood of malignant neoplasms on the body:

Clinically, the term "neoplasm" implies a local overgrowth of any tissue of the body. On the skin, they are represented by primary and secondary tumors, nevi and hemoderma.
In dermatological practice, tumors are divided into benign and malignant. A detailed photo and a detailed description of each of them will be given below.
The study of skin neoplasms is still ongoing. The exact reasons for their occurrence have not been established, but scientists put forward several theories on this score.
Provoking factors can be:
Types of neoplasms on the skin
Neoplasms on the skin by their origin can be divided into primary (those that are formed from the skin tissue itself) and secondary (those that metastasize into the dermis and epidermis from foci of other localization). The latter also include hemoderma. They arise due to the pathological proliferation of malignant cells of the hematopoietic system.
There is a division of neoplasms into benign, precancerous (precancerous) and malignant (cancer itself). This classification allows you to determine the method of treatment and life prognosis for the patient.

Nevi should be distinguished from skin tumors. These are benign neoplasms that belong to skin malformations.
Malignant neoplasms
Neoplasms on the skin of a malignant nature in the Russian Federation in the structure of oncological morbidity today are 9.8% and 13.7% in men and women, respectively. Persons living in areas with high photoinsolation and having fair skin are especially susceptible to the disease. The number of new cases of skin cancer has increased by a third over the past ten years.
 Types of malignant neoplasms on the skin, their structure.
Types of malignant neoplasms on the skin, their structure. Malignant skin tumors include:
- basal cell carcinoma;
- kaposi's sarcoma;
- liposarcoma;
- squamous cell carcinoma;
- melanoma, etc.
Basalioma
One of the most common epithelial skin tumors. It is formed from atypical cells of the basal layer of the epidermis, from where it got its name. The tumor is characterized by long-term progression, peripheral growth, during which the destruction of the surrounding tissues occurs. Basal cell carcinoma is not prone to metastasis.
This pathology develops mainly in the elderly and old people, localized mainly on the face, neck and head (its scalp). Sometimes basal cell carcinoma is referred to as precancer. under the influence of some factors, it degenerates into metatypical cancer.
The first manifestation of an emerging tumor is a dense hemispherical nodule that does not rise above the skin. Its color usually coincides with the color of the skin or differs slightly (slight pink tint).

At the initial stage, the patient does not make complaints. Over the course of several years, the papule grows, reaching 1 or 2 cm in diameter. Its center gradually collapses, bleeds and crusts.
Under the latter, an erosion or ulcer with a narrow ridge along the edges is found, which, over time, scar and grows along the periphery.
Basalioma reaches a size of 10 centimeters or more. The once pink papule turns either into a flat plaque with scaling, or a node that rises noticeably above the surface of the skin, or a deep ulcer that destroys the underlying tissue (up to the bone).
Liposarcoma
This is a neoplasm on the skin of fat cells of mesenchymal origin. In the photos below, you can see what size these tumors reach. Descriptions in clinical reference books speak of liposarcoma as a mass that tends to appear on the buttocks, thighs, and retroperitoneal tissue. It is more common in men over 40.

Initially, a swelling appears, then a node. There are no subjective sensations yet. On palpation, the nodule is dense, elastic, mobile.
Subsequently, the tumor grows, turns red, and inflammatory processes begin. Large liposarcoma can compress the nerves and blood vessels and even grow in them, causing tissue trophic disorders and pain.
Kaposi's sarcoma
This is a systemic multifocal disease of vascular origin with a predominant lesion of the skin, lymphatic system and internal organs. It refers to tumors of an endothelial nature and develops mainly in individuals with severe immunosuppression.

By morphology, skin foci of sarcoma are quite diverse. They come in the form of spots, nodules, infiltrative plaques, etc.
There are several types of sarcoma:
- Classic (European).
- Endemic (African).
- Epidemic (with HIV).
- Immunosuppressive (immunodeficiency caused by medications and therapeutic manipulations).
The first type is observed in the elderly and old people, has a favorable course. Elements grow for a long time, tens of years in the proximal direction and do not give the patient unpleasant sensations. The formations are most often localized on the lower extremities, represent bluish-red spots up to 5 cm in diameter with smooth edges, resemble hematomas.
In the process of growth, they are transformed into nodules, merge. Large nodes darken and ultimately ulcerate. Edema occurs along the edges of the elements, caused by stagnation of lymph in the lymphatic bed.
The African type is difficult, affects the young. A fulminant course of the disease is often observed. African Kaposi's sarcoma manifests itself in several types of formations - from nodes to lymphadenopathy.
The most malignant type of elements of this type of sarcoma is considered "flowering" (growths in the form of vegetation - in appearance it resembles cauliflower). It is characterized by deep lesions of the dermis, subcutaneous tissue and underlying tissues down to the bone.
With HIV infection, a tumor can be localized literally anywhere in the body, even affecting internal organs. The most common sites are the mouth, stomach, and duodenum. The current is heavy. The immunosuppressive type is similar in its manifestation to the HIV-associated one.
Squamous cell carcinoma
Malignant tumor from the epithelium. It is formed from atypical keratinocytes that proliferate randomly. The process begins in the epidermis, gradually moving into deeper layers. The tumor is characterized by a tendency to metastatic process.
Squamous cell carcinoma occurs 10 times less often than basal cell carcinoma. They are more often affected by white-skinned men, whose place of residence is a sunny warm climate.

The localization of spinocellular epithelioma is different. The most favorite place for the formation of squamous cell carcinoma is the border of the transition of the mucous membrane into the skin. These areas include the lips and genitals.
At the initial stage of cancer development, an infiltrate with a towering hyperkeratotic (rough) surface occurs. The color of the formation is usually gray or yellow-brown.
Complaints at first, as with basalioma, are absent. In the process of growth, the tumor can reach sizes up to 1 cm.At this moment, a dense knot is already felt, and continues to grow. Eventually, the carcinoma approaches the size of a walnut.
The tumor grows in two directions - above or deep into the tissues. The latter is usually accompanied by the formation of an ulcer, which affects not only the dermis and epidermis, but also reaches the bone and muscle tissue.
The ulcer in squamous cell carcinoma does not heal. The patient suffers from excruciating pain in the place of its formation. In the future, a violation of the general state of health and infectious complications associated with immunosuppressive processes accompanying any oncopathology join the complaints.
Melanoma
This is a tumor of neuroectodermal origin. It consists of malignant melanocytes. He considers UV radiation to be the main provoking factor.
Melanoma develops both from a pre-existing nevus (birthmark) and on clean skin.

Signs of malignancy include:
- asymmetry;
- fuzzy edges;
- uneven color;
- diameter over 6 mm;
- the evolution of the age spot (any changes in the mole - sudden growth, color change, etc.) is the most typical sign!
Benign neoplasms
Neoplasms on the skin belonging to the category of benign, as seen in the photo and by their description, are not prone to rapid growth, metastasis and relapse after removal.
 Differences between benign and malignant moles.
Differences between benign and malignant moles. These tumors include:
- atheroma;
- hemangioma;
- lymphangioma;
- warts;
- moles (nevi);
- fibroids, etc.
 The structure of a lipoma (a benign tumor, popularly referred to as a wen)
The structure of a lipoma (a benign tumor, popularly referred to as a wen) | View | Description |
| Atheroma | The defeat of the sebaceous gland in the form of a cyst-like growth. The place of localization is the face. A towering formation, indistinguishable from normal skin in color, is tightly soldered to it at one point. The contours are clear. Palpation of atheroma is painless. |
| Hemangioma | Neoplasm of vascular genesis, refers to childhood tumors. It can be either an independent disease or a manifestation of another pathology. The course depends on the patient's age, location, size and depth to which the hemangioma has grown. Frequent placement - head, face, neck, but other localization is also possible. The first manifestation is a red nodule (papule) up to 5 mm in diameter. From complaints - bleeding when accidentally touched, sometimes - dysfunction of the organ where the tumor is located. |
| Lymphangioma | There are two possible development options - congenital defect or consequences of impaired lymph flow. The tumor can be located anywhere, but more often it is the oral cavity, neck, upper limbs. Capillary lymphangiomas are multiple vesicles with a yellowish transparent liquid inside. The same tumors that have arisen as a result of impaired lymph circulation look like plaques or spots, the diameter of which is slowly increasing. |
| Lipoma | Tumor of adipose tissue. Most often they have a nodal shape. The course is asymptomatic. It is a painless pale pink neoplasm on the pedicle. Doughy consistency. The borders are fuzzy. |
| Seborrheic warts | Also called "senile". They arise as a result of impaired differentiation of cells in the basal layer of the epidermis. Appearance - nodules or plaques that rise above the skin. The surface is bumpy. The shape is usually round or oval. The color of the wart ranges from yellow-brown to black. |
| Birthmarks | Or nevi. They are a developmental defect and consist of unchanged melanocytes. The color of the rash is characteristic - from light brown to black, which is associated with a different amount of melanin (dark pigment) in the cells. More often moles have a smooth surface, sometimes they rise above the skin. |
| Fibroma | Fibroma is a tumor that forms from connective tissue. Thick to the touch. Reaches large sizes. Malignancy (transition to malignant formation) of the tumor is possible. |
Neoplasms on the skin (photos and descriptions are presented above) of a benign nature, despite their relatively safe nature, sometimes can still turn into precancerous and even cancer.
Precancerous conditions
Precancrosis is a pathological condition of any tissue of the body, which with varying degrees of probability can contribute to the onset of a malignant process.
The following diseases are considered skin precancerous:
- bowen's disease;
- paget's disease, etc.
Bowen's disease - intraepidermal cancer, prone to the transition to squamous cell. It is an inflammatory disease of a chronic nature, which is associated with an excessive proliferation of atypical keratinocytes. Occurs in older people.

The tumor has invasive growth, grows not only in the epidermis, but also in deeper tissues. It can be located anywhere on the skin and mucous membranes, but more often on the trunk.
The elements look like spots of pink shade with indistinct rounded edges. Under them there is an infiltrate, due to which the formations rise slightly. They are rough to the touch, covered with scales. When sloughing off the latter, an erosive, bleeding surface opens.
Paget's disease is a metastatic adenocarcinoma. The source of growth, as in Buen's disease, is located intraepidermally. The typical location is the mammary glands, most precisely the nipple zone and its areola.

The growth of the tumor is infiltrating (it grows to the underlying tissues). Clinically manifests itself as a unilateral itchy plaque with clear contours in women over 40 years of age. The surface is covered with scales and crusts. The element increases in size, begins to metastasize. The outcome is breast cancer.
Diagnostics
Skin neoplasms, photos and descriptions of which were presented above, are diagnosed using general principles. These include the mandatory collection of anamnesis (patient complaints, clinical manifestations of the disease), examination of the patient, a thorough visual examination of the formations and the analysis of data from clinical and instrumental examination methods (MRI, radiography).

The main thing in the final diagnosis is the histological method. It is a microscopic examination of an area of \u200b\u200bpathologically altered tissue in order to identify atypical cells.
Treatment of neoplasms on the skin
The methods of treating skin neoplasms include drug, radiation and surgical. The latter is radical (i.e. allows you to get rid of the disease as completely as possible).
Skin neoplasms are medically treated with antibiotic therapy (photos and detailed descriptions of drugs can be found in clinical reference books), NSAIDs, opioid analgesics and hemostatic drugs. This method is used as a symptomatic treatment, it makes it possible to alleviate the patient's condition, to somewhat improve the quality of life.
The surgical method is based on the elimination of the neoplasm. The goal of treatment is to finally get rid of the disease, prevent relapses.
Radiation therapy is more often performed for malignant processes, especially in cases where surgical resolution is impossible. Also, the goal is to prevent the resumption of tumor growth and its metastases.
Removal of skin lesions
Ways to remove skin lesions are:

In order not to miss the moment when new growths on the skin begin to threaten life, you need to understand what you have to deal with. Having studied the photos and descriptions of common pathologies, one can assume the source of the disease and contact a specialist in a timely manner.
A view of skin lesions
How to distinguish a dangerous mole from a safe one:
Characteristics of benign skin neoplasms:
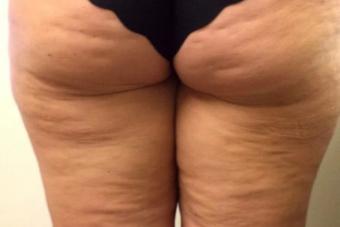
Skin neoplasms are malignant or benign lesions, growths on the skin as a result of the proliferation of abnormally dividing dermal cells. It is worth noting that it is recommended to remove even benign formations on the skin, since any injury or exposure to UV rays increases the risk of their degeneration.
Causes and mechanism of development
In the human body in full health conditions, the proportions of dead and new cells are approximately equal. However, under certain conditions and the influence of certain factors, the process of rapid uncontrolled cell division is triggered, and the cells multiply before reaching the state of maturity, as a result of which they lose their ability to perform their functions.
Many factors are capable of provoking uncontrolled cell division, but the most important of them is frequent trauma to the skin, in which cells of a certain area of \u200b\u200bthe skin are forced to regenerate and renew themselves very often and actively, as a result of which this process can become uncontrollable. In addition, any radiation (including UV) can stimulate the appearance of neoplasms.
Heredity and fair skin with many moles can also be factors in the development of a tumor.
Any benign formation on the skin does not pose a serious danger to life, but with its significant size, it can cause disturbances in the functioning of organs and systems (for example, cause pain by squeezing nerve endings, or disrupt the flow of blood and lymph when the vascular network is compressed in a certain area ). Factors such as frequent rough mechanical action on the skin, infections, and chronic skin diseases significantly increase the risk of skin formations. In extremely rare cases, cancerous metastases from another organ can lead to a malignant formation on the skin.
It is worth noting that a large number of moles or other benign neoplasms (papillomas, warts) is an indication of the person's predisposition to cancer.
Types of neoplasms on the skin
Neoplasms are divided into three types:
- benign: moles or nevi, fibromas, lymphangiomas, adenomas, hemangiomas, atheromas, neurofibromas, papillomas, lipomas and some others.
- borderline (or precancerous) tumors: keratoacanthoma, cutaneous horn, senile keratoma, pigmented xeroderma, etc.
- malignant: sarcoma, melanoma, basalioma, epithelioma.
They all differ in their ability to metastasize, complications and other signs.
Benign formations
Benign tumor cells can be distinguished because their original functions remain intact. Such formations are characterized by: slow growth, in the process of development they put pressure on nearby tissues, but do not penetrate into them due to the presence of a connective tissue capsule.


Old age

- Primary the cutaneous horn is formed on healthy skin, arises spontaneously, does not have an inflammatory element.
- Secondary develops after other skin conditions such as solar keratosis and lupus erythematosus. After complete formation, the tumor takes the form of a horny cone-shaped formation. This disease is characterized by a long course and a tendency to degeneration.
Malignant tumors
The cells of such tumors are extremely difficult to differentiate at an early stage of development, since they have lost the ability to perform their own functions, can grow into nearby healthy organs and tissues, and often metastasize through blood and lymphatic vessels, forming tumors throughout the body.
The main signs that indicate the degeneration of benign formations (age spots, nevi, etc.) into malignant ones are:

Consider what formations are malignant:

Regular examination at the dispensary and self-examination makes it possible to timely assess the condition of the skin, diagnose changes in the formations and consult a specialist.
Treatment and prevention
 There are no special measures that can prevent the development of cancer. However, as a preventive measure for a large number of moles, after a mandatory consultation with a specialist, they must be removed. In the case of an existing genetic predisposition, it is necessary to limit exposure to the open sun, to use protective lotions and creams, to avoid contact with chemically aggressive substances, and not to consume foods that can cause the development of oncology.
There are no special measures that can prevent the development of cancer. However, as a preventive measure for a large number of moles, after a mandatory consultation with a specialist, they must be removed. In the case of an existing genetic predisposition, it is necessary to limit exposure to the open sun, to use protective lotions and creams, to avoid contact with chemically aggressive substances, and not to consume foods that can cause the development of oncology.
In most cases, for the treatment of neoplasms on the skin, a surgical technique is used, when using which there is a complete excision of the affected, and, for the prevention of recurrence, partly of nearby healthy tissues.
For the treatment of benign neoplasms, methods of cryodestruction and electrocoagulation are used, as well as the radio wave method.
If the cancer is inoperable, radiation and chemotherapy are used for treatment. When a tumor initially develops as malignant, experts give an unfavorable prognosis, since in this case there is a high likelihood of deep metastasis to the internal organs, even with minor manifestations on the skin. With the timely start of surgical treatment, any formation that did not have time to degenerate into a malignant one is completely cured without further recurrence.
Various skin neoplasms are very common. In the structure of primary visits to polyclinic dermatologists, they account for 20-25% of all dermatological diseases. More and more application in the practice of dermatologists and cosmetologists is found in the hardware room, which makes it possible to diagnose the type and nature of the disease with high reliability.
Skin neoplasms (neoplastic formations, tumors) represent a limited quantitative growth or increase in the size of qualitatively altered pathological cells included in skin structures.
Classification of neoplasms
In most cases, neoplastic lesions are harmless to health and present primarily a cosmetic problem. At the same time, benign and malignant types of pathological elements are often outwardly similar to each other. They can arise primarily, transform from the cells of benign tumors, or arise in the place of the latter.
Depending on the structure and nature of growth, all types of neoplasms on the skin are combined into four large groups:
- Benign.
- Malignant.
- Borderline, or precancerous conditions.
- Tumor-like formations, or malformations.
Benign skin neoplasms
They are characterized by slow growth, during which their cellular elements remain within the tumor, without growing into adjacent tissues. The neoplasm, evenly increasing, pushes and squeezes healthy tissues, as a result of which the latter, as it were, play the role of a capsule. Although benign tumors are atypical, metastasis of their cells is absent.
The most common neoplastic formations are:
- lipoma;
- atheroma;
- hemangioma and lymphangioma;
- fibroma and neurofibroma;
- nevus (birthmark).
Under the influence of unfavorable external or internal stimuli, they (especially a nevus) can transform into malignant tumors.

Malignant neoplasms of the skin
Unlike benign ones, they have rapid cell division, infiltrating (invasive) growth of immature atypical cells. First, they spread along the directions of minimum resistance, that is, along the intercellular spaces, along the surface of nerves, blood and lymphatic vessels, and membrane septa.
After that, cell complexes destroy obstacles and grow into surrounding tissues and vessels, destroying them in the process of their growth. Once in the bloodstream, the cells of the malignant tumor spread to nearby and distant tissues and organs, forming metastases. Tumor growth can be exophytic (outward, to the surface) and endophytic (into the underlying skin layers, into muscles, etc.).
Malignant dermatological neoplasms include:
- basal cell carcinoma, or basalioma;
- squamous cell skin cancer;
- melanoma arising on the background of nevi with a "borderline" component;
- liposarcoma and fibrosarcoma;
- angiosarcoma (Kaposi's sarcoma);
- paget's breast cancer (rare in young people).


In the general structure of cancers, skin localization is about 30%. Such a high incidence, in comparison with other localizations of cancer, is explained by:
- significant spread of oncogenic viruses;
- a decrease in the level of the body's immune defense in many people;
- the influence of a large number of chemical and other carcinogenic components in food and air, household products;
- an increase in the general radioactive background;
- Excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays on many sunbathers.
Basal cell carcinoma accounts for 45 to 90% of all malignant skin tumors. Its annual growth is on average from 3 to 10%.
Another example is melanoma, which, although it makes up less than 5% of all skin cancers, is more common in young people (under 30), especially among women. The lifetime risk of developing it for people with white skin is 2%. It increases with age and reaches its maximum after 80 years. Melanoma is considered the most dangerous species due to its rapid growth and high mortality. Of all other skin cancers, it accounts for the highest mortality rate.
Borderline tumors, or precancerous conditions
Skin neoplasms that, with a statistically predictable frequency, under certain conditions or over time, are prone to cancerous transformation. These include:
- senile keratosis;
- borderline pigmented nevus;
- cutaneous horn;
- pigmented xeroderma;
- erythroplasia, or Keir's disease, always turning into squamous cell skin cancer;
- bowen's disease, which transforms into metastatic cancer without treatment.
Tumor formations
They are congenital in nature and can manifest themselves at different age periods. They are a pathological mixture of separate normal components that make up the structure of an organ. The increase in the size of these formations is not associated with a real atypical growth of the main functional elements, but with sclerotic transformation in the stroma (supporting structures), the occurrence of edema and circulatory disorders, the accumulation of glandular secretions, etc. Their tissue is morphologically identical to normal, but does not have functionality. Tumor-like formations, which mainly include epidermal melanocytic nevi and nevi of the sebaceous glands, can be combined with true tumors or serve as a background for the latter.
A number of tumors develop mainly towards the end of middle age and in old age. These include age-related skin neoplasms such as:
- Adenomas of the sebaceous glands, which are usually located on the face or back. These are dense formations with a smooth surface up to 10 mm, most often on a stem.
- Soft fibroma, malignant transformation for which is uncharacteristic. It appears in old age, usually in the axillary and groin areas, on the neck and back of the chest.
- Senile keratosis, which occurs mainly after 50 years, less often after 40 years. It represents dense layers of keratinized epithelium of brown or grayish color in the form of crusts with flat scales. After their mechanical rejection, a rough surface remains, sometimes blood drops "protrude". The main localization sites are the anterior and posterior surfaces of the chest, cheeks and forehead, and the skin of the temporal regions. Senile keratosis is often prone to degeneration into squamous cell skin cancer. It must be differentiated from melanoma.
- Keratoacanthoma, the differential diagnosis of which with squamous cell carcinoma presents certain difficulties. The tumor-like formation is elevated above the skin surface and has a crater-like depression in the center, which is filled with a horny mass. Keratoacanthoma occurs after 50 years of age on open parts of the body and most often goes away on its own with the formation of a scar, but sometimes it can degenerate into cancer.
- Cutaneous horn - develops on the face or exposed areas of the body that are subject to frequent friction. It occurs after the age of 60-70 years. The tumor has the form of a dense cone of yellow, pink, brownish or gray color. It is prone to malignant degeneration or may be an early stage of squamous cell carcinoma.
- Paget's cancer - usually localized in the nipple-areola zone, sometimes with the formation of a node around it. The tumor less often affects the skin of the external genital organs of a woman, the penis and the skin of the perineum. In women it can appear after 60, and in men after 70 years and is much more aggressive. The disease can manifest itself in three forms: pink papular rashes with small scales; a small rash on an ulcerating surface and a wet nipple; small crusts on the skin and weeping under them like eczema.

Treatment
Removal of benign formations and skin malformations is carried out mainly for cosmetic purposes or when they are subject to constant mechanical irritation or damage in certain areas of the skin. In other cases, it is only possible to periodically monitor them to prevent malignant transformation and growth.
Treatment of tumors of other types consists in their removal by thermal (cryodestruction), chemical (liquid nitrogen), pharmacological, surgical methods, or by radiation exposure if other methods cannot be used. The most effective and reliable is the surgical removal of skin neoplasms by simple excision, radio wave or laser method.
Traditional surgical excision with a scalpel makes it possible to carry out histological control of the remote area in order to exclude the presence of malignant cells. The disadvantages are difficult visual control due to bleeding, damage to tissues adjacent to the tumor, and the possibility of the introduction of pathologically altered tumor cells into adjacent zones. In addition, excision with a scalpel often leaves behind an aesthetic defect in the form of a rough scar.
In contrast, laser removal of skin neoplasms is carried out without direct contact with tissues. It is characterized by high accuracy, absence of bleeding and rough postoperative scars, and also excludes the drift of pathological cells into the tissue bordering on the tumor. However, the main disadvantage of laser removal is the destruction of the cells of the entire tumor, and therefore it is impossible to conduct its further histological examination.
The method of removing a pathological skin area using a radio wave knife of the "Surgitron" apparatus has all the advantages of a laser operation. At the same time, this method, possessing high accuracy and narrow directivity of the radio wave beam, allows you to keep the tumor itself intact for histological examination.
The value of differential diagnosis
All benign and borderline skin neoplasms are dynamically developing structures, some of which can undergo malignant transformation. In addition, on simple visual inspection, some of the different types of elements have significant similarities with each other and with malignant species.
This explains the importance of instrumental screening of neoplasms using dermatoscopes. Digital epiluminescence dermoscopy, with a sensitivity of up to 95% and a specificity of up to 79-93.5%, in combination with an automatic analysis using computer software, allows you to completely exclude subjective assessment.
The ability to carry out objective differential diagnostics with a high degree of reliability makes it possible to identify precancerous and malignant neoplasms at the early stages of their development and choose the appropriate treatment method.