Growths can appear in any person, regardless of age and gender. In most cases, they do not pose any threat to humans. But if growths on the skin appear in uncomfortable places, are constantly injured, change their shape and size, you should look closely at them and, if necessary, visit a doctor.
The growths on the skin are usually divided into several types. These are benign, malignant and borderline lesions, which are also called precancerous. Each group can include its own certain growths that differ in appearance, structure and characteristics. Benign formations include:
- atheroma and lipoma,
- hemangioma and papilloma,
- mole and lymphangioma,
- fibroma and nevus,
- neurofibroma.

Such formations that appear on the body do not pose any threat. However, if they are placed in a place where they are constantly exposed to friction and injury, then in the future this can lead to disruption of the internal system of the body. It should also be borne in mind that under the influence of certain external factors, safe growths can gradually transform into malignant formations. The growths of a malignant nature include:
- sarcoma,
- basal cell carcinoma,
- melanoma,
- liposarcoma.
These growths tend to grow rapidly, affecting healthy tissues and cells. Very often they provoke the appearance of metastases, thereby affecting the internal organs. Doctors in such cases give an unfavorable prognosis. The fact is that malignant formations are very difficult to treat and often cause repeated relapses. If metastases penetrate to vital organs, and a person detects this with a delay, then a lethal outcome is possible. Skin conditions of a borderline nature, which are considered precancerous, are divided into:
- pigmented xeroderma,
- bowen's dermatosis,
- senile keratoma,
- cutaneous horn.

All these formations from safe growths can degenerate into more dangerous conditions. This can be due to genetic factors, hereditary predisposition of the body, or due to other provoking reasons.
Growths on the skin of the hands
On the skin surface of the upper extremities, growths can appear at absolutely any age. They rarely provoke pain, but it is also difficult to call them absolutely harmless. Sometimes such a formation can appear due to the ongoing deformation of the bones. In this case, a person runs the risk of facing certain unpleasant consequences.
Hemangioma can often be found on the hand. This growth can reach a large size, it is burgundy or dark blue. Hemangioma belongs to benign formations, it does not pose a threat to human life. However, it is easy to injure, which is accompanied by profuse bleeding, which is why doctors recommend removing such a growth. The procedure is carried out in various ways:
- laser exposure,
- sclerotherapy,
- surgical excision.

Warts and papillomas can often be seen on the hands. These are also benign formations, consisting mainly of epithelial tissues. The cause of their occurrence is the human papillomavirus, which can infect anyone.
Outwardly, such growths look like small horny outgrowths protruding above the surface of the skin. They are completely painless. If there are too many warts or papillomas on the hands, then we can talk about a significant decrease in immunity. And if a person begins to take strengthening and antiviral drugs in a timely manner, then such formations will eventually disappear by themselves.
You should not try to remove the growths on your hands yourself. Such manipulations will not be effective and may provoke some complications. Usually, formations that appear on the hands are associated with disorders that occur with bone and articular tissue. Therefore, they need to be removed only promptly.
Growths on the skin of the legs
The fair sex is more likely to encounter formations in the leg area. Growths appear on the lower limbs under the influence of harmful external factors. In most cases, this is due to the regular wearing of uncomfortable, tight, high-heeled shoes. As a result, the foot is faced with an uneven distribution of the load, which is why various growths begin to appear.

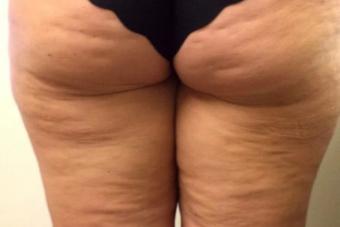
Some formations cause a lot of discomfort by their presence. So a lipoma, also called a wen, forms under the knee on the back of the leg. Outwardly, it resembles a small seal. It does not deliver any painful sensations, but from an aesthetic point of view, it interferes and causes inconvenience. Moreover, the lipoma grows and grows in size over time.
Lower limb growths can be treated in a number of ways. In this case, they resort to surgical intervention only when the growth by its presence can provoke serious consequences for the entire musculoskeletal system.
Scalp growth
Warts are more often seen on the scalp. Their appearance resembles small oval-shaped nodules. They are located under the hair, slightly protruding above the surface of the skin.
The main provoking factor in their appearance is the papillomavirus, which is considered contagious and can be transmitted from one person to another. If the immune system is extremely weakened and unable to resist the virus, then small warts begin to appear on the scalp.

Growths on the skin of the face
When neoplasms appear on the face, it becomes a real aesthetic problem. Usually, such growths have a color similar to the epidermis, or a brown tint. It can be:
- nevi,
- warts,
- moles.
Warts appear on the skin surface of the face due to close contact with a person who has already been infected with the papilloma virus. The wart can be transmitted in other ways:
- unprotected intercourse;
- during childbirth from mother to child;
- through infected household items.
Birthmarks and nevi are made up of cells called melanocytes. Their color can be light and dark; such growths do not pose any particular danger. But if they begin to change shape, quickly increase in size and cause discomfort, then you should definitely see a specialist.

In addition, when injured, a mole can degenerate into a malignant formation. In this case, it becomes dangerous to human health, the doctor recommends removing it by surgical excision or laser exposure.
Malignant and benign growths
Since some growths from benign can transform into malignant, this process should be recognized in time. Benign growths grow rather slowly. They rarely touch internal tissues and do not press on nearby surfaces. Their structure is similar to that from which they were formed.
As for malignant growths, they tend to grow rapidly and increase in size. In this case, the nearby tissue is always affected. Malignant formations, which can appear on the face, back and other parts of the body, further metastases. And if this happened, then such a progressive growth is difficult to treat.
Periungual, plantar, filiform warts
One of the most unpleasant growths that a person often encounters is a wart. It can appear on absolutely any part of the body. However, in most cases, this growth affects the lower extremities. Experts identify the following types of formations:
- periungual,
- plantar,
- threadlike character.
Periungual warts are considered benign formations that do not pose any threat to human health. They appear near the nail plate, under it and in the cuticle area. The provoking factor of their occurrence is the virus of the second type, which is transmitted from one person to another. Infection can also occur through minor injuries and small cuts in the skin.

Plantar warts are localized in the toes and around the entire perimeter of the foot. They are distinguished by their dense structure and rounded shape. The reason for their appearance is the human papillomavirus present in the body. Plantar warts cause a lot of discomfort, making it difficult to walk and wear your favorite shoes. While walking, a person feels an unpleasant itching, therefore, this type of growth should be disposed of as soon as they are detected.
Threaded growths are very thin. The place of their localization is the folds of the skin and the surface of the face. They can be up to five millimeters long. A feature of such warts is their ability to infect healthy areas of the epidermis. The color of filamentous warts can be flesh-colored or light brown.
Soft fibroma
Under the fibroma, a benign formation is hidden. It develops from the cells of the connective tissue themselves. Outwardly, the growth looks like a cluster of small nodules that have a warty or completely smooth surface. The color of this formation can be:
- gray,
- black and blue,
- brown.

Fibroma grows rather slowly without causing discomfort to a person. This growth does not pose any danger. However, under the influence of certain external factors, safe fibroma can transform into fibrosarcoma, which is considered a malignant formation. Therefore, many experts recommend removing such a build-up using laser exposure.
Neurofibroma, consisting of nerve cells, may also appear on the human body. It forms under the skin surface in the area of \u200b\u200bfatty tissue. The tubercle itself has a dense structure. It is usually removed by surgery or drug therapy.
Some people may experience such a phenomenon as the proliferation of epidermal cells. In this case, a small cone-shaped elevation is formed, which is characterized by a scaly structure and is called a cutaneous horn. The build-up has many layers, which makes it a real aesthetic problem.
Usually, people who have reached old age encounter the cutaneous horn. The disease is painless, but at the same time the skin surface is exposed to inflammatory processes. And if in time a person does not begin to take appropriate therapeutic measures, then the formation turns into a malignant form. Therefore, it is better to delete it.

Keratinous squamous carcinoma
Keratinizing squamous cancer is one of the most common types of malignant tumors. At the initial stages, the upper layer of the epidermis is affected, then the tumor itself begins to develop. Most often, it develops from the following types of growths:
- keratosis,
- cutaneous horn,
- keratoacanthomas.
The provoking factors that contribute to the occurrence of flat cancer are:
- excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays;
- received chemical or thermal burn;
- existing precancerous skin diseases;
- constant contact with hazardous chemicals.
Such growths can be recognized by their red tint and the resulting crust, which can bleed. If a person notices such signs in himself, he should immediately see a specialist.
Treatment of skin growths
The mainstay of treatment for skin growths is their removal. Most often, a laser beam is used, since such an effect is considered the most effective and efficient. Also, the laser prevents malignant cells from developing and penetrating further into the layers of the epidermis. Benign growths are removed by the following methods:
- radio wave method,
- electrocoagulation,
- cryodestruction.
If the growths began to transform into cancers, then the doctor may prescribe chemical or radiation therapy. It is better to deal with such phenomena in the early stages, until the benign form has passed into the malignant stage. If surgery is carried out in a timely manner, then the therapeutic result will be positive. But you can only fight against warts on your own.

Surgical operations
Surgical intervention is used in cases where the growth is located above the surface of the skin. In this case, the method of surgical excision is used. But there must be an indication for this method of influence.
When the growth has taken root into the layers of the epidermis, it is not recommended to remove it in this way. Otherwise, the process of recovery and rehabilitation can take a long time and during this period a person will have to face tangible discomfort.
Laser therapy
Laser therapy hides the effect of a laser beam. During this procedure, the keratinized tissue of the build-up is simply removed and cut off. In this case, painful sensations do not arise, and the wound does not bleed. Usually, moles and warts are removed with a laser.
The whole procedure takes a few minutes, after which the person can continue to lead the usual way of life. There are no marks or scars on the treated area.

Such a method as cryodestruction is based on the treatment of the build-up with nitrogen at a very cold temperature. This method is not used as widely as a laser, but it also allows you to get rid of various types of growths.
With cryodestruction, bleeding also does not occur. The tissues of the existing formation are simply destroyed and fall off. A healthy skin surface remains on the treated area. However, this method is not suitable for getting rid of growths that have acquired a malignant form.
Folk remedies
You can remove growths with lotions and compresses prepared on the basis of potatoes, apples and celandine. The most pronounced effect is given by potatoes. Grate the unpeeled tuber, put the resulting mass on a cling film. Then apply the finished compress and fix it with a bandage in the area where there is a growth. Keep it for several hours, and in order to completely get rid of neoplasms, such manipulations will have to be repeated daily for a month.
Another way that allows you to quickly and very easily remove existing growths at home. To do this, potato juice can be mixed with garlic or aloe juice. Take the components in equal proportions. A piece of gauze is moistened in the resulting liquid, which is then applied to the neoplasms. The tool will help remove even an old, large wart.
Prevention
The main prevention of the transformation of benign growths into malignant forms is their timely removal. Especially when it comes to those formations that over time begin to change shape and size.
People who have many moles and nevi on their bodies should avoid overexposure to sunlight. You need to monitor your diet. If possible, carcinogenic foods should be eliminated from the diet. Food should be healthy and minimally cooked. These small rules will help protect against the possible development of skin cancer.
Many people mistakenly refer to any growths in the body as cancerous tumors. This is a gross mistake, since the formations have a complex classification, each species has individual characteristics, symptoms and prognosis.
The proposed article will help to understand this issue: it examines in detail the main types and the most common forms of neoplasms.
What are neoplasms?
Tumors are called neoplasms, the study of which is engaged in oncology. In essence, they are a cluster of identical cells, which is localized in a certain area. Today this problem is widespread and is considered one of the main social problems.
All neoplasms can be divided into two main groups - benign and malignant tumors, each of them has several hundred varieties.
Causes of neoplasms
Given the variety of forms and types of neoplasms, they can arise for various reasons.
Types of neoplasms on the skin
All neoplasms on the skin are divided into benign and malignant tumors. Sometimes the borderline form is still distinguished, which is precancerous stage and over time can develop into a malignant tumor. All these groups include a large number of very different formations, the most common options are discussed in more detail below.
Malignant neoplasms are tumors that gradually grow over time, wedging in and destroying adjacent tissues. The destruction of the nerves encountered on their way leads to acute pain, and vascular damage leads to the opening of internal bleeding.
Tumor cells do not have adhesion and spread throughout the body along with blood, settling in internal organs or tissues, which leads to the formation of metastases. Very often, even after treatment or surgery, relapses may occur.
It develops from the pigment cells of moles; this is one of the most common forms of malignant neoplasms.
Melanoma is a common cancer, this form of the disease is characterized by an increased degree of aggressiveness, the prognosis in most cases is unfavorable. Most often, melanoma begins to develop on new moles, although in some cases old pigments are also exposed to this.
A number of characteristic manifestations can indicate such a diagnosis, therefore, at the first signs, you should immediately seek professional medical help, since at later stages, treatment is much more difficult.
Photo
Below is a photo that demonstrates the external manifestation of melanoma:


Symptoms
The main symptoms that occur when melanoma occurs are listed below:
- A rapid increase in the size of a mole, in just six months it can increase several times.
- A change in the color of a mole, it can be either lightening or darkening. However, it can change its color over the entire surface or in certain places.
- A change in shape, usually with a lack of symmetry.
- No clear boundaries, since the pigment merges with the skin.
- The appearance of ulcers at the site of the mole.
- Sharp pain.
- Loss of hairs growing on a mole.
It is another form of blood cancer, in this case, the tumor arises from the accumulation of epithelial cells. The elderly are at risk, although under the influence of provoking factors, such a neoplasm can occur in any person.
Unlike many other forms of cancer, basalioma does not metastasize, the course of the disease is actually always benign and most experts agree that such a diagnosis cannot be fatal.
The only exception is squamous cell type of basalioma, but it occurs only in 20% of all cases. However, there is always an extremely high likelihood of relapse: not a single method of treatment is able to guarantee a complete cure today.
Basal cell carcinoma should not be started as it is much easier to get rid of it at an early stage. Ulcers 10 cm or larger usually involve internal tissues and nerves, making therapy difficult. In some situations, death occurs from possible complications.
Photo
Below is a photo of a basal cell carcinoma, which gives an idea of \u200b\u200bwhat this neoplasm looks like:


Symptoms
At the initial stage, basal cell carcinoma is practically invisible and it is often not possible to recognize it in a timely manner, but then the following symptoms begin to appear:
- The appearance of surface formations, they are usually solitary and have a dense structure.
- All formations necessarily have a small internal depression.
- The shape can be different, but the boundaries of the neoplasm are always clearly defined, the diameter usually does not exceed a centimeter.
- The resulting tumor rises slightly above the outer layers of the skin.
- The appearance of minor itching, which is initially absent.
- The presence of visually distinguishable nodules, which are especially noticeable when the skin is pulled. Their color can be white, sometimes yellowish or grayish shades are found.
- Painful sensations that begin to arise as the neoplasm grows.
- Crusts on the surface of the tumor, their removal usually leads to the opening of bleeding.
It was named after the Hungarian dermatologist who first described this disease, which primarily affects patients with HIV infection.
Kaposi's sarcoma is characterized by multiple lesions of malignant neoplasms. This process is usually provoked by the herpes simplex virus type 8, therefore, not only people with HIV infection, but also local residents of equatorial Africa are at risk; Mediterranean residents who have reached old age, and patients who have undergone internal organ transplants.
When an appropriate diagnosis is made, local or systemic treatment can be prescribed, depending on the stage of the disease and other features of the situation.
By itself, Kaposi's sarcoma does not pose a threat to health, but it significantly impairs the aesthetics of appearance and leads to psychological discomfort. It can also cause complications that disrupt the functioning of the respiratory or digestive system, which is much more dangerous than the neoplasms themselves.
Photo
The photo below of the external symptoms of Kaposi's sarcoma allows you to understand what such neoplasms look like:


Symptoms
The presence of Kaposi's sarcoma is usually indicated by the following symptomatology characteristic of this disease:
- The appearance of spots on the skin, which can be pink, red, blue or purple. When touched or other mechanical impact, they do not brighten.
- The appearance of a blistering rash, which is similar to the external manifestation of lichen redness and can sometimes interfere with diagnosis. There is a gradual growth of the nodes, sometimes they reach the size of a rather large walnut.
- The affected area often dries up and begins to peel off, a spider vein appears on the nodes.
- Painful sensations that arise with mechanical pressure on the nodes. In some situations, for example, with lesions of the oral mucosa, the pain may never stop.
It is the most common and well-known type of malignant neoplasms affecting soft tissues. Usually this disease occurs in male patients over 40 years of age who have any kind of benign tumors.
At risk are people in contact with asbestos, as well as taking various hormonal drugs. When diagnosing the disease, specialists face a number of difficulties, since at the initial stages it is extremely difficult to recognize liposarcoma, and the tumors themselves are not palpable even during palpation.
To date, the following forms of this neoplasm are distinguished:
- Low-grade liposarcoma is the most common type, outwardly, neoplasms are similar to ordinary fatty compounds, which tend to actively grow.
- Myxoid liposarcoma is a borderline form, the tumor cells look and behave normally when examined in detail, but the neoplasm can begin to grow at any time.
- Pleomorphic liposarcoma is extremely rare, it affects mostly only the limbs.
- Dedifferentiated liposarcoma is a subspecies of the classical form, but the neoplasm is characterized by more aggressive behavior, there is a tendency to frequent metastases.
- Mixed liposarcoma is a combined combination of signs of several other forms at once, occurs in extremely rare cases.
Photo
Below is a photo of liposarcoma:


Symptoms
The onset of liposarcoma is usually accompanied by the following manifestations:
- Problems breathing, speaking, swallowing, and urinating.
- Painful sensations.
- A sharp decrease or increase in body weight.
- The appearance of nodes, which gradually change their color and turn blue.
- Numbness of the affected area if nerve endings were affected during the growth of the nodes.
- General deterioration in health.
- Fatigue too quickly, even after a long rest.
- Poisoning of the body with various substances produced during pathological processes.
It should be noted that in the initial stages, the disease is asymptomatic, all manifestations occur as the tumor forms.
It is a rarer type of malignant neoplasm, but it can affect all people, regardless of gender, age or other criteria.
Such tumors affect the fibers of the connective tissues of muscles or tendons. Fibrosarcoma can occur on the skin of any part of the body, but most often it affects the feet, much less often the face or body. The development of neoplasms and other pathological processes occur in the subcutaneous space, the skin itself is affected only in the most aggressive forms of the disease.
Photo
Below is a photo showing fibrosarcoma affecting the skin:


Symptoms
Fibrosarcoma may not have any symptoms for a long time, but then the following manifestations will indicate it:
- Formation of a dense subcutaneous node.
- The affected area becomes bluish brown.
- Painful sensations are completely absent.
- Feeling of weakness, apathetic state.
- A sharp decrease in body weight.
- The onset of a feverish state.
Benign neoplasms also represent tumors that are the result of pathological processes, but the rate of their development is too slow or the disease does not progress at all. The danger is that they can change their shape and become malignant neoplasms.
It is a tumor of the sebaceous glands, the cause of its occurrence is actually always a blockage.
The occurrence of atheroma can be provoked by:
- Thickening of the upper layers of the epidermis, as this leads to a deterioration in the outflow of the produced sebum and the subsequent blockage of the ducts.
- Changes in the hormonal background can also cause this disease, since against their background there is a change in the density and composition of fat.
- Aggressive environmental impact and poor environmental conditions place a person at risk.
Photo
Below is a photo of the skin affected by atheroma:


Symptoms
The main symptom is the appearance of spherical formations that look like this:
- The tumor is always round and regular.
- The appearance of a tumor occurs on the scalp or face, back, neck, armpits or in the area of \u200b\u200bthe genital folds, since there are a large number of sebaceous glands in these places.
- The boundaries are clearly defined and can be seen with a simple inspection.
- The surface is smooth, the structure is dense.
- Painful sensations are present only in case of complications, when inflammation and suppuration occur.
It is another neoplasm of a benevolent nature, a tumor develops from an accumulation of cells on the inner surface of blood vessels.
In the overwhelming majority of cases, the hemangioma is a single structure, although sometimes there are several formations. Most often, the disease affects the scalp or neck, but it also occurs on the eyelids, forehead, inside or outside of the cheeks, nose and areas around it.
Sometimes the area near the genitals is affected, which can cause a number of complications if infection occurs. Various forms of hemangioma are distinguished, the classification is carried out depending on which vessels the tumor develops from.
Moles and nevi
Moles are distinguished by their diversity and are the most common form of benign neoplasms that is known to every person.
Some moles are congenital; modern medicine associates their appearance with malformations of embryonic development and the migration of pigment cells into the skin. At the birth of a child, such neoplasms are invisible, but they begin to manifest themselves in the first years of life.
There are also acquired moles, which arise due to excessive insolation of the skin, changes in hormonal levels, or exposure to various infections. Small neoplasms pose no threat, but large moles can cause malignant tumors.
Photo
Below is a photo of moles:


Symptoms
As already noted, moles differ in their variety, below are examples of how they might look:
- The smallest moles have a diameter of 0.5 to 1.5 cm, all neoplasms with a diameter of more than 10 cm are considered large.
- The color can also vary: it is dark brown or flesh, which makes the mole almost invisible.
- Flat moles are small spots, but there are also bulky neoplasms in the form of peas.
- This is another type of benign tumors that develops from connective tissue fibers.
May be present in a person from birth or have an acquired character. In most cases, it affects the skin and soft tissues, but sometimes the tumor occurs in the internal cavities. Experts distinguish between hard and soft forms, the second type most often occurs in women.
Photo
Below is a photo of a fibroma:


Symptoms
The main symptoms of fibroma differ depending on the form, the features of the external manifestation are described below:
- Solid fibroma is a protruding growth of skin that has a low level of mobility. The tumor can be single or multiple, affects any part of the body or limbs. The color can range from flesh to pink. Most often, the fibroma has a smooth surface and is located on the stem.
- Soft fibroma similar to a pouch located on the leg, and has a pink or brownish color. This neoplasm can occur in the armpits, in the immediate vicinity of the mammary glands or genitals, as well as on the front of the neck.
It is the last type of benign tumors that will be discussed in this article. Its development always occurs from the nerve sheaths.
When neurofibroma occurs in childhood, the tumor develops from peripheral nerves, and when signs of neoplasm appear at the age of 10 years and older, development is carried out from the central nerves. In most cases, especially when neurofibroma occurs at an older age, the phenomenon is hereditary.
Photo
Below is a photo of neurofibroma:


Symptoms
Clinical manifestations in this neoplasm are completely absent, it can be suspected in the following cases:
- Formation of knotty spots located on the legs.
- The spread of age spots that look like freckles.
- Milky coffee stains.
Neurofibroma can affect any part of the human body with the exception of the feet and palms.
Precancerous conditions
Precancerous conditions are usually understood as pathological processes leading to changes in tissues, which greatly increases the risk of malignant neoplasms. Below are the main types of such conditions.
Today it is considered a rare ailment that affects the skin and mucous membranes, and also increases the likelihood of developing into invasive cancer.
At risk are usually persons over 70 years old regardless of gender, among the factors provoking Bowen's disease are exposure to chemicals, ultraviolet radiation or dangerous doses of radiation.
In some cases, the cause of the disease can be mechanical injury or the presence of dermatological lesions in a chronic form. The main danger to humans lies in the risk of the transition of Bowen's disease to squamous cell skin cancer, which is accompanied by tumor growth and metastasis.
Photo
Below is a photo showing the external manifestations of Bowen's disease:


Symptoms
Bowen's disease has characteristic symptoms, which are described below:
- The appearance of a red spot on any part of the body, the lesion is usually round in shape and uneven borders.
- The appearance of a copper-red plaque that develops in the place where the spot was originally located.
- Covering the affected area with yellow or white scales that hide the constantly weeping skin surface. Bleeding when removing scales is completely absent.
- Gradually, the structure of the plaque changes, it becomes warty and uneven.
- The appearance of ulcers indicates the transition of the disease to cancer.
It is a hereditary disease that always becomes chronic. The features of the course are discussed below.
The disease is most often found in Africa and the Middle East, the first symptoms appear even in childhood. At risk are children born in closely related marriages.
Pigmented xeroderma affects persons of either sex, but among girls this ailment is more common. Sometimes it is latent, in such cases, excessive ultraviolet radiation can become a provoking factor.
Photo
Below is a photo showing the external manifestations of xeroderma pigmentosa:


Symptoms
The disease begins to manifest itself at the age of six months to a year, exacerbation occurs in the spring or summer.
Symptoms are as follows:
- The appearance of edema, blistering and redness of the skin in places that have been exposed to ultraviolet radiation.
- Preservation of age spots, superficially similar to freckles, which remain after the passage of inflammation.
- Thinning of the skin, increased dryness and cracking occurs with relapses of the disease.
- The appearance of papillomas and warty formations in the affected areas is one of the late stages of the disease.
- Eye lesions and the development of ophthalmic diseases in parallel with xeroderma pigmentosa are observed in 80% of cases.
- Growth retardation and deterioration of the teeth are other symptoms that often accompany disease.
In rare cases, pigmented xeroderma is accompanied by the appearance of malignant neoplasms already in the early stages.
It is a precancerous condition that occurs mainly in the elderly, due to which it received the appropriate name.
Senile keratoma is caused by overgrowth of the upper layers of the epidermis, which is accompanied by keratinization of some cells. At risk are people over 50 years old, regardless of gender, who have a tendency to dry out the skin. In most cases, open areas of the body are affected, since the provoking factor is exposure to ultraviolet rays.
Photo
Below is a photograph showing the external signs of senile keratoma:


Symptoms
The symptoms that occur with senile keratoma are described below:
- The primary sign is the appearance of a stain, which may have a yellowish or brownish tint.
- In most cases, lesions are multiple in nature, occasionally there are single spots.
- Over time, the affected area becomes pigmented and discolored, becoming red or brown.
- As the spot grows, a papule with multiple shallow depressions forms on its surface.
- A round plaque about 6 cm in diameter is the final form of the lesion.
- In some cases, the plaque becomes covered with keratinized scales, the removal of which leads to the opening of bleeding.
It is one of the forms of neoplasms, which consists entirely of cells of the prickly layer of the epidermis.
Externally this neoplasm resembles the horn of an animal, due to which it received the appropriate name. In most cases, the cutaneous horn occurs in the elderly, although it can occur at any age. The provoking factors are mechanical trauma to the skin or severe viral infections.
Photo
Below is a photograph of a cutaneous horn:


Symptoms
When a cutaneous horn occurs, the following characteristic symptoms are usually observed:
- The appearance of a neoplasm of a conical shape, which has a yellowish or brown color.
- Dense structure of the neoplasm.
- Slow growth that only occurs in length.
- In some cases, a red rim is noticeable around the formed horn.
- Inflammatory processes can occur only near the base of the horn and are temporary.
Treatment of neoplasms on the skin
Today, there are the following methods for treating neoplasms on the skin:
- Chemotherapy.
- Radiation therapy.
- Surgical excision.
Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are practiced only in inoperable cases, but in a situation with malignant neoplasms, the prognosis is practically always unfavorable, due to frequent relapses and lesions of internal organs, leading to death.
Removal of skin lesions
Surgical intervention allows you to completely get rid of benign neoplasms or precancerous conditions. The process involves removing the affected area, as well as some of the adjacent healthy tissue.
Today it is practiced laser removal of neoplasms, which reduces the likelihood of relapses, since the surface is cauterized at the same time, which does not allow the spread of cancer cells.
In this article, we will tell you about the most common skin growths. You will learn about benign and malignant skin tumors and how to prevent skin diseases.
Skin neoplasms are various lesions of the skin. They can be both malignant and benign. Often they look like tumors or they look like some kind of discoloration in certain areas of the skin or mucous membrane. We will write more about this in our article. For greater clarity, let's say that any neoplasm is not good and it is better to consult a specialist immediately after its detection. Even benign skin lesions after trauma or excessive radiation can turn into oncology over time. This cannot be allowed.
Where do skin neoplasms come from?
Under ideal conditions, the number of dead cells, as well as new ones, should be equal, but this is not always the case. Sometimes the process of "birth" of new cells gets out of control and there are much more of them than is required, and these cells do not even have time to fully mature. That is, they cannot perform their functions in the body. Such an excess of unnecessary and unnecessary skin cells is a neoplasm. The uncontrolled process of cell proliferation can be caused by many factors, but the most common of them are:
- Frequent skin lesions;
- Frequent exposure (including solar radiation);
- Genetic predisposition;
The vast majority of neoplasms are benign and do not pose any threat to human life, but in some cases they can cause some discomfort and need to be removed. For example, if a benign skin tumor grows to such an extent that it can constrict blood vessels or its pigment will start to spoil the appearance of the skin, especially in open areas.
Under certain conditions, skin trauma or high radiation exposure, even a simple sunburn in large quantities can cause benign skin lesions, which did not bring any discomfort in life, can cause a benign lesion to "degenerate" into a malignant one.
Types of neoplasms on the skin
All neoplasms on the skin are divided into three main types - these are benign, malignant and precancerous or borderline. Their main differences are in the ability to metastasize, lead to complications of varying degrees, or even death.
Let's take a closer look at each of these types of neoplasms.
Benign skin lesions
The most common of this type of skin lesions are the following:
This is a fatty tumor, which is popularly called a wen. Most often, it forms on those places of the skin in which the amount of subcutaneous fat is extremely small, for example, on the upper back, in the shoulder girdle, on the thighs. It does not touch the skin itself, but grows mainly into the deeper layers of the skin. In the overwhelming majority of cases, it does not require treatment, only if its size will interfere with the patient's normal movement, but this happens extremely rarely.
(papillomas) viral. It is transmitted through objects with which the patient was in contact. Outwardly, it resembles a nodule or papilla. A particular risk of catching (it is he who is the cause of the appearance of warts) is observed in people with reduced immunological activity and increased skin sweating.
Warts can grow to the size of a pea, or they can grow into huge plaques. They are treated with simple medical treatment, or, in special cases, surgically removed. Also, very often you can find various alternative methods of treating warts.

Nevus (birthmarks)
There are also other names - birthmark or. They can be completely different colors, from light pink to almost black. Sizes from 0.1 cm to 10 cm. Moles can be both congenital and formed during life. They do not cause any discomfort. Often, more or less distinct moles appear in adolescence, in infants it is very rare to find a mole, but doctors believe that they are, only of an extremely small size. A mole can appear anywhere on the body, even on mucous membranes, such as in the mouth. Moreover, more often nevi appear on the female body.

A benign tumor that appears in different parts of the body. It can be on the body right from birth, or it can be formed at any age. Fibroma occurs in both sexes equally. This is one of those neoplasms that can form both on the body itself and on internal organs. Fibroids are conventionally divided into two types - soft and hard. Soft ones are more common in women, and hard ones appear in both women and men. There is no significant difference between soft and hard fibroids.

More often appears in people of advanced age on the head and on areas of the body that are hidden by clothing. It is because of this that they are also called senile warts. They look like small brown or black bumps. Doctors believe that the appearance of seborrheic warts can be caused by eating a large amount of animal fats, a lack of vitamins and high sun exposure. Often, senile warts are not treated.

Precancerous or borderline skin lesions
These are a kind of borderline types of formations that can be considered as the initial stages of cancer or, over time, develop into oncology. They often appear in older people, but there are exceptions.
Pigmented xeroderma or simply xeroderma
It is a hereditary disorder that results in increased sensitivity to ultraviolet (sunlight) light. The first symptoms appear by the age of three. This is a fairly rare disease. Doctors attribute it to a precancerous skin condition. It is one of the few precancerous diseases that occurs in young people rather than old people. The active period of the disease falls in the spring and summer due to the greater solar activity. In the vast majority of cases, the scalp, face and neck are affected. This is because the skin is unable to produce an enzyme that repairs UV damage.

As the name suggests, this disease manifests itself in elderly people. Often these are yellow or drill brown rashes no more than one centimeter in diameter. Over time, they can become covered with various scales, which naturally flake off. At this time, blood may appear on the affected area, but there is nothing to worry about. becomes malignant if a seal appears at its base, but this happens extremely rarely.

Paget's disease
This disease occurs mainly in women over forty. Seals and peeling of the skin begin to appear around the nipple. Natural liquid is released. In the course of the development of the disease, a crust is formed, but the very development of the disease can take many years. Some oncologists consider Paget's disease an initial stage of cancer, but so far official medicine has not confirmed this, despite the fact that it is also called breast cancer. There are also complications of this disease on the bone tissue.

As the name implies, older people are more susceptible to this disease. The cutaneous horn is a layering of epidermal cells one on top of another in such a way that outwardly it looks like a horn, like in animals, of course not of the same size, but there is no aesthetics in it. At the moment, there are different data on how much this disease often spills over into full-fledged cancer. At the first manifestations of this disease, it is better to consult a doctor. The cutaneous horn is quite easily removed surgically.

Malignant formations on the skin
Malignant neoplasms on the skin are a full-fledged cancer that gives metastases. These are complex diseases that require immediate treatment, as they may well be fatal.
A malignant tumor, which most often manifests itself on the skin, less often on the mucous membrane, for example, in the eye, in the mouth, in the rectum. Our body reacts very weakly to this disease, which provokes its rapid development, which can be fatal. can develop due to excessive UV radiation from the sun. People with fair skin and older people are more susceptible to this disease. This is the most common form of skin cancer. It can appear in a person after a simple injury to a nevus or a burn. So be careful with moles on your body.

A person's predisposition to oncological diseases can also be determined by a large number of moles, warts and other benign formations on the skin. Often, if there are more than eight moles on the body, then this is already an "alarm bell". You need to constantly examine yourself and, no matter how ridiculous it may sound, count moles on your body. If there are more of them, then it is better to consult a specialist. In addition, it is worth limiting your stay in the sun in open clothes in the summer. The most dangerous hours for the skin are from 11:00 to 15:00. Of course, one cannot say that solar radiation will lead to cancer, but as a preventive measure you need to take care of yourself.
Another name for this disease is squamous cell skin cancer. This swelling occurs on those areas of the skin that are most in contact with ultraviolet radiation, such as the face or hands. Also, its development can be affected by high temperatures, contact with various chemicals. Most often it occurs in the elderly, but there are cases of this disease in children. The disease occurs in both sexes equally. Basal cell carcinoma is almost painless and does not cause any particular discomfort to the patient. Because of this, it is still often referred to as a borderline disease. One of the features of this type of cancer is almost 100% recurrence.

The disease is common in people with AIDS and older men. It is expressed in the appearance on the skin of the legs of lilac spots that have no clear boundaries. After a while, small nodules appear in these places. Very often, neoplasms appear on the upper palate and other mucous membranes. These are lilac foci up to two centimeters in diameter. The risk group includes HIV-infected people, people with transplanted organs and men living in the Mediterranean.
It should be noted that this disease is multifocal, in contrast to most types of skin cancer.

Diagnosis of neoplasms on the body
The diagnosis of all skin diseases, both benign and malignant, lies primarily with the patient himself. Only self-examination and regular visual inspection of your body will help identify neoplasms. Specialists at the hospital will already diagnose this formation and take appropriate measures. Do not self-medicate.
Also, you should regularly visit a dermatologist and take appropriate tests. This is especially true for people who have many moles on their body and too light skin.
Treatment methods for skin diseases
In most cases, benign neoplasms are not treated in any way and are left as they are. In cases with malignant skin lesions, surgical intervention is used. The neoplasm and affected areas of the skin are cut out together with the adjacent healthy ones. But this method can cause a relapse. In some cases, other methods of treatment are used, for example, cryodestruction (freezing of the tumor).
Removal of neoplasms with a laser
We should also mention laser removal of skin diseases. This is a fairly new method of treating skin lesions and skin oncology, but it has proven itself from the best side. When the tumor is removed, relapse occurs much less frequently than with surgery.
The essence of laser removal is that the neoplasm is exposed to direct and alternating current in limited quantities, which leads to their removal. It is the safest, most reliable and painless method of treatment today.
More than 90% of people on the planet have age spots, moles and various formations on the skin. In the vast majority, these are benign tumors or spots that do not require any treatment at all and do not interfere with the carriers in any way. But it should be remembered that even a simple mole can, under certain conditions, become a cancerous tumor on the skin. You need to carefully monitor all moles on the body, and visually inspect yourself as often as possible in order to avoid more serious complications in the future.
Anna Sokolova's video story about neoplasms and what to do if they bother you.
Related Articles

Benign skin neoplasms are pathological changes in the size and number of cells, which leads to overgrowth of the dermis and the appearance of skin growth. The pathology that has arisen on human skin can have a different structure, but the general mechanism is the rapid multiplication of cells. The ICD-10 code classifies the benign formations as D10 or D36.
The second name for skin formations is neoplasia, or tumor. Pathology rarely transforms into malignant neoplasms and only as a result of chemical or physical exposure to external factors.
Benign skin lesions show distinctive features by which it is possible to determine their nature. The dermatologist identifies pathology according to the criteria:
- gradual increase;
- delayed development;
- education does not grow into nearby tissues and organs;
- the presence of a capsule that expands and puts pressure on neighboring organs.
This pathology does not pose a danger to the patient's life, but it brings tangible discomfort, increasing to an impressive size. Timely removal with an increase in the neoplasm will exclude the possibility of tumor metastasis.
Varieties of skin formations
Benign formations are of two types: congenital and acquired. Congenital formations are considered to be warts and moles of various shapes and colors. Superficial and subcutaneous formations resulting from metabolic dysfunction, decreased immunity, and viral diseases are recognized as acquired pathologies.
The classification of congenital and acquired skin diseases is diverse. Each type of skin growth shows its own shape, color, structural features and signs of occurrence.
Neurofibroma
The cell that forms the nerve sheaths becomes the foundation for the growth of neurofibroma. The mass looks like a bump, hard to the touch, reaching three centimeters in diameter.
Neurofibroma can be single and multiple. Multiple lesions are called neurofibromatosis and are considered the consequences of a genetic disorder that is inherited. Isolated pathologies rarely transform into malignant tumors, but bring tangible discomfort and pain to the owner. The skin tubercle is characterized by profuse pigmentation - more often the tumor is brown, red or dark brown. Neurofibroma is located in the subcutaneous tissue of the epidermis.
The disease is characterized by the absence of symptoms at the initial stage of development. Reaching an impressive size, the tumor presses on the nerve endings, and the patient experiences pain. Localization sites: on the face, on the skin of the back, abdominal cavity, arms, on the leg. The first symptoms of neurofibroma are brown or red spots in various areas of the human body. Neurofibroma can be cured with conservative therapy or surgery.
Fibroma
Connective tissue is the main component of fibroids. The tumor has a dense consistency, hard to the touch and is characterized by a light pink tint. This neoplasia reaches a maximum of three centimeters and occurs mainly in women who have reached the age of twenty.
There are known soft and hard types of fibroids. A hard cutaneous growth forms near the top layers of the skin. Soft fibroma is a flexible and soft-touch sac that appears on the neck, chest, armpits and groin folds in women who have reached adulthood. Often, a black or gray fibroma appears on the human body, showing a smooth surface. Doctors recommend removing fibroids: there remains a risk of metastasis and transformation of pathology into fibrosarcoma, even in favorable conditions. Regular physical and chemical damage to the tumor provokes rapid growth and the occurrence of skin cancers.
Fibroids can be cured using traditional surgical removal with a scalpel, laser, electrocoagulation and radio wave method. Laser and radio wave methods exclude further recurrence of pathology and give favorable forecasts.
Lipoma
A neoplasm that forms from adipose tissue and is localized in the layer of connective tissue is called a lipoma or wen. Reaching a large size, the lipoma grows into nearby tissues and reaches the bone surface. Often, the tumor spreads to nearby muscles and blood vessels. The lipoma is round and soft to the touch. The human body can be affected by both single and multiple wen. They appear in any part of the body where there is a fatty layer, which is a favorable environment for the development of this skin disease. Localization sites can be different: wen affects the face, neck, back, upper and lower extremities, the region of the head, eyelids and mouth.
The onset of the disease does not depend on gender, body weight or heredity. Pathology appears in men and women, in children. Fats do not pose a particular danger to human life, but sometimes transformation into liposarcoma is noted. To avoid unwanted transformation, doctors recommend removing the neoplasm in the early stages of development. This tactic will also help to avoid a cosmetic defect at the site of the operation. Methods of treatment and removal of a wen include surgical intervention using a scalpel, laser method, radio wave and puncture-aspiration principles of pathology elimination.
Atheroma
Blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands provokes the appearance of a residual cyst - atheroma. The specified tumor consists of products of the production of sebaceous glands, which are in the form of an odorless curd mass. On palpation, a dense consistency and clear contours of pathology are noted.
There are single and multiple atheromas. The phenomenon of multiple atheromas is called atheromatosis. Superficial atheromas mainly occur, the localization of which can be different: on the back, head, neck, face, in the thigh, groin, lower and upper limbs of a person. Factors of occurrence involve non-compliance with hygiene rules, trauma to hair follicles, metabolic diseases and unprofessional depilation.
With regular physical and chemical exposure, atheroma turns into an inflammatory and edematous state and acquires a red tint. If an infection enters the tumor cavity, there is an accumulation of pus and an independent eruption of a greasy consistency.
Dermatologists and oncologists advise removing atheroma that has reached a small size, since there is a risk of transformation of pathology into liposarcoma. The malignant variant of atheroma is characterized by rapid growth, compression of the surrounding vessels, nerve endings and nearby tissues. Liposarcoma poses a danger to human life, as it provokes anemia, vascular blockage, intoxication syndrome and metastasis to the internal organs of a person.
Lymphangioma
This type of tumor is congenital and occurs as a result of pathological changes in the lymphatic vessels. In rare cases, the pathology is acquired in nature. A congenital neoplasm is formed as a result of dysfunction of the outflow of lymphatic vessels, which provokes changes in the structure of the vessel membrane and the appearance of a tumor-like growth. The acquired form of the disease appears as a result of infectious lesions of the human skin.
Pathology looks like a blue growth that rises above the skin. On palpation, a dense consistency and clear boundaries of pathology are noted. Sizes range from one to five millimeters. Children under the age of three are at risk of education. In the process of development, there is a slow growth of education with intermittent periods, when the growth is rapidly increasing in size.
When a lymphangioma occurs, only surgical intervention is used, since the growth often puts pressure on such vital organs as the larynx, lungs, trachea. Modern methods of neoplasm elimination are sclerosed injections into the growth cavity, moxibustion using diathermocoagulation, electrocoagulation and freezing the growth using cryodestruction.
Wart and papilloma
Infectious infection of the skin and mucous membranes provokes the emergence of the papilloma virus, which manifests itself in the form of warts on various areas of the human body. The growth has distinctive features: multiple and single nodules of various shapes, brown, flesh-colored or light pink, reaching several centimeters in diameter.
Skin growths have different habitats: on the face, neck, groin, genitals, on the back and abdomen. Localization of papillomas in the area of \u200b\u200binternal organs was recorded. Warts and papillomas appear as a result of nervous tension, frequent stress, autonomic disorders and decreased immunity. Skin disease is sexually transmitted and as a result of the general use of hygiene products such as washcloths, towels, and hair removal items.
Warts rarely metastasize to cancer and do not pose a threat to human health.
Getting rid of papilloma involves complex therapy, which includes strengthening the immune system, adhering to proper nutrition, introducing physical activity, taking medications and removing skin growth in case of pain or discomfort. It is possible to eliminate papilloma using laser coagulation, freezing using the method of cryodestruction and electrocoagulation.
Nevus and birthmark
The specified neoplasm manifests itself in the form of excessive pigmentation on the skin. The shape, size and color are varied. The nevus can reach several tens of centimeters in diameter. The accumulation of pigment cells of the nevus is congenital and acquired. Also distinguish between benign and malignant age spots. The first category is characterized by symmetrical, clear forms, the same color shade and sizes, reaching five to six millimeters. Metastatic skin pathologies have uneven and asymmetrical edges, a multi-colored pigmented surface and dimensions of more than six millimeters.
The factors that provoke the occurrence of congenital pigmentation include the effect of toxic compounds and electromagnetic radiation on the fetus in the womb, diseases of the internal organs of the lower pelvis, genetic predisposition and the occurrence of pathologies during pregnancy. The appearance of acquired moles is influenced by hormonal imbalances in adolescence, mechanical damage to the skin, oral contraceptives, harmful ultraviolet radiation and infectious diseases of the skin. A large number of nevi are observed in men and women who have reached the age of twenty-five.
Hemangioma
The described type of skin tumor affects the walls of blood vessels and forms in the subcutaneous layer of the body. Hemangioma rises above the surface of the skin and is not subject to pigmentation. The pathology is characterized by rapid spontaneous growth and a decrease in volumes under pressure. Mostly pathology occurs in children during the first years of life. The sites of hemangioma can be different, but it mainly appears in the head and neck area. Cases of hemangioma of internal organs have been recorded. There are a number of types of skin pathology:
- With cavernous hemangioma, there is a deep location of the pathology in the skin layers of the human body. Education has a knot shape and a blue tint. It is diagnosed immediately after the birth of the child.
- With capillary hemangioma, the occurrence of pathological changes in the epithelial layer was recorded, covering large areas of the skin and having a red or blue color.
- With combined pathology, the simultaneous appearance of a tricky and capillary hemangioma is observed.
- The mixed form of skin disease involves the process of involving the vascular membranes and connective tissues.
The disease appears as a result of hormonal characteristics of the fetus, infectious diseases of a pregnant woman in the initial stages and taking medications while carrying a child.
Inflammatory processes of hemangioma cause complications such as open bleeding, which can only be restored with the help of surgery. When localized near a vital organ and a rapid increase in size, a tumor can interfere with the functioning of nearby organs and tissues and, thereby, worsen the patient's quality of life. To remove this skin defect, a sclerosing method is used, which causes hemangioma necrosis, cryodestruction, coagulation and traditional surgical intervention.
Keratoma
The basis of this skin tumor is keratinocytes, which form the stratum corneum of the skin. Dead cells transform into a growth, which is a spot or a nodule covered with a crust. Keratoma has various localization sites and most often occurs on the back, head, face, in the region of the lower and upper extremities. This type of skin pathology requires urgent treatment, since the keratinous cells that form the keratoma are similar to the cells of malignant tumors.
Single and multiple keratomas are distinguished. The second type of pathology occurs extremely rarely and there are a maximum of three skin nodes. The formation of multiple neoplasms on one area of \u200b\u200bthe body indicates the danger of skin cancer. The causes of education include pathological changes in the functioning of cells, hormonal failure, harmful ultraviolet radiation, genetic predisposition and vitamin deficiency. The following types of keratomas are determined:
- With a solar neoplasm, the formation of flaky spots is observed, reaching several centimeters in diameter. The build-up does not cause discomfort or pain to the patient. Common sites of tumor localization: hand, foot, face and trunk.
- A horny neoplasm forms in the form of a light brown or gray spot protruding over the human skin. The growth significantly protrudes above the skin surface and flakes off profusely. Common sites include the eyelids, forehead, lips, cheeks, nose, and mucous membranes.
- With senile keratoma, dense light brown spots appear, reaching several centimeters in diameter. In the process of development of the build-up, multiple layers are formed, gradually cracking. This type of keratoma grows slowly and is localized mainly in the head, back, chest and in parts of the body with rich hair.
- The follicular formation is a light pink and flesh-colored nodule that reaches two centimeters in diameter. The surface of the keratoma is covered with bumps and rises above the skin of the body. Mostly this tumor appears on the lower limbs, lips, cheeks, nasolabial folds and palms.
If the neoplasm does not pose a risk of transition to a cancerous tumor and does not reach a large size, doctors recommend the use of medical and non-traditional methods of treatment. At the slightest suspicion of the transformation of a skin growth into a cancerous tumor, experts recommend removing the tumor. Keratoma can be eliminated using cryodestruction, radio wave method, laser, electrocoagulation and traditional surgical intervention.
Dermatofibroma
This type of neoplasm occurs as a result of capillary changes and consists of connective tissue. The tumor is characterized by the absence of pain and slow development. The formation is a rounded deep-lying node protruding several millimeters above the skin surface. Mostly the growth occurs in young women who have reached the age of thirty.
Do benign tumors hide the danger?
A benign neoplasm can transform into an oncological disease. The medical science of dermatovenerology is engaged in diagnostics, study and prevention, and only a dermatologist or oncologist can determine the danger.
If education poses a threat to life, the doctor prescribes a radical removal. Further therapeutic treatment or complete removal is determined by benign and malignant signs of pathology. Scientists have proven that the most dangerous are birthmarks and nevi of a congenital nature, therefore dermatologists recommend removing neoplasms immediately. Skin pathological changes are often the cause of discomfort and painful sensations, which becomes an additional reason for the elimination of the tumor.
Skin neoplasms are the result of intensive division of cells in the epidermis and are benign and malignant in nature, capable of developing into skin cancer.
Moles, papillomas, nevi and many other skin growths are present on the skin of the vast majority of people.
Some growths do not pose a threat to health, but there are also those that, under the influence of negative factors, change and develop into malignant tumors. In order not to miss the moment when a harmless mole begins to transform into skin cancer, it is necessary to independently monitor the condition of all skin growths and undergo regular medical examinations.
Types of skin growths
All neoplasms developing from skin cells are classified into:
1. Benign, not posing a serious threat, but capable of delivering physical and mental discomfort when widely localized or located on areas of the body not covered by clothing.
2. Malignant, which is essentially a cancerous tumor. These growths quickly grow, affect the deep layers of the dermis and spread metastases throughout the body.
3. Borderline, potentially capable of transforming into a malignant form.
To make an appointment
- Telephone
Let's consider the features of these skin growths in more detail.
Benign:
It is formed during the blockage of the sebaceous gland and looks like a compacted "ball" rising above the skin, which does not cause discomfort. Atheromas can form anywhere on the body, including the genital area; a neoplasm can be either single or multiple. In case of suppuration and inflammation, the atheroma can be removed by surgical excision or laser.



If the work of the ducts of the sebaceous glands is seriously impaired, then without special treatment of the underlying problem, they will be re-clogged and, as a result, atheromas will appear again and again, usually in the same place.
A vascular neoplasm, which can be localized in both the upper and deep layers of the skin, as well as internal organs and affect the vascular network. It has a burgundy or bluish-black shade, can reach large sizes. For treatment, laser removal of hemangiomas, sclerotherapy or a surgical method is used.



Hemangiomas are most common on the body, but sometimes they can develop on the scalp, face, neck, upper and lower limbs. The neoplasm itself is not dangerous, but it is very easy to injure it. Hemangioma injuries are accompanied by profuse bleeding.
This type of tumor develops on the vessels of the lymphatic system, is characterized by slow growth. The disease occurs even during the intrauterine development of the fetus. Under the influence of unfavorable factors, the neoplasm, as a rule, increases significantly in size, which becomes an indication for its surgical removal.



Lymphangioma mainly affects children and is easily diagnosed during the first year of a child's life. The tumor itself is not dangerous, but its tendency to spontaneous and almost instantaneous growth can harm the child's internal organs and even threaten his life.
Lipoma or wen is a benign tumor that develops under the skin from adipose tissue cells. A neoplasm can occur in almost any part of the body where, in one way or another, subcutaneous fat is present. The neoplasm is felt under the skin as a small movable lump; the tumor is absolutely painless.



5. Papillomas and warts
Warts and papillomas are benign neoplasms that develop from epithelial tissue. They have a similar viral origin, but different places of formation and development. The reason for the appearance of papillomas and warts is the very widespread human papillomavirus (HPV) in the world.



Nevi and moles are formed from melanocytes - cells containing the main coloring pigment of the body. As a rule, most of these neoplasms are harmless to health. However, their size and location can create certain discomfort, especially if they are located on the face or exposed parts of the body.
Fibroma is a benign neoplasm that develops from connective tissue cells. The tumor has the form of spherical nodules protruding above the skin with a smooth or warty surface. The color of fibroids can be bluish-black, gray, brown. More detailed information on fibromas can be found in the article "Skin fibroma. Description, symptoms, consequences. Laser removal".



The neoplasm grows slowly, usually without causing much discomfort to the patient. Often, fibroma does not pose a danger to life, however, when exposed to unfavorable external factors, as well as various carcinogens, it can develop into a malignant form - fibrosarcoma. The safest and most effective method for removing fibroids is laser therapy.
Neurofibroma is a benign neoplasm that develops from nerve cells. Most often, the tumor is located under the skin, in the area of \u200b\u200bsubcutaneous fat. However, in some cases, it can also affect soft tissues, as well as the roots of the spinal cord.



The neoplasm looks like a dense tubercle with a pigmented surface. It can take on a multiple form, and in this case requires treatment with medication or surgical methods.
Sign up for laser removal of neoplasms
- Telephone